@syneki/notion-cms v1.0.0
Use Notion as a Content Management System.
🚀 Get started • 🔧 Configure • 🔍 Query • 🏗 Extend
⚠ Pre-release
This project is currently in pre-release, you can use it but some features are lacking and few things will have to change in a near future.
- Query multiple pages from a database
- Query a single page
- Transform page content into HTML
- Ability to extends the renderer
- Easily map your page properties
- Ability to create custom parsers
- Create renderer for all of the Notion base blocks
- Handle relation property
- Handle page cover
- Handle file property
- Handle rollup property
Do not hesitate to open an issue to provide your feedback, report bugs and to propose new features.
🚀 Getting started
Install libraries
$ npm install @syneki/notion-cms @syneki/notion-renderer
$ yarn add @syneki/notion-cms @syneki/notion-renderer⚠ We highly recommend to use a Static Website Generator to use NotionCMS. The Notion API is extremely slow, avoid querying it on each visit.
Create a database
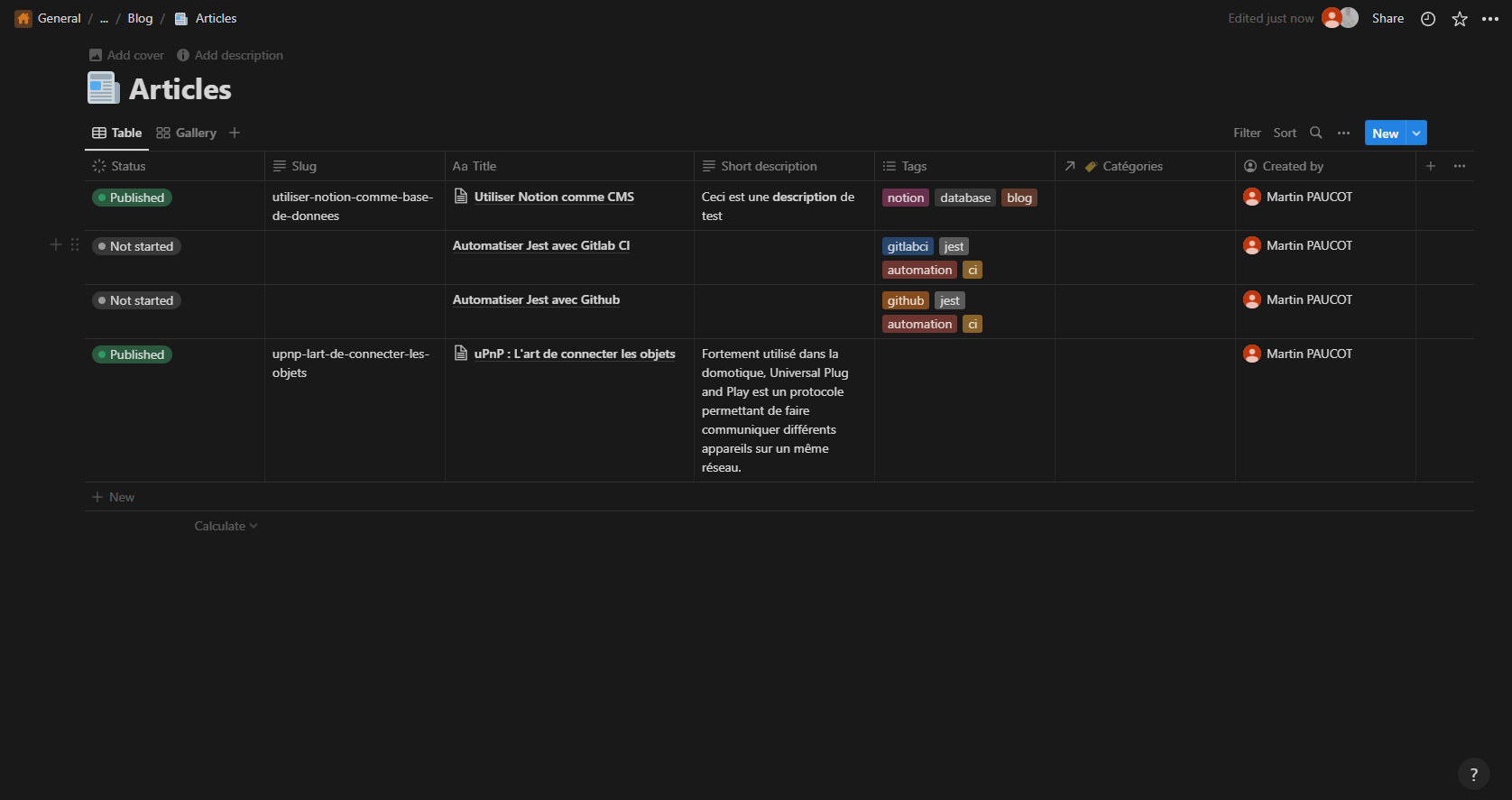
Query your database
import { NotionCMS, NotionDatabase } from '@syneki/notion-cms';
const cms = new NotionCMS({
auth: process.env.NOTION_TOKEN,
renderer,
});
const database = new NotionDatabase({
cms,
databaseId: '<my-database-id>',
});
// Query multiple pages
const posts = await database.list();
// Retreive a single page by ID
const post = await database.get('<my-page-id>');
// Retreive a single page by property
const postBySlug = await database.findFirst({
property: 'slug',
rich_text: { equals: 'my-super-post' },
});
// Retreive the content of a page in HTML
const content = await database.getContent(postBySlug.id);Get a Notion Token
To interact with Notion you need to create an integration and give it the correct permissions.
