@ng-web-apis/audio v4.12.0
 Web Audio API for Angular
Web Audio API for Angular
This is a library for declarative use of Web Audio API with Angular 7+. It is a complete conversion to declarative Angular directives, if you find any inconsistencies or errors, please file an issue. Watch out for 💡 emoji in this README for additional features and special use cases.
How to use
After you installed the package, you must add
@ng-web-apis/audio/polyfillto yourpolyfills.ts. It is required to normalize things likewebkitAudioContext, otherwise your code would fail.
You can build audio graph with directives. For example, here's a typical echo feedback loop:
<audio
src="/demo.wav"
waMediaElementAudioSourceNode
>
<ng-container
#node="AudioNode"
waDelayNode
[delayTime]="delayTime"
>
<ng-container
waGainNode
[gain]="gain"
>
<ng-container [waOutput]="node"></ng-container>
<ng-container waAudioDestinationNode></ng-container>
</ng-container>
</ng-container>
<ng-container waAudioDestinationNode></ng-container>
</audio>💡 AudioBufferService
This library has AudioBufferService with fetch method, returning
Promise which allows you to
easily turn your hosted audio file into AudioBuffer
through GET requests. Result is stored in service's cache so same file is not requested again while application is
running.
This service is also used within directives that have AudioBuffer inputs (such as AudioBufferSourceNode or ConvolverNode) so you can just pass string URL, as well as an actual AudioBuffer. For example:
<button
#source="AudioNode"
buffer="/demo.wav"
waAudioBufferSourceNode
(click)="source.start()"
>
Play
<ng-container waAudioDestinationNode></ng-container>
</button>Supported nodes
You can use following audio nodes through directives of the same name (prefixed with wa standing for Web API):
Terminal nodes
💡 Not required if you only need one, global context will be created when needed
💡 Also gives you access to AudioListener parameters such as positionX
💡 Additionally supports empty
autoplayattribute similar toaudiotag so it would start rendering immediately💡 Also gives you access to AudioListener parameters such as positionX
💡 Use it to terminate branch of your graph
💡 can be used multiple times inside single BaseAudioContext referencing the same BaseAudioContext.destination
💡 Has
(quiet)output to watch for particular graph branch going almost silent for 5 seconds straight so you can remove branch after all effects played out to silence to free up resources
Sources
💡 Additionally supports setting URL to media file as buffer so it will be fetched and turned into AudioBuffer
💡 Additionally supports empty
autoplayattribute similar toaudiotag so it would start playing immediately💡 Additionally supports empty
autoplayattribute similar toaudiotag so it would start playing immediately- MediaStreamAudioSourceNode
💡 Additionally supports empty
autoplayattribute similar toaudiotag so it would start playing immediately
Processors
- BiquadFilterNode
💡 Use
Channeldirective to merge channels, see example in Special cases section💡 Additionally supports setting URL to media file as buffer so it will be fetched and turned into AudioBuffer
- GainNode
- IIRFilterNode
- PannerNode
- ScriptProcessorNode
- StereoPannerNode
- WaveShaperNode
AudioWorkletNode
You can use AudioWorkletNode in supporting browsers. To register your AudioWorkletProcessors in a global default AudioContext you can use tokens:
@NgModule({
bootstrap: [AppComponent],
declarations: [AppComponent],
providers: [
{
provide: AUDIO_WORKLET_PROCESSORS,
useValue: 'assets/my-processor.js',
multi: true,
},
],
})
export class AppModule {}@Component({
selector: 'app',
templateUrl: './app.component.html',
})
export class App {
constructor(@Inject(AUDIO_WORKLET_PROCESSORS_READY) readonly processorsReady: Promise<boolean>) {}
// ...
