@rsksmart/rbank.js v0.1.1
rbank-js
Rbank handler library. Note: This library does work with a very specific set of smart contracts.
We highly recommend reading this article explaining the details of the Rbank operation.
Installation
To install this library just execute:
$ npm i --save @rsksmart/rbank.jsUsage
Core
Importing the library and creating an instance.
import Rbank from '@rsksmart/rbank.js';
const rbank = new Rbank();By default, as a shortcut, the core package lets you to do some quick operations as getting
quick information about markets registered in the controller. After setting the controller address as
shown in the following controller section, you might get the markets as instances of Market.
rbank.eventualMarkets
.then((markets) => {
markets.forEach((market) => console.log(market.address));
});You can even query a specific market by its position on the array or its on-chain address:
rbank.eventualMarket(0)
.then((market) => market.eventualBalance)
.then(console.log)
.catch(console.error);
rbank.eventualMarket('0xe78A0F7E598Cc8b0Bb87894B0F60dD2a88d6a8Ab')
.then((market) => market.eventualBalance)
.then(console.log)
.catch(console.error);Controller
The controller, as its name suggests, tracks the whole Rbank operation and keep detailed account of all the markets registered within it.
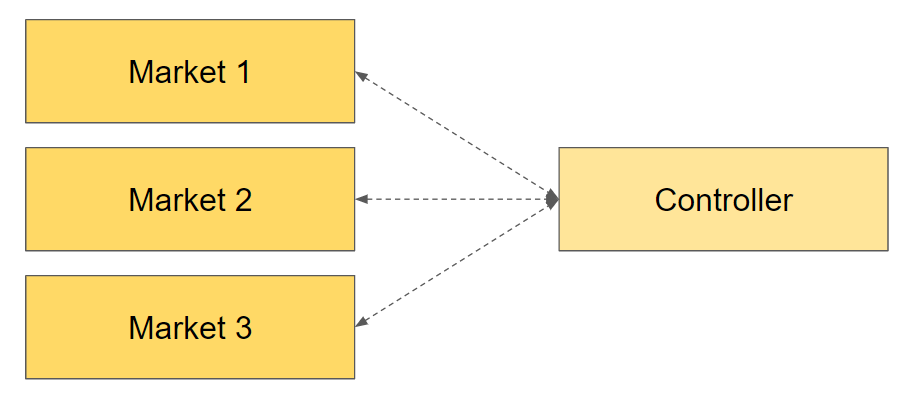
You can use the library to create a new controller. This operation returns a promise of the address that the controller smart contract got on chain and can be used to start the core instance.
rbank.Controller.create()
.then((controllerAddress) => {
rbank.controller = controllerAddress;
})
.catch(console.error);To initialize the controller instance, as seen in the code above, you only have to set the desired controller smart contract on-chain address. However, by retrieving the controller from rbank, you don't get the address of the controller, but an instance. If you want to get the address of the controller, get it from the controller instance.
console.log(rbank.controller.address);You can have access to both, the collateral and liquidation factors.
rbank.controller.eventualCollateralFactor
.then((collateralFactor) => {
// do something with this factor.
console.log(collateralFactor);
})
.catch(console.error);
rbank.controller.eventualLiquidationFactor
.then((liquidationFactor) => {
// do something with this factor.
console.log(liquidationFactor);
})
.catch(console.error);The contoller also let to set values for both, the collateral and liquidation factors.
const collateralFactor = 15;
rbank.controller.setCollateralFactor(collateralFactor)
.then(console.log)
.catch(console.error);
const liquidationFactor = 15;
rbank.controller.setLiquidationFactor(liquidationFactor)
.then(console.log)
.catch(console.error);Other operations related to the controller are (all the operations that involve on-chain reading and writing return promises):
eventualMarketListSize: Promise<number>setMarketPrice(marketAddress, marketPrice): Promise<TXResult>eventualMarketPrice(marketAddress): Promise<number>getAccountValues(account): Promise<AccountValues>getAccountLiquidity(account): Promise<number>getEventualMarketAddress(marketIdx): Promise<string>
The source controller file is fully documented and you can check the signature of each method.
Market management
As seen on the controller section, the relation between a market and the controller is bidirectional.
In order to create a new market you will have to associate the token it will handle and other information.
 .
.
In order to create a new market you should have the associated on-chain ERC20 token pool address
as well as the base borrow rate this market will handle. Once you get the market address on-chain,
you can register it into the controller.
const tokenAddress = '0xe78A0F7E598Cc8b0Bb87894B0F60dD2a88d6a8Ab';
const baseBorrowRate = 15;
rbank.Market.create(tokenAddress, baseBorrowRate)
.then((marketAddress) => [
rbank.controller.addMarket(marketAddress),
new rbank.Market(marketAddress),
])
.then((results) => Promise.all(results))
.then(([addingMarketTxObject, marketInstance]) => {
console.log(`Tx Hash: ${addingMarketTxObject.transactionHash}`);
return marketInstance.setControllerAddress(rbank.controller.address);
})
.then((settingControllerTxObject) => {
console.log(settingControllerTxObject.transactionHash);
})
.catch(console.error);Other operations related to the market are (all the operations that involve on-chain reading and writing return promises):
address: stringeventualController: Promise<string>eventualBaseBorrowRate: Promise<number>eventualBalance: Promise<number>setControllerAddress(controllerAddress): Promise<TXResult>supply(amount, from = ''): Promise<TXResult>borrow(amount, from = ''): Promise<TXResult>supplyOf(from = ''): Promise<number>
Development
Just clone this repo and install npm dependencies:
$ git clone git@github.com:rsksmart/rbank-js.git
$ cd rbank-js
$ npm iUsage
On development stages, this package is not available on npm. To make it available for other projects you can link them by:
- Go to the project directory.
- Build it, test it and finally exectue
npm linkto make it globally available in the local host. - Go to the other project where you need to use this library and execute
npm link @rsksmart/rbank.js. Note: the package is not going to be linked as a dependency in the target projectpackage.jsonfile, but it's going to be available to be used.
Any change on this library will be automatically reflected on all the projects that have linked the library into them.
Testing
In order to run the test in this project you should have a console running with ganache-cli
ganache-cli installation
You might want to have ganache-cli installed globally.
$ npm i -g ganache-cliPreparation prior to the testing
You have to guarantee having the specific version of smart contracts, simply do as follows:
$ cd dependencies/DeFiProt
$ git pull origin/masterSometimes it would be necessary to guarantee having everything built up from scratch. In order to have the project ready to be tested do as follows:
$ npm i
$ npm run deploy:controller
$ npm run deploy:market
$ npm run bootstrapThese commands, install npm dependencies, compile smart contracts and copy the resulting json
files into the respective packages, link all the internal packages together.
Running the tests
You should be located at this project root and run the tests.
$ npm test4 years ago