@pxtrick/fsm v0.0.7
FSM (Finite-State Machine)
A JavaScript module which provides simple finite-state machine behavior.
These core elements of a traditional finite-state machine are available for configuration:
- State names
- State transitions (or "events")
- Initial state
- Pre-transition behavior
- Post-transition behavior
- Actions always occurring upon state entry
- Actions always occurring upon state exit
Input Configuration Specification
(See configuration sample below for JSON structure)
startState: The state at which a newly created state machine will be initialized. type: stringstates: An object specifying all possible name-value object pairs for states and transition events. type: JS objectevents: Contains named objects which give details for the possible transition events for this state. type: JS objecttoState: The state name to which we will transition when receiving this event. type: stringonBefore: A callback which is fired before the state change has occurred. type: functiononAfter: A callback which is fired after the state change has occurred. type: function
actions: The actions which will always be executed when a state is entered or exited. (This is kind of conceptually similar to the execution order of constructors/destructors.) type: JS objectonEnter: A callback which is fired every time the state is entered, regardless of where it just transitioned from. type: functiononExit: A callback which is fired every time the state is exited, regardless of where it is transitioning to. type: function
NOTE: During creation of a new state machine object, the configuration is validated. If errors are found, the value returned by method isValid() will be false, and the value from method status() will hold the status code of the problem.
Sample Module Usage (example 1)
Let's model a simple light switch; Here's the state diagram:
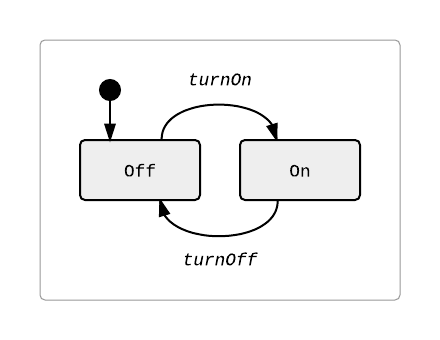 And the corresponding code would be ...
And the corresponding code would be ...
// +-----------------------+
// | Model a light switch. |
// +-----------------------+
var config = {
startState: 'Off',
states: {
'Off': { events: { 'turnOn': { toState: 'On' } } },
'On': { events: { 'turnOff': { toState: 'Off' } } }
}
};
// Load the module and call the factory method to create a new instance.
var FSM = require('@pxtrick/fsm');
var fsm = FSM.newFSM(config);
if (fsm.isValid()) {
// Handle state-changing events.
fsm.handleEvent('turnOn'); // fsm.currentState() === 'On';
fsm.handleEvent('turnOff'); // fsm.currentState() === 'Off';
}NOTE: For brevity, the idempotent transitions of [Off]->(turnOff)->[Off] and [On]->(turnOn)->[On] are not included in this code example.
Sample Module Usage (example 2)
Let's model a more complex login sequence; Here's the state diagram:
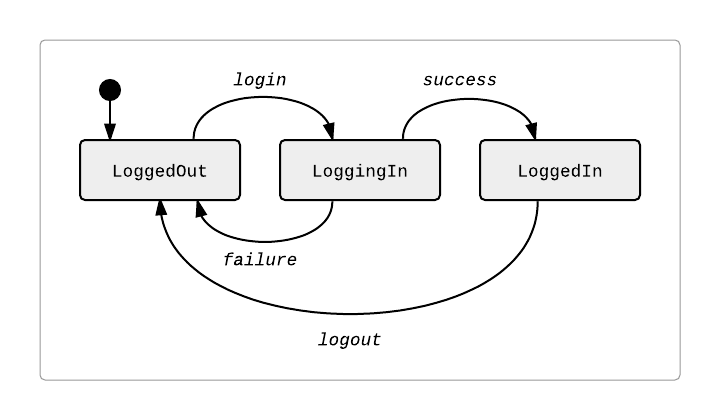 And the corresponding code would be ...
And the corresponding code would be ...
// +-------------------------+
// | Model a login sequence. |
// +-------------------------+
var config = {
startState: 'LoggedOut',
states: {
'LoggedOut': {
events: {
'login': { toState: 'LoggingIn'}
},
actions: {
onEnter: function() { console.log('You have been logged out.') }
}
},
'LoggingIn': {
events: {
'success': { toState: 'LoggedIn'},
'failure': {
toState: 'LoggedOut',
onBefore: function() { console.log('Login FAILED.') }
}
}
},
'LoggedIn': {
events: {
'logout': {
toState: 'LoggedOut',
onAfter: function() { console.log('Thanks for playing!') }
}
},
actions: {
onEnter: function() { console.log('You are now logged in.') }
}
}
}
};
// Load the module and call the factory method to create a new instance.
var FSM = require('@pxtrick/fsm');
var fsm = FSM.newFSM(config);
if (fsm.isValid()) {
// Handle state-changing events.
fsm.handleEvent('login'); // fsm.currentState() === 'LoggingIn';
fsm.handleEvent('failure'); // fsm.currentState() === 'LoggedOut';
fsm.handleEvent('login'); // fsm.currentState() === 'LoggingIn';
fsm.handleEvent('success'); // fsm.currentState() === 'LoggedIn';
fsm.handleEvent('logout'); // fsm.currentState() === 'LoggedOut';
}NOTE: For brevity, no idempotent transitions are included in this code example.
Dependencies:
This module is dependent on lodash.