@orzfly/clipanion v3.0.0-pre.0
Clipanion
Type-safe CLI library with no runtime dependencies
Installation
⚠️ Important: This documentation is about Clipanion 3, which is still in development and hasn't been published to the npm registry yet. For Clipanion 2, please check the following document, which shows the decorator syntax you might have seen before.
yarn add clipanion@arcanis/clipanionWhy
- Clipanion supports advanced typing mechanisms
- Clipanion supports nested commands (
yarn workspaces list) - Clipanion supports transparent option proxying without
--(for exampleyarn dlx eslint --fix) - Clipanion supports all option types you could think of (including negations, batches, ...)
- Clipanion offers a Typanion integration for increased validation capabilities
- Clipanion generates an optimized state machine out of your commands
- Clipanion generates good-looking help pages out of the box
- Clipanion offers common optional command entries out-of-the-box (e.g. version command, help command)
Clipanion is used in Yarn with great success.
Recommended Usage
In essence you just need to declare a class that extends the Command abstract class, and implement the execute method. This function will then be called by Clipanion and its return value will be set as exit code by the engine (by default the exit code will be 0, which means success).
Options and command paths are set using the Command option declarators. Because you're in a regular class, you can easily create command that extend others! If you use TypeScript, all property types will be properly inferred with no extra work required - even your validators support coercion (cf Typanion's documentation for more details).
import {Cli, Command, Argument, Builtins} from 'clipanion';
import * as yup from 'yup';
// greet [-v,--verbose] [--name ARG]
class GreetCommand extends Command {
verbose = Option.Boolean(`-v,--verbose`, false);
name = Option.String(`--name`);
static paths = [[`greet`]];
async execute() {
if (typeof this.name === `undefined`) {
this.context.stdout.write(`You're not registered.\n`);
} else {
this.context.stdout.write(`Hello, ${this.name}!\n`);
}
}
}
// add <a> <b>
class AddCommand extends Command {
a = Option.String({required: true, validator: t.isNumber()});
b = Option.String({required: true, validator: t.isNumber()});
static paths = [[`fibo`]];
async execute() {
this.context.stdout.write(`${this.a + this.b}\n`);
}
}
const cli = new Cli({
binaryLabel: `My Utility`,
binaryName: `bin`,
binaryVersion: `1.0.0`,
});
cli.register(Builtins.HelpCommand);
cli.register(Builtins.VersionCommand);
cli.register(GreetCommand);
cli.register(AddCommand);
cli.runExit(process.argv.slice(2), {
...Cli.defaultContext,
});Declarators
The optionNames parameters all indicate that you should put there a comma-separated list of option names (along with their leading -). For example, -v,--verbose is a valid parameter.
static paths: string[][]
Specifies the CLI paths that should trigger the command.
class WorkspaceCommand extends Command {
static paths = [[`workspaces`, `foreach`]];
// ...
}Generates a command that will be called by running yarn workspaces foreach on the command line (assuming the binary name is yarn). You can add as many paths as you want to a single command, for example here the command would be callable via either yarn install or yarn i:
class InstallCommand extends Command {
static paths = [[`install`], [`i`]];
// ...
}By default commands are connected on the main entry point (as if they had an empty path), but if you add even one explicit path this behavior will be disabled. If you still want the command to be available on both a named path and as a default entry point (for example like the classic yarn command, which is an alias for yarn install), simply use Command.Default:
class InstallCommand extends Command {
static paths = [[`install`], Command.Default];
// ...
}Runing any of yarn or yarn install will then trigger the function, as expected.
Option.Array(optionNames: string, default?: string[], opts?: {...})
| Option | type | Description |
|---|---|---|
arity | number | Number of arguments for the option |
description | string | Short description for the help message |
hidden | boolean | Hide the option from any usage list |
Specifies that the command accepts a set of string arguments. The arity parameter defines how many values need to be accepted for each item. If no default value is provided, the option will start as undefined.
class RunCommand extends Command {
args = Option.Array('--arg');
points = Option.Array('--point', {arity: 3});
// ...
