@codexteam/ajax v4.2.0
AJAX
Module for async requests on a native JavaScript for a browser.
Package has been renamed from
codex.ajaxto@codexteam/ajax
Features
- zero-dependencies
- Promises based
- custom callback for a progress event
- easy-to-use
transportmethod: ask user for a file(s) and upload it object,FormDataorHTMLFormElementdata is being supported
Installation
You can install this package via NPM or Yarn
npm install @codexteam/ajaxyarn add @codexteam/ajaxRequire package on your script page.
const ajax = require('@codexteam/ajax');Also you can get this module from CDN or download a bundle file and use it locally.
Usage
There are a few public functions available to be used by user. All of them return Promise.
- ajax.get() — wrapper for a GET request
- ajax.post() — wrapper for a POST request
- ajax.request() — main function to make requests (GET, POST, HEAD, PUT, DELETE, ...)
- ajax.transport() — ask user for a file and upload it
- ajax.selectFiles() — ask user for a file and return files array
Callbacks format
successCallback and errorCallback have the same input object response as a param.
| param | type | description |
|---|---|---|
| response.body | object or string | Response body parsed JSON or a string |
| response.code | number | Response code |
| response.headers | object | Response headers object |
Example
function successCallback(response) {
console.log('Response:', response.body);
}function errorCallback(response) {
console.log(`Error code ${response.code}. Response:`, response.body);
}ajax.get()
Wrapper for a GET request over an ajax.request() function.
| param | type | default value | description |
|---|---|---|---|
| url | string | '' | Request URL |
| data | object | null | Data to be sent |
| headers | object | null | Custom headers object |
| progress | function | (percentage) => {} | Progress callback |
| ratio | number | 90 | Max % of bar for uploading progress |
| beforeSend | function | null | Fire callback before sending a request |
Example
ajax.get({
url: '/getUserData',
data: {
user: 22
}
})
.then(successCallback)
.catch(errorCallback);ajax.post()
Wrapper for a POST request over an ajax.request() function.
| param | type | default value | description |
|---|---|---|---|
| url | string | '' | Request URL |
| data | object, FormData or HTMLFormElement | null | Data to be sent |
| type | string | ajax.contentType.JSON | Header from ajax.contentType object |
| headers | object | null | Custom headers object |
| progress | function | (percentage) => {} | Progress callback |
| ratio | number | 90 | Max % of bar for uploading progress |
| beforeSend | function | null | Fire callback before sending a request |
Example
Simple POST request
ajax.post({
url: '/saveArticle',
data: {
title: 'Awesome article',
text: 'will be written later',
isPublished: false
},
/**
* Choose the content type you need
*/
// type: ajax.contentType.JSON /* (default) */
// type: ajax.contentType.URLENCODED
// type: ajax.contentType.FORM
})
.then(successCallback)
.catch(errorCallback);Example
To send any form you can pass HTMLFormElement as a data to ajax.post().
<form id="form-element">
<input type="text" name="firstName" placeholder="First name">
<input type="text" name="lastName" placeholder="Last name">
<input type="file" name="profileImage" accept="image/*">
<button onclick="event.preventDefault(); sendForm()">Send form</button>
</form>
<script>
function sendForm() {
var form = document.getElementById('form-element');
ajax.post({
url:'/addUser',
data: form
})
.then(successCallback)
.catch(errorCallback);
}
</script>ajax.request()
Main function for all requests.
| param | type | default value | description |
|---|---|---|---|
| url | string | '' | Request URL |
| method | string | 'GET' | Request method |
| data | object | null | Data to be sent |
| headers | object | null | Custom headers object |
| progress | function | (percentage) => {} | Progress callback |
| ratio | number | 90 | Max % of bar for uploading progress |
| beforeSend | function | (files) => {} | Fire callback before sending a request |
Example
ajax.request({
url: '/joinSurvey',
method: 'POST',
data: {
user: 22
}
})
.then(successCallback)
.catch(errorCallback);ajax.transport()
This is a function for uploading files from client.
User will be asked to choose a file (or multiple) to be uploaded. Then FormData object will be sent to the server via ajax.post() function.
| param | type | default value | description |
|---|---|---|---|
| url | string | '' | Request URL |
| data | object | null | Additional data to be sent |
| accept | string | null | Mime-types of accepted files |
| multiple | boolean | false | Let user choose more than one file |
| fieldName | string | 'files' | Name of field in form with files |
| headers | object | null | Custom headers object |
| progress | function | (percentage) => {} | Progress callback |
| ratio | number | 90 | Max % of bar for uploading progress |
| beforeSend | function | (files) => {} | Fire callback with chosen files before sending |
Example
ajax.transport({
url: '/uploadImage',
accept: 'image/*',
progress: function (percentage) {
document.title = `${percentage}%`;
},
ratio: 95,
fieldName: 'image'
})
.then(successCallback)
.catch(errorCallback);Example
One simple button for uploading files.
