1.2.14 • Published 8 months ago
@dulysse1/ts-helper v1.2.14
🛠 ts-helper 🛠
- Typescript library for type helpers ✨
Getting Started 🆙
Prerequisites
Install Typescript on your project
npm install typescript --save-devOr
yarn add typescript --devOr
pnpm i -D typescriptFor best results, add this to your tsconfig.json
{
"compilerOptions": {
"strictNullChecks": true, // highly recommended (required by few utilities)
"strict": true, // this is optional, but enable whenever possible
"lib": ["es2015"] // this is the lowest supported standard library
}
}How to use ? 🤔
With EcmaScript module ✅
import type { Num, Arr, Str } from "@dulysse1/ts-helper";
// now you can create your types!Documentation 🧗
Here some examples:
👉 Numbers
⚠️ Returns an absolute result with a precision of two decimals for numbers that don't reach compiler limits, otherwise it returns an
explicit result. ⚠️New feature since version
1.2.6! The multiply function allow onefloattype 🤯🤯🤯
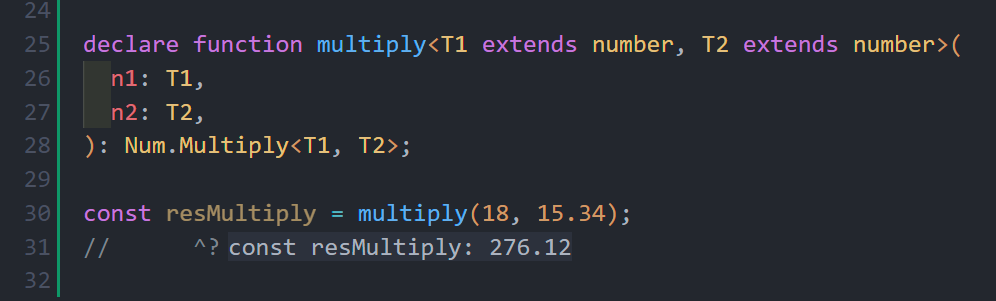
- New feature since version
1.2.2! Add and Substract functions allowfloattype 🤯🤯
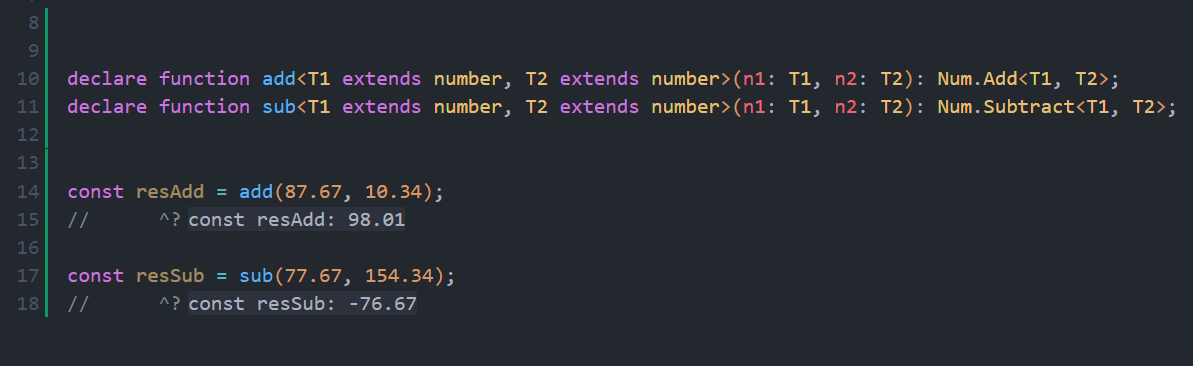
- New feature since version
1.1.1! Eval function return type for calculation 🤯
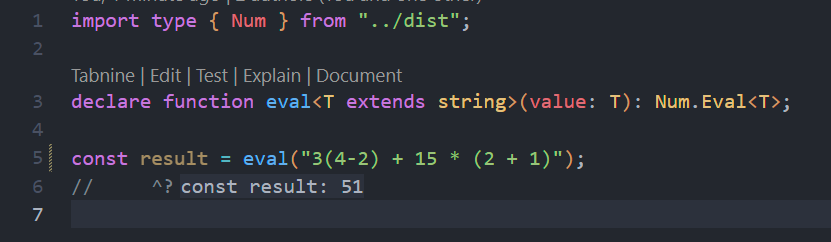
- Check if a number is
positive
import type { Num } from "@dulysse1/ts-helper";
type A = Num.IsPositive<-2343>; // false
type B = Num.IsPositive<134>; // true
type C = Num.IsPositive<0>; // true- Add two numbers
import type { Num } from "@dulysse1/ts-helper";
type A = Num.Add<10, 10>; // 20
type B = Num.Add<-10, 10>; // 0
type C = Num.Add<-23, -34>; // -57
type C = Num.Add<87.67, 10.34>; // 98.01 NEW!- Substract two numbers
import type { Num } from "@dulysse1/ts-helper";
type A = Num.Subtract<10, 10>; // 0
type B = Num.Subtract<10, -40>; // 50
type C = Num.Subtract<12.4, 3.2>; // 9.2 NEW!- Multiply two numbers
import type { Num } from "@dulysse1/ts-helper";
type A = Num.Multiply<10, 10>; // 100
type B = Num.Multiply<-6, 7>; // -42
type C = Num.Multiply<234, 783>; // number- Divide two numbers
import type { Num } from "@dulysse1/ts-helper";
type A = Num.Divide<20, 10>; // 2
type B = Num.Divide<0, 7>; // 0
type C = Num.Divide<7, 0>; // number- Get the
factorialof one number
import type { Num } from "@dulysse1/ts-helper";