}Generates:
run --arg value1 --arg value2
# => TestCommand {"args": ["value1", "value2"]}
run --point x y z --point a b c
# => TestCommand {"points": [["x", "y", "z"], ["a", "b", "c"]]}Option.Boolean(optionNames: string, default?: boolean, opts?: {...})
| Option | type | Description |
|---|---|---|
description | string | Short description for the help message |
hidden | boolean | Hide the option from any usage list |
Specifies that the command accepts a boolean flag as an option. If no default value is provided, the option will start as undefined.
class TestCommand extends Command {
flag = Option.Boolean(`--flag`);
// ...
}Generates:
run --flag
# => TestCommand {"flag": true}Option.Counter(optionNames: string, default?: number, opts?: {...})
| Option | type | Description |
|---|---|---|
description | string | Short description for the help message |
hidden | boolean | Hide the option from any usage list |
Specifies that the command accepts a boolean flag as an option. Contrary to classic boolean options, each detected occurence will cause the counter to be incremented. Each time the argument is negated (--no-<name>), the counter will be reset to 0. If no default value is provided, the option will start as undefined.
class TestCommand extends Command {
verbose = Option.Counter(`-v,--verbose`);
// ...
}Generates:
run -v
# => TestCommand {"verbose": 1}
run -vv
# => TestCommand {"verbose": 2}
run --verbose -v --verbose -v
# => TestCommand {"verbose": 4}
run --verbose -v --verbose -v --no-verbose
# => TestCommand {"verbose": 0}Option.Proxy(opts?: {...})
| Option | type | Description |
|---|---|---|
required | number | Number of required trailing arguments |
Specifies that the command accepts an infinite set of positional arguments that will not be consumed by the options of the Command instance. Use this decorator instead of Command.Rest when you wish to forward arguments to another command parsing them in any way. By default no arguments are required, but this can be changed by setting the required option.
class RunCommand extends Command {
args = Option.Proxy();
// ...
}Generates:
run
# => TestCommand {"values": []}
run value1 value2
# => TestCommand {"values": ["value1", "value2"]}
run value1 --foo
# => TestCommand {"values": ["value1", "--foo"]}
run --bar=baz
# => TestCommand {"values": ["--bar=baz"]}Note: Proxying can only happen once per command. Once triggered, a command can't get out of "proxy mode", all remaining arguments being proxied into a list. "Proxy mode" can be triggered in the following ways:
By passing a positional or an option that doesn't have any listeners attached to it. This happens when the listeners don't exist in the first place.
By passing a positional that doesn't have any remaining listeners attached to it. This happens when the listeners have already consumed a positional.
By passing the
--separator before an option that has a listener attached to it. This will cause Clipanion to activate "proxy mode" for all arguments after the separator, without proxying the separator itself. In all other cases, the separator will be proxied and not consumed by Clipanion.
Option.Rest(opts?: {...})
| Option | type | Description |
|---|---|---|
required | number | Number of required trailing arguments |
Specifies that the command accepts an unlimited number of positional arguments. By default no arguments are required, but this can be changed by setting the required option.
class RunCommand extends Command {
values = Option.Rest();
// ...
}Generates:
run
# => TestCommand {"values": []}
run value1 value2
# => TestCommand {"values": ["value1", "value2"]}
run value1
# => TestCommand {"values": ["value1"]}
run
# => TestCommand {"values": []}Note: Rest arguments are strictly positionals. All options found between rest arguments will be consumed as options of the Command instance. If you wish to forward a list of option to another command without having to parse them yourself, use Command.Proxy instead.
Note: Rest arguments can be surrounded by other finite non-optional positionals such as Option.String({required: true}). Having multiple rest arguments in the same command is however invalid.
Advanced Example:
class CopyCommand extends Command {
sources = Option.Rest({required: 1});
destination = Option.String();
force = Option.Boolean(`-f,--force`);
reflink = Option.String(`--reflink`, {tolerateBoolean: true});
// ...
