@donsi/rdform v0.0.7
RDForm
RDForm is a jQuery plugin for creating and editing RDF data in a clean and modern HTML form.
With templates based on the RDFa notation (see template documentation) its easy to create classes, properties with datatypes, resources and class-relations.
The inserting of existing data and the output is done as a JavaScript object with the JSON-LD notation.
For a running example see https://simeonackermann.github.io/RDForm/.
This software is currently in a very early state. Please be careful when use it in a productive environment.
Screenshot
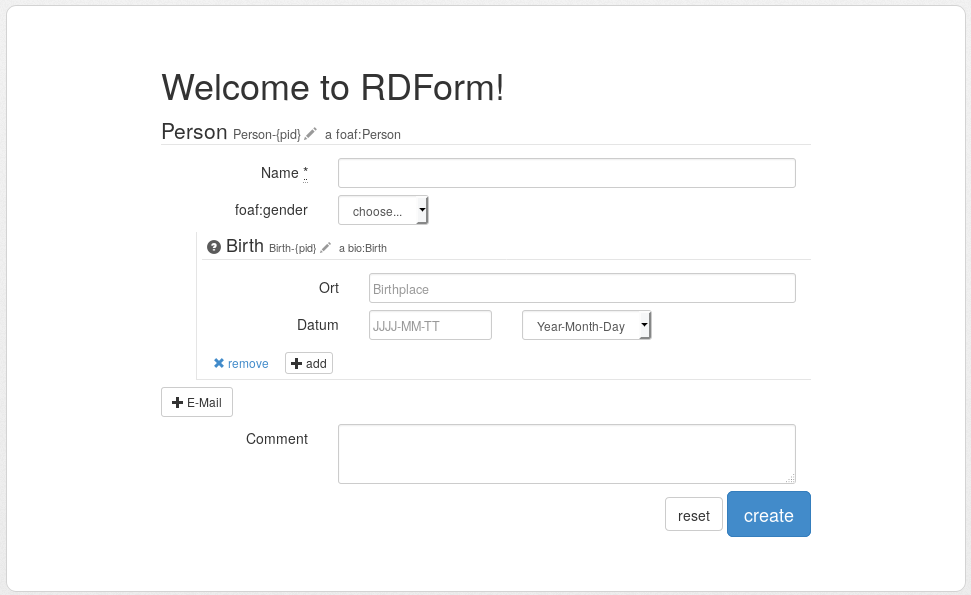
Installation
Via npm
npm i @donsi/rdform
Manually
- download the source code
- open index.html in your browser for a sample form.
- to create an own form, edit templates/form.html to your requirements or create a new file
The load of templates and hooks requires a running http server. You can use docker for example:
docker run --name rdform -v $(pwd):/usr/share/nginx/html -p 8080:80 nginxand access at http://localhost:8080
Integrate
If you want to integrate RDForm into an existing project you have to include jQuery (> 1.8) (and for a good style Bootstrap). Have a look at index.html for the right structure.
The basic initialization of the plugin with callback function on submit is:
$(document).ready(function(){
$(".rdform").RDForm({
template: "templates/form.html",
submit: function() {
console.log( JSON.stringify(this, null, '\t') );
}
});
});Documentation
Content
- Parameter
- Template Documentation - Classes - Literal-Properties - Class-Resources - External resources - Hidden-Properties - Wildcards - Translation
- Insert Data
- Hooking
Paramter
The following parameters can given to the plugin (see Installation above):
| Parameter (Type) | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
template (String) | templates/form.html | Path to the template file |
data (Object) | null | Array or Object of existing data to insert |
hooks (String) | null | Path to the hooks file |
prefixes (Object) | { foaf: ..., rdf: ..., rdfs: ..., ...} (see rdform.js) | Object with prefiex and URIs |
base (String) | null | Base URI |
lang (String) | null | Path to the language file |
cache (Boolean) | false | true or false, loads template from cache |
verbose (Boolean) | false | true or false, output all messages and the result |
debug (Boolean) false | log error, warnings and infos into the console | |
submit (Function) | null | Submit callback function, will be called after submit the form |
abort (Function) | null | Abort callback function, will be called on aborting the form |
Template Documentation
To visualize a class, its properties and the resources in a form the plugin needs a template. The templates are based on the RDFa notation which adds RDF attributes to HTML elements. With that kind of templates its possible to describe RDF-ontologies on the HTML-way and to define the layout like labels, legends, placeholder and so on.
Some default templates can by found in the subfolder templates. The path of the current template must be given as model argument to the plugin (see installation).
The base structure of an example template is:
<form prefix="foaf http://xmlns.com/foaf/0.1/ rdfs http://www.w3.org/2000/01/rdf-schema#" base="http://example.com/">
<legend>A person</legend>
<div typeof="foaf:Person" resource="Person-{rdfs:label}">
<label>The label</label>
<input name="rdfs:label" datatype="xsd:string" />
</div>
</form>The JavaScript output for this template will be:
{
"@id": "http://example.com/Person-Max_Mustermann",
"@type": [
"http://xmlns.com/foaf/0.1/Person"
],
"http://www.w3.org/2000/01/rdf-schema#label": [
{
"@type": "xsd:string",
"@value": "Max Mustermann"
}
]
}The Form
The root element should be a <form />...</form> tag and contains all further classes and properties.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
prefix | Optional, Prefixes fo all resources. The form is "PREFIX URI PREFIX URI ..." |
base | Optional, Base URI |
Classes
Classes are described by a <div typeof="...">...</div> tag.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
typeof | Type of the class |
resource | Class uri |
id | Optional class ID to reference classes with same typeof |
typeof-select | Optional, show select form lets users choose the type of the class. The value must be a JSON object with label and value pairs. |
Example (with legend and help message):
<legend>Birth</legend>
<div typeof="bio:Birth" resource="Birth-123">
<p class="help">I'm a help message...</p>
...