type A = Num.Factorial<0>; // 1
type B = Num.Factorial<-3>; // -6
type C = Num.Factorial<5>; // 120- Check if a number is
even
import type { Num } from "@dulysse1/ts-helper";
type A = Num.IsEven<0>; // true
type B = Num.IsEven<-3>; // false
type C = Num.IsEven<5.5>; // false- Check if a number is
odd
import type { Num } from "@dulysse1/ts-helper";
type A = Num.IsOdd<0>; // false
type B = Num.IsOdd<-3>; // true
type C = Num.IsOdd<5.5>; // true- Check if a number is
float
import type { Num } from "@dulysse1/ts-helper";
type A = Num.IsFloat<0>; // false
type B = Num.IsFloat<-3>; // false
type C = Num.IsFloat<5.5>; // true- Parse a string to
floatnumber
import type { Num } from "@dulysse1/ts-helper";
type A = Num.ParseFloat<"0">; // 0
type B = Num.ParseFloat<"-3">; // -3
type C = Num.ParseFloat<"5.5">; // 5.5- Parse a string to
integernumber
import type { Num } from "@dulysse1/ts-helper";
type A = Num.ParseInt<"0">; // 0
type B = Num.ParseInt<"-3">; // -3
type C = Num.ParseInt<"5.5">; // 5👉 Object
- Get keys of object by an optional filter
import type { Obj } from "@dulysse1/ts-helper";
type A = Obj.KeyOf<{ a: string; b: number }, string>; // "a"- Merge two type objects
import type { Obj } from "@dulysse1/ts-helper";
type A = type A = Obj.Merge<
{ a: string; },
{ b: number; }
>; // { a: string; b: number; }👉 String
- Split a string to array
import type { Str } from "@dulysse1/ts-helper";
type A = Str.Split<"coucou">; // ["c", "o", "u", "c", "o", "u"]
type B = Str.Split<"coucou", "c">; // ["ou", "ou"]- Replace all iteration of one character
import type { Str } from "@dulysse1/ts-helper";
type A = Str.ReplaceAll<"coucou", "c", "x">; // "xouxou"👉 Array
- Check if array is a
tuple
import type { Arr } from "@dulysse1/ts-helper";
type A = Arr.IsTuple<number[]>; // false
type B = Arr.IsTuple<[1, 2, 3]>; // true- Reverse an array
import type { Arr } from "@dulysse1/ts-helper";
type A = Arr.Reverse<[1, 2, 3]>; // [3, 2, 1]👉 Any
- Use a strict any type : The only valid way to use
anyas type. it's provide you to override the default eslint@typescript-eslint/no-explicit-anyrule. But be careful ! Don't use this type in your code for bad reasons.
declare type IAnyFunction = (...args: Any.Strict[]) => Any.Strict; // "right way !"