}Generates:
run src dest
# => CopyCommand {"sources": ["src"], "destination": "dest"}
run src1 src2 dest
# => CopyCommand {"sources": ["src1", "src2"], "destination": "dest"}
run src1 --force src2 dest
# => CopyCommand {"sources": ["src1", "src2"], "destination": "dest", "force": true}
run src1 src2 --reflink=always dest
# => CopyCommand {"sources": ["src1", "src2"], "destination": "dest", "reflink": "always"}
run src
# => Invalid! - Not enough positional arguments.
run dest
# => Invalid! - Not enough positional arguments.Option.String(optionNames: string, default?: string, opts?: {...})
| Option | type | Description |
|---|---|---|
arity | number | Number of arguments for the option |
description | string | Short description for the help message |
hidden | boolean | Hide the option from any usage list |
tolerateBoolean | boolean | Accept the option even if no argument is provided |
Specifies that the command accepts an option that takes arguments (by default one, unless overriden via arity). If no default value is provided, the option will start as undefined.
class TestCommand extends Command {
arg = Option.String(`-a,--arg`);
// ...
}Generates:
run --arg value
run --arg=value
run -a value
run -a=value
# => TestCommand {"arg": "value"}
run --arg=-42
# => TestCommand {"arg": "-42"}
run --arg -42
# => Invalid! Option `-42` doesn't exist.Be careful, by default, options that accept an argument must receive one on the CLI (ie --foo --bar wouldn't be valid if --foo accepts an argument).
This behaviour can be toggled off if the tolerateBoolean option is set. In this case, the option will act like a boolean flag if it doesn't have a value. Note that with this option on, arguments values can only be specified using the --foo=ARG syntax, which makes this option incompatible with arities higher than one.
class TestCommand extends Command {
debug = Option.String(`--inspect`, {tolerateBoolean: true});
// ...
}Generates:
run --inspect
# => TestCommand {"debug": true}
run --inspect=1234
# => TestCommand {"debug": "1234"}
run --inspect 1234
# Invalid!Option.String(opts: {...})
| Option | type | Description |
|---|---|---|
required | boolean | Whether the positional argument is required or not |
Specifies that the command accepts a positional argument. By default it will be required, but this can be toggled off using required.
class TestCommand extends Command {
foo = Option.String();
// ...
}Generates:
run value