}You can then instantiate your AudioWorkletNode:
<ng-container
*ngIf="processorsReady | async"
waAudioWorkletNode
name="my-processor"
>
<ng-container waAudioDestinationNode></ng-container>
</ng-container>If you need to create your own node with custom
AudioParam and control it declaratively you can extend
WebAudioWorklet class and add audioParam decorator to new component's inputs:
@Directive({
selector: '[my-worklet-node]',
exportAs: 'AudioNode',
providers: [asAudioNode(MyWorklet)],
})
export class MyWorklet extends WebAudioWorklet {
@Input()
@audioParam()
customParam?: AudioParamInput;
constructor(
@Inject(AUDIO_CONTEXT) context: BaseAudioContext,
@SkipSelf() @Inject(AUDIO_NODE) node: AudioNode | null,
) {
super(context, node, 'my-processor');
}
}💡 AudioParam
Since work with AudioParam is imperative in its nature, there are difference to native API when working with declarative inputs and directives.
NOTE: You can always access directives through template reference variables / @ViewChild and since they extend native nodes work with AudioParam in traditional Web Audio fashion
AudioParam inputs for directives accept following arguments:
numberto set in instantly, equivalent to setting AudioParam.valueAudioParamCurveto set array of values over given duration, equivalent to AudioParam.setValueCurveAtTime called with AudioContext.currentTimeexport type AudioParamCurve = { readonly value: number[]; readonly duration: number; }AudioParamAutomationto linearly or exponentially ramp to given value starting from AudioContext.currentTimeexport type AudioParamAutomation = { readonly value: number; readonly duration: number; readonly mode: 'instant' | 'linear' | 'exponential'; };AudioParamAutomation[]to schedule multiple changes in value, stacking one after another
You can use waAudioParam pipe to turn your number values into AudioParamAutomation (default mode is exponential,
so last argument can be omitted) or number arrays to AudioParamCurve (second argument duration is in seconds):
<ng-container
waGainNode
gain="0"
[gain]="gain | waAudioParam : 0.1 : 'linear'"
></ng-container>This way values would change smoothly rather than abruptly, causing audio artifacts.
NOTE: You can set initial value for AudioParam through argument binding combined with dynamic property binding as seen above.
To schedule an audio envelope looking something like this:
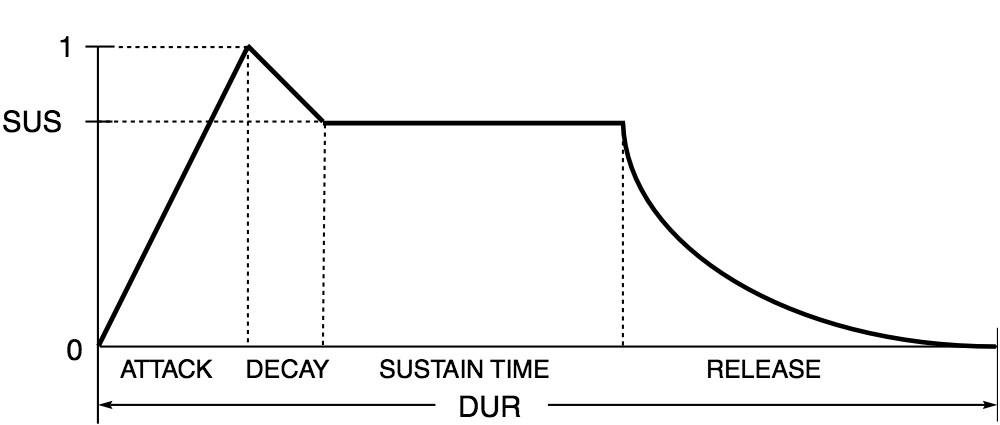
You would need to pass the following array of AudioParamAutomation items:
const envelope = [
{
value: 0,
duration: 0,
mode: 'instant',
},
{
value: 1,
duration: ATTACK_TIME,
mode: 'linear',
},
{
value: SUS,
duration: DECAY_TIME,
mode: 'linear',
},
{
value: SUS,
duration: SUSTAIN_TIME,
mode: 'instant',
},
{
value: 0,
duration: RELEASE_TIME,
mode: 'exponential',
},
];💡 Special cases
- Use
waOutputdirective when you need non-linear graph (see feedback loop example above) or to manually connect AudioNode to AudioNode or AudioParam - Use
waPeriodicWavepipe to create PeriodicWave for OscillatorNode - All node directives are exported as
AudioNodeso you can use them with template reference variables (see feedback loop example above) - Use