const name: Any.Strict = {}; // "wrong way !"And many more besides! 😲
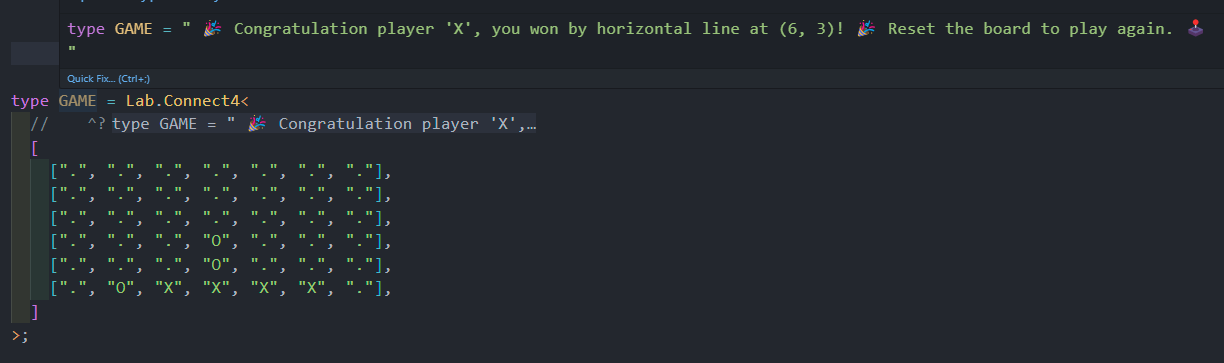
- New feature since version
1.2.3! There is now alabwith experimental types to show the power of@dulysse1/ts-helper!
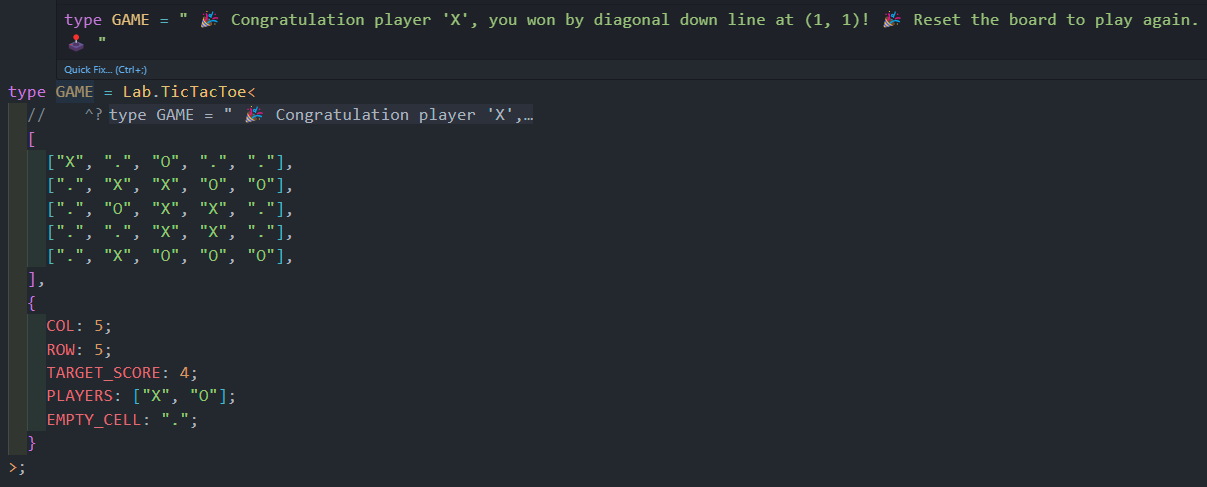
Do you have any ideas or recommendations for improvement? 🤔
Contact me! 😃
Author: Ulysse Dupont
Contact: ulyssedupont2707@gmail.com
1.2.0
10 months ago
1.1.1
11 months ago
1.0.2
12 months ago
1.1.0
11 months ago
1.0.1
12 months ago
1.2.8
8 months ago
1.2.7
8 months ago
1.2.6
8 months ago
1.2.5
8 months ago
1.2.4
8 months ago
1.2.3
9 months ago
1.1.4
11 months ago
1.2.2
10 months ago
1.1.3
11 months ago
1.2.1
10 months ago
1.1.2
11 months ago
1.2.9
8 months ago
1.2.12
8 months ago
1.2.13
8 months ago
1.2.10
8 months ago
1.2.11
8 months ago
1.2.14
8 months ago
1.0.0
2 years ago