<button onclick='ajax.transport({url: "/uploadFiles"}).then(successCallback).catch(errorCallback)'>Upload file<button>ajax.selectFiles()
Ask user for a file (or multiple) and process it. FileList object will be returned in Promise.
| param | type | default value | description |
|---|---|---|---|
| accept | string | null | Mime-types of accepted files |
| multiple | boolean | false | Let user choose more than one file |
Example
ajax.selectFiles({
accept: 'image/*'
})
.then(successCallback);Params
List of params, their types, descriptions and examples.
url string
Target page URL. By default current page url will be used.
/user/22, /getPage, /saveArticle
method string
Used in
ajax.request()function only
Request method.
GET, POST
Read more about available request methods methods on the page at developer.mozilla.org.
data object|FormData|HTMLFormElement
You can pass data as object, FormData or HTMLFormElement.
Data will be encoded automatically.
ajax.request({
url: '/joinSurvey',
method: 'POST',
data: {user: 22}
})
.then(successCallback)
.catch(errorCallback);ajax.request({
url: '/sendForm',
method: 'POST',
data: new FormData(document.getElementById('my-form'))
})
.then(successCallback)
.catch(errorCallback);For
ajax.get()you can passobjectdata
ajax.get({
url: '/getUserData',
data: {
user: 22
}
})
.then(successCallback)
.catch(errorCallback);is the same as
ajax.get({
url: '/getUserData?user=22'
})
.then(successCallback)
.catch(errorCallback);For
ajax.transport()should passobjectdata if it is necessary
You can send additional data with files.
ajax.transport({
url: '/uploadImage',
accept: 'image/*',
data: {
visible: true,
caption: 'Amazing pic'
},
fieldName: 'image'
})
.then(successCallback)
.catch(errorCallback);type string
Specify the content type of data to be encoded (by ajax module) and sent.
You can get value for this param from ajax.contentType object. Data will be encoded that way.
| ajax.contentType | value |
|---|---|
| JSON | application/json; charset=utf-8 |
| URLENCODED | application/x-www-form-urlencoded; charset=utf-8 |
| FORM | multipart/form-data |
const params = {
// ...
type: ajax.contentType.JSON
// type: ajax.contentType.URLENCODED
// type: ajax.contentType.FORM
};headers object
Object of custom headers which will be added to request.
headers = {
'authorization': 'Bearer eyJhbGciJ9...TJVA95OrM7h7HgQ',
// ...
}progress function
Almost all requests have responses. To show a correct progress for a call we need to combine a request progress (uploading) and a response progress (downloading). This ajax module uses one progress callback for it.
/**
* @param {number} percentage - progress value from 0 to 100
*/
var progressCallback = function progressCallback(percentage) {
document.title = `${percentage}%`;
};Check out ratio param to show progress more accurate.
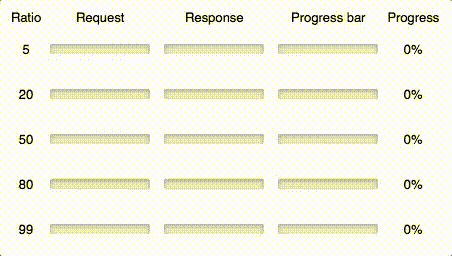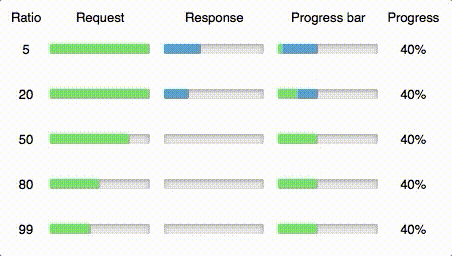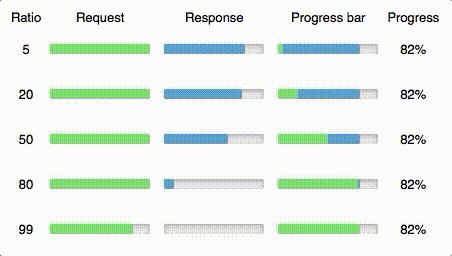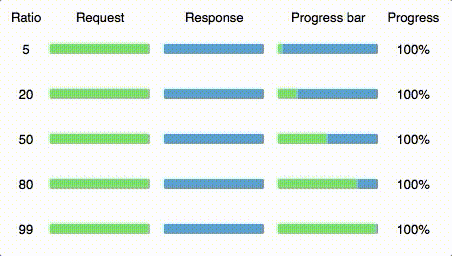
ratio number
Used with
progressparam
Value should be in the 0-100 interval.
If you know that some requests may take more time than their responses or vice versa, you can set up a ratio param and define a boundary between them on the progress bar.
For example if you want to show progress for a file uploading process, you know that uploading will take a much more time than downloading response, then pass bigger ratio (~95). When you want to download big file — use smaller ratio (~5).
accept string
Used in
ajax.transport()function only
String of available types of files to be chosen by user.
*/* — any files (default)
image/* — only images
image/png, image/jpg, image/bmp — restrict accepted types
Read more about MIME-types on the page at developer.mozilla.org.
multiple boolean
Used in
ajax.transport()function only
false by default. User can choose only one file.
If you want to allow user choose more than a one file to be uploaded, then pass a true value.
fieldName string
Used in
ajax.transport()function only
Name of data field with the file or array of files.
files by default.