# => TestCommand {"foo": "value"}Note that Clipanion supports required positional arguments both at the beginning and the end of the positional argument list (which allows you to build CLI for things like cp). For that to work, make sure to list your arguments in the right order:
class TestCommand extends Command {
foo = Option.String({required: false});
bar = Option.String();
// ...
}Generates:
run value1 value2
# => TestCommand {"foo": "value1", "bar": "value2"}
run value
# => TestCommand {"foo": undefined, "bar": "value"}
run
# Invalid!Command Help Pages
Clipanion automatically adds support for the -h option to all the commands that you define. The information printed will come from the usage property attached to the class. For example, the following command:
class YarnAdd extends Command {
static usage = Command.Usage({
description: `remove dependencies from the project`,
details: `
This command will remove the specified packages from the current workspace. If the \`-A,--all\` option is set, the operation will be applied to all workspaces from the current project.
`,
examples: [[
`Remove a dependency from the current project`,
`$0 remove lodash`,
], [
`Remove a dependency from all workspaces at once`,
`$0 remove lodash --all`,
]],
});
}Will generate something like this:
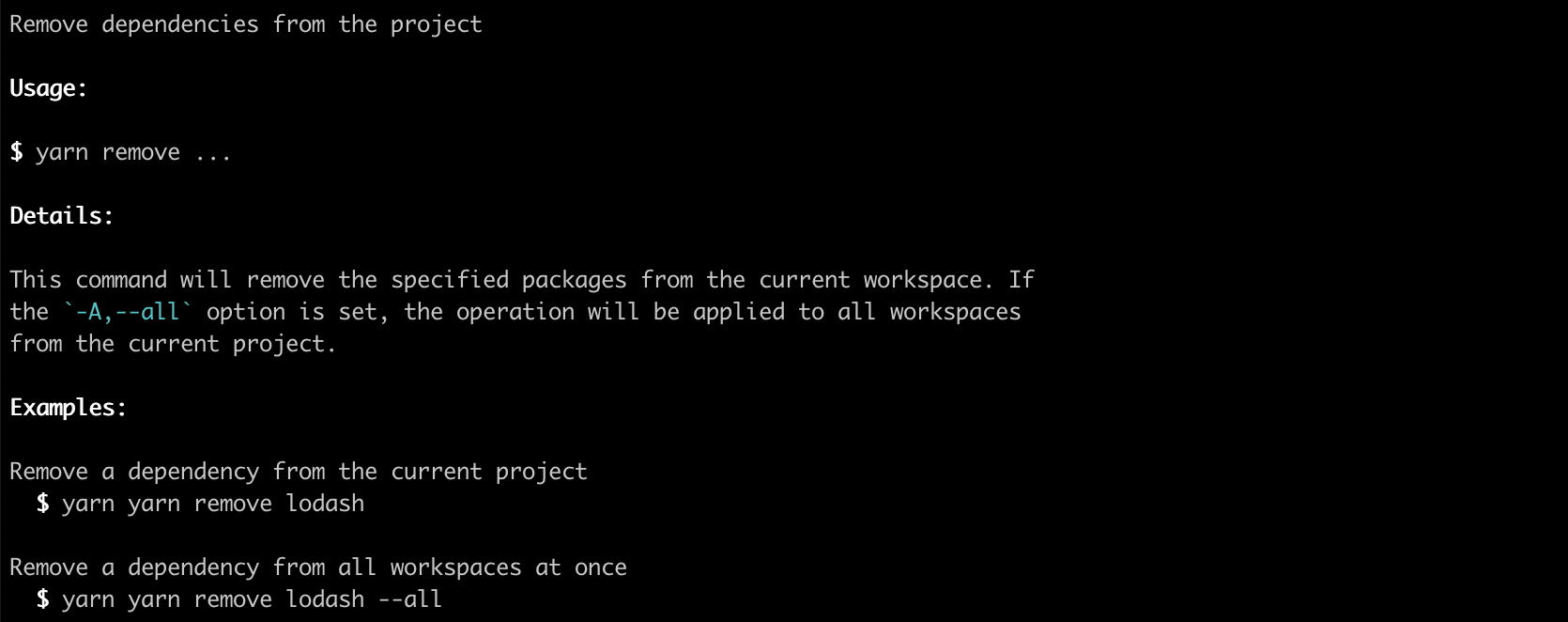
Note that the inline code blocks will be automatically highlighted.
Optional Built-in Command Entries
Clipanion offers common optional command entries out-of-the-box, under the Builtins namespace.
They have to be manually registered:
cli.register(Builtins.HelpCommand);
cli.register(Builtins.VersionCommand);Help Command - General Help Page
Paths:
-h,--help
The Builtins.HelpCommand command displays the list of commands available to the application, printing a block similar to the following.
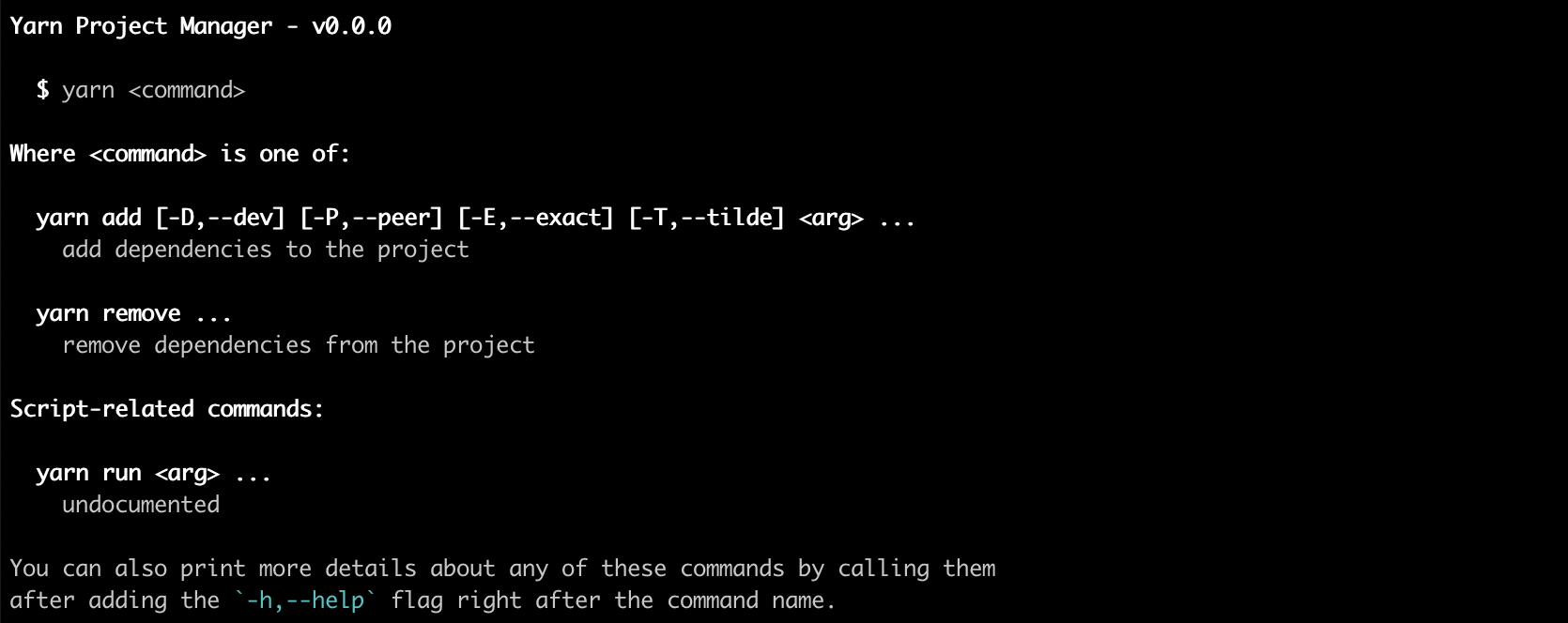
Version Command
Paths:
-v,--version
The Builtins.Version command displays the version of the binary provided under binaryVersion when creating the CLI.
Composition
Commands can call each other by making use of their cli internal property:
class FooCommand extends Command {
static paths = [[`foo`]];
async execute() {
this.context.stdout.write(`Hello World\n`);
}
}
class BarCommand extends Command {
static paths = [[`bar`]];
async execute() {
this.cli.run([`foo`]);
}
}Inheritance
Commands can extend each other and inherit options from each other:
abstract class BaseCommand extends Command {
cwd = Option.String(`--cwd`, {hidden: true});
abstract execute(): Promise<number | void>;