</div>Literal Properties
Literals are described by a <input type="literal" name="..." />.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
type="literal" | Defines an input as an literal property |
name | Name of the property |
| Optional Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
datatype | Datatype, e.g. xsd:string, xsd:date, |
value | Prefilled value |
placeholder | Placeholder |
multiple | The property can be multipled by clicking an add-button |
required | Required property, cannot be empty |
additional | Additional, by default hidden property. Can be added it by clicking an add-button |
readonly | Cannot be edited |
hidden | Hide this literal in the form |
boolean | Boolean property, shown as ` |
textarea | Multiple line text, shown as <textarea /> |
select | Select a property from multiple options, shown as <select /> |
select-options | Required for attribute select. JSON object with label/value pairs. >` |
help | Short help text for the property |
Example:
<input type="literal" name="foaf:firstName" datatype="xsd:string" required placeholder="Name..." help="The name of the person" />Special literals are booleans, textareas and select-lists.
Booleans
Are described as checkboxes in the form and can be 1|0 or true|false. They are initialized by adding the attribute boolean to a literal property.
Textareas
Are multiple line texts and initialized by adding the attribute textarea to a literal property.
Dates
Properties of type xsd:date will rendered with a date-type select option. To define the date format you can use xsd:gYearMonth or xsd:gYear as datatype.
Select-Lists
To get a select list add the attributes select and select-options='...'. the value of select-options must be a JSON object with a label and value pair.
Example:
<input name="foaf:gender" type="literal" select select-options='{"female":"female", "male":"male", "not-specified":"Not specified"}' datatype="xsd:string" />Class Resources
Classes can contain resource properties, which containing a reference to another class.
Example:
<div typeof="foaf:Person" resource="Person-{pid}">
<input name="pid" type="hidden" />
<input name="bio:event" type="resource" value="bio:Birth"
arguments='{"pid":"{pid}"}' additional
/>
</div>
<div typeof="bio:Birth" resource="Birth-{pid}">
<input name="dc:date" type="literal" datatype="xsd:date" placeholder="JJJJ-MM-TT" />
</div>If you need to reference classes with same typeof add the id attribute. Example:
<div typeof="foaf:Person" resource="Person">
<input name="bio:event" type="resource" value="BirthEvent" />
<input name="bio:event" type="resource" value="DeathEvent" />
</div>
<div typeof="bio:Event" id="BirthEvent" resource="Birth">
<input name="dc:date" type="literal" datatype="xsd:date" placeholder="JJJJ-MM-TT" />
</div>
<div typeof="bio:Event" id="DeathEvent" resource="Death">
<input name="dc:date" type="literal" datatype="xsd:date" placeholder="JJJJ-MM-TT" />
</div>External Resources
Example:
<input type="resource" name="gnd" external />Select-Lists
To get a select list add the attributes select and select-options='...'. the value of select-options must be a JSON object with a label and value pair.
Example:
<input name="foaf:knows" type="resource" select select-options='{"ex:p1":"Person 1", "ex:p2":"Person 2"}' external />Multiple external select resources are not yet supported.
Hidden Properties
Example:
<input type="hidden" name="id" />Wildcards
With wildcards the class identifier or a property value can point to another property value of the same class. Just write the name of the property into brackets.
Example:
<div typeof="Person" resource="Person-{id}">
<input name="id" type="hidden" value="{label}-123" />
<input name="label" type="literal" />
</div>Wildcard Functions
To the returned value of a wildcard a function can applied. Basically you can use the string functions toUpperCase and toLowerCase, while writing the function name into braces just before the wildcard-identifier:
<input name="id" type="literal" value="{(toLowerCase)label}" />Custom functions can written into the return statement of the __wildcardFcts method in your hooks file (see hooks.js for examples). E.g:
__wildcardFcts : function() {
return {
foo: function(str) {
return str + "bar";
},
};
}And called just before the wilcard-identifier as above.
Translation
Strings in legends, labels and placeholder can translated with l(My Label). The translation files are stored in lang/ (currently only english and german) and must be given as lang argument to the plugin.
Example:
$(".rdform").RDForm({
template: "templates/form.html",
lang: "de"
});Insert Data
Existing data can inserted as json-ld javascript object. The form of the data should fit to the loaded template. RDForm will insert the data into the form fields.
Example:
var data = {
"@id": "http://json-ld.org/playground/Person-Karl",
"@type": [
"http://xmlns.com/foaf/0.1/Person"
],
"http://xmlns.com/foaf/0.1/name": [
{
"@type": "xsd:string",
"@value": "Karl"
}
]
};
$(".rdform").RDForm({
template: "templates/form.html",
data: data
});Hooking
With hooks own JavaScript methods can affect the application execution on certain points. Have a look at js/hooks/hooks.js for more information.
License
RDForm is licensed under the GNU General Public License Version 2, June 1991.