waChanneldirective within ChannelMergerNode and directwaOutputdirective to it in order to perform channel merging:
<!-- Inverting left and right channel -->
<audio
src="/demo.wav"
waMediaElementAudioSourceNode
>
<ng-container waChannelSplitterNode>
<ng-container [waOutput]="right"></ng-container>
<ng-container [waOutput]="left"></ng-container>
</ng-container>
<ng-container waChannelMergerNode>
<ng-container
#left="AudioNode"
waChannel
></ng-container>
<ng-container
#right="AudioNode"
waChannel
></ng-container>
<ng-container waAudioDestinationNode></ng-container>
</ng-container>
</audio>💡 Tokens
- You can check Web Audio API support in current
browser by injecting
WEB_AUDIO_SUPPORTtoken - You can check AudioWorklet support in current browser
by injecting
AUDIO_WORKLET_SUPPORTtoken - You can inject BaseAudioContext through
AUDIO_CONTEXTtoken - AudioContext is created by default with default options when token is requested
- You can also provide custom BaseAudioContext through that token
- Provide
FEEDBACK_COEFFICIENTSandFEEDFORWARD_COEFFICIENTStokens to be able to create IIRFilterNode - Provide
MEDIA_STREAMtoken to be able to create MediaStreamAudioSourceNode - All node directives provide underlying AudioNode as
AUDIO_NODEtoken - Use
AUDIO_WORKLET_PROCESSORStoken to declare array of AudioWorkletProcessors to be added to default AudioContext - Inject
AUDIO_WORKLET_PROCESSORS_READYtoken to initialize provided AudioWorkletProcessors loading and watch for Promise resolution before instantiating dependent AudioWorkletNodes
Browser support
| 12+ | 31+ | 34+ | 9+ |
Note that some features (AudioWorklet etc.) were added later and are supported only by more recent versions
IMPORTANT: You must add @ng-web-apis/audio/polyfill to your polyfills.ts, otherwise you will get
ReferenceError: X is not defined in browsers for entities they do not support
💡 StereoPannerNode is emulated with PannerNode in browsers that do not support it yet
💡 positionX (orientationX) and other similar properties of AudioListener and PannerNode fall back to setPosition (setOrientation) method if browser does not support it
Angular Universal
If you want to use this package with SSR, you need to mock native Web Audio API classes on the server:
import '@ng-web-apis/audio/mocks';It is recommended to keep the import statement at the top of your
server.tsormain.server.tsfile.
Demo
You can try online demo here
See also
Other Web APIs for Angular by @ng-web-apis
10 months ago
1 year ago
1 year ago
1 year ago
1 year ago
1 year ago
1 year ago
1 year ago
1 year ago
1 year ago
1 year ago
1 year ago
1 year ago
1 year ago
1 year ago
1 year ago
1 year ago
1 year ago
2 years ago
2 years ago
2 years ago
2 years ago
2 years ago
2 years ago
2 years ago
2 years ago
2 years ago
2 years ago
2 years ago
2 years ago
3 years ago
2 years ago
2 years ago
3 years ago
3 years ago
3 years ago
5 years ago
5 years ago
5 years ago
5 years ago
5 years ago
5 years ago
5 years ago
5 years ago
5 years ago
5 years ago
5 years ago
6 years ago
6 years ago
6 years ago
6 years ago
6 years ago
6 years ago
6 years ago
6 years ago
6 years ago