Create a new integration by heading to the following link.
You should then be able to get an Internal Integration Token.
:warning: Make sure that you are giving the correct permissions. If the token is directly accessible from your Frontend it can be a real problem!
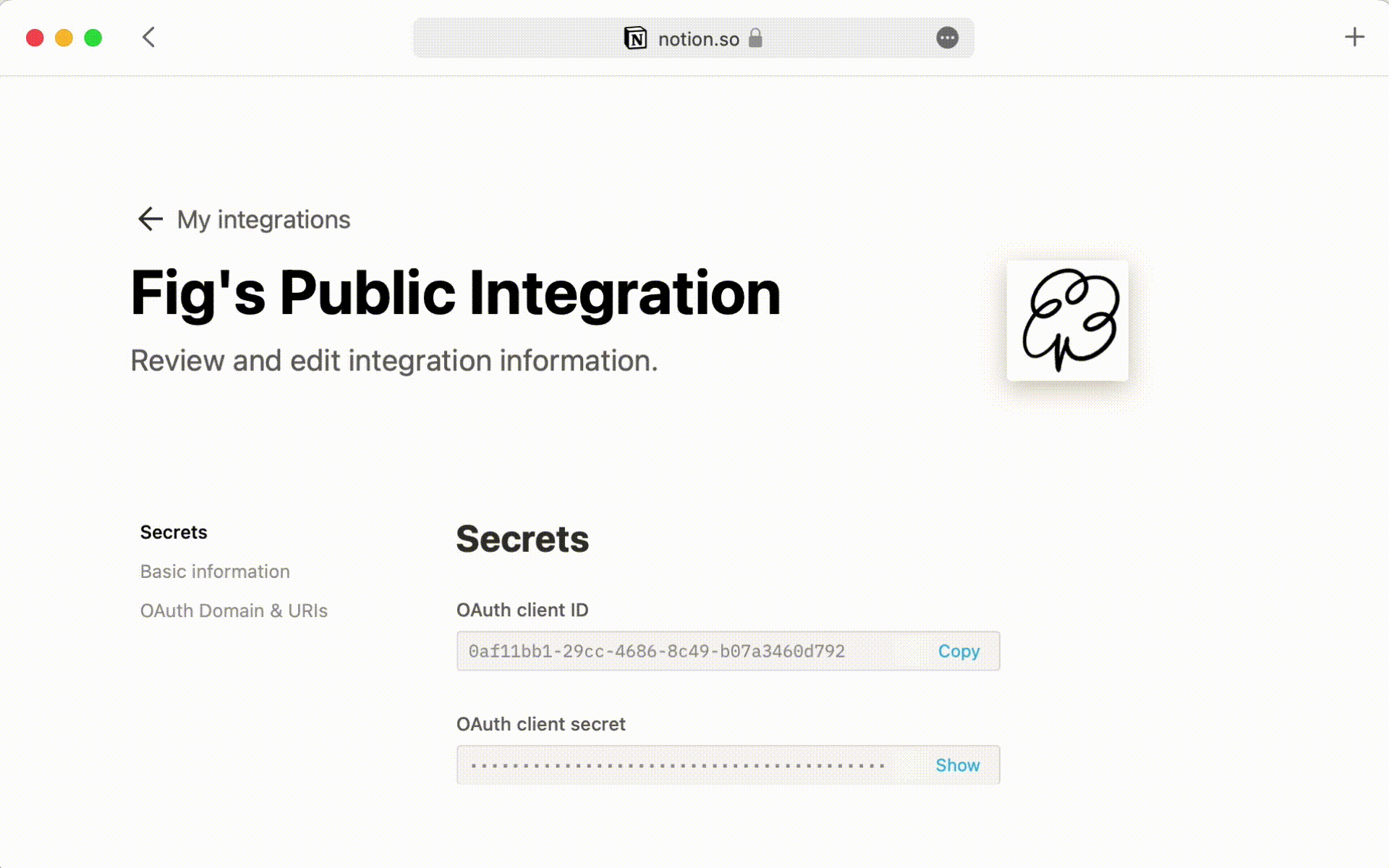