@haroldiedema/flow-graph v1.0.3
Flow-Graph
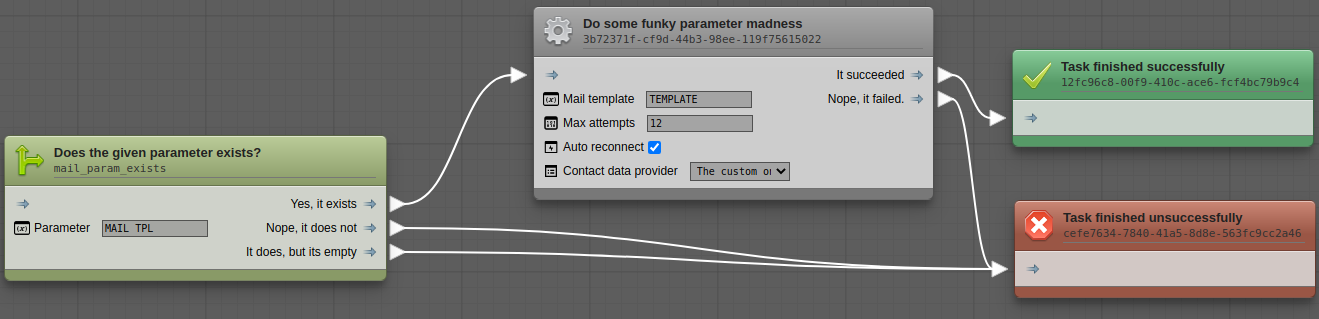
Flow-graph is a zero-dependency graph visualizer and editor. It is designed for building and maintaining business automation processes, but can be utilized for other purposes as well.
Installation
Using yarn
$ yarn add @haroldiedema/flow-graphOr NPM
npm i -S @haroldiedema/flow-graphGetting started
In order to initialize flow-graph, we first need a point in our DOM to attach to. This element will function as 'viewport' for our graph editor.
<div id="fg"></div>import {FlowGraph} from '@haroldiedema/flow-graph';
const fg = new FlowGraph(document.getElementById('fg'));You will now see an empty grid in which you can pan the camera around. You won't be able to do anything else yet, because the template registry is currently empty.
Node templates
Before you can add nodes to the graph, flow-graph needs to know about what can be added to it. You'll need to define templates which consist of a unique identifier that identifies the template, a display name, a description, input and output sockets and so on.
A template can be defined like this:
import {FlowGraph, NodeType} from '@haroldiedema/flow-graph';
const fg = new FlowGraph(document.getElementById('fg'));
fg.registerNodeTemplate({
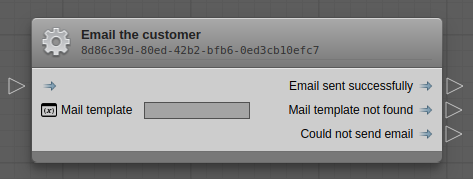
name: "Email the customer",
type: "ACTION",
systemName: "my.backend.logic.sendMailByTemplate",
description: "Send an email to the customer by the given mail template.",
inputs: [
{
name: "MAIL_TEMPLATE",
type: "string",
label: "Mail template"
}
],
outputs: [
{
name: "success",
label: "Email sent successfully"
}, {
name: "tpl_not_found",
label: "Mail template not found"
}, {
name: "failed",
label: "Could not send email"
}
]
});When you right-click on the grid, the fuzzy-finder will open and you'll see that the node "Email the customer" is now available. Clicking it will insert the node into the graph at the location of the cursor when you opened the fuzzy-finder.
Template parameters
| name | type | description |
|---|---|---|
name | string | The display name of the node. |
type | NodeType | Denotes the visual representation of a node. Can be one of the following: ACTION, CONDITION, SUCCESS, FAILURE. |
systemName | string | This name isn't used by flow-graph itself, but exported to the JSON object when the graph is exported. This name is used to identify the functionality of the node by your own software. |
description | string | A longer description of the node. Visible when hovering over an option inside the fuzzy-finder. |
inputs | Input[] | A list of inputs. See below. |
outputs | OutputSocket[] | A list of output sockets. See below |
Input parameters
| name | type | description |
|---|---|---|
name | string | The name of the socket. Used in the parameters object of the exported JSON. |
type | string | The data type of the input. Can be one of string, number, boolean or select. |
label | string | The label to display in the rendered node for this input. |
items | object | A key/value object of items to show if type is set to select. |
Output parameters
| name | type | description |
|---|---|---|
name | string | The name - or rather identifier - of the output socket. This is a key in the exitStates object in the exported JSON that connects this node to another. |
label | string | The label to show on the rendered node for this output socket. |
Importing & Exporting graphs
const data = fg.export();The method export of FlowGraph will return a JSON object that represents the
current state of the graph. The steps object contains a list of placed nodes,
indexed by the ID of the node. Exit states of nodes reference the ID of the node
to determine where to go next in the process/flow.
{
"steps": {
"step2": {
"systemName": "my.backend.logic.sendMailByTemplate",
"parameters": {
"MAIL_TEMPLATE": ""
},
"exitStates": {},
"position": {
"x": 774,
"y": 199
}
},
"entry": {
"systemName": "my.backend.logic.sendMailByTemplate",
"parameters": {
"MAIL_TEMPLATE": ""
},
"exitStates": {
"success": "step2",
"tpl_not_found": "step2",
"failed": "step2"
},
"position": {
"x": 193,
"y": 207
}
}
}
}The same object can be imported using the import method on FlowGraph.
fg.import(data);Importing data will clear the existing graph before rendering the imported data.
Events
The FlowGraph instance is an EventEmitter type. You can listen to these
events by using the once, on or when methods.
For example:
fg.on('select', (node: Node) => {
console.log(`${node.systemName} is selected!`);
});The listen methods return an EventSubscriber object which can be used to
unsubscribe a listener like so:
const subscriber = fg.on('select', (node: Node) => {
// Do stuff.
});
// Unsubscribe.
subscriber.unsubscribe();
// Or...
fg.off(subscriber);select
Callback signature:
(node: Node) => any
Invokes the given callback function when a node is selected by the user.
deselect
Callback signature:
(node: Node) => any
Invokes the given callback function when a node is deselected by the user.