}
class FooCommand extends BaseCommand {
foo = Option.String(`-f,--foo`);
async execute() {
this.context.stdout.write(`Hello from ${this.cwd ?? process.cwd()}!\n`);
this.context.stdout.write(`This is foo: ${this.foo}.\n`);
}
}Note: Because of the class initialization order, positional arguments of a subclass will be consumed before positional arguments of a superclass. Because of this, it is not recommended to inherit anything other than named options and regular methods.
Lazy evaluation
Many commands have the following form:
import {uniqBy} from 'lodash';
export class MyCommand extends Command {
async execute() {
// ...
}
}While it works just fine, if you have a lot of command, each with its own set of dependencies (here, lodash), the startup time may suffer. This is because the import statements will always be eagerly evaluated, even if the command doesn't end up being used in the end. To solve this problem, you can move your imports inside the body of the execute function, thus making sure they'll only be evaluated if actually relevant:
export class MyCommand extends Command {
async execute() {
const {uniqBy} = await import(`lodash`);
// ...
}
}This strategy is slightly harder to read, so it may not be necessary in every situation. If you like living on the edge, the babel-plugin-lazy-import plugin is meant to automatically apply this kind of transformation - although it requires you to run Babel on your sources.
Contexts
Commands share what is called a context. Contexts are a set of values defined when calling the run function from the CLI instance that will be made available to the commands via this.context. The default context contains properties for stdin, stdout, and stderr, but you can easily define a custom context that extends the default one:
import {BaseContext, Command} from 'clipanion';
type MyContext = BaseContext & {
cwd: string;
};
class PwdCommand extends Command<MyContext> {
async execute() {
this.context.stdout.write(`${this.context.cwd}\n`);
}
}
const cli = Cli.from<MyContext>([
PwdCommands,
]);
cli.runExit(process.argv.slice(2), {
...Cli.defaultContext,
cwd: process.cwd(),
});Note that the context must be fully defined when calling run and runExit on the main CLI instance, but can be omitted or only partially specified when using this.cli.run (in which case only the specified fields will be changed).
License (MIT)
Copyright © 2019 Mael Nison
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.
5 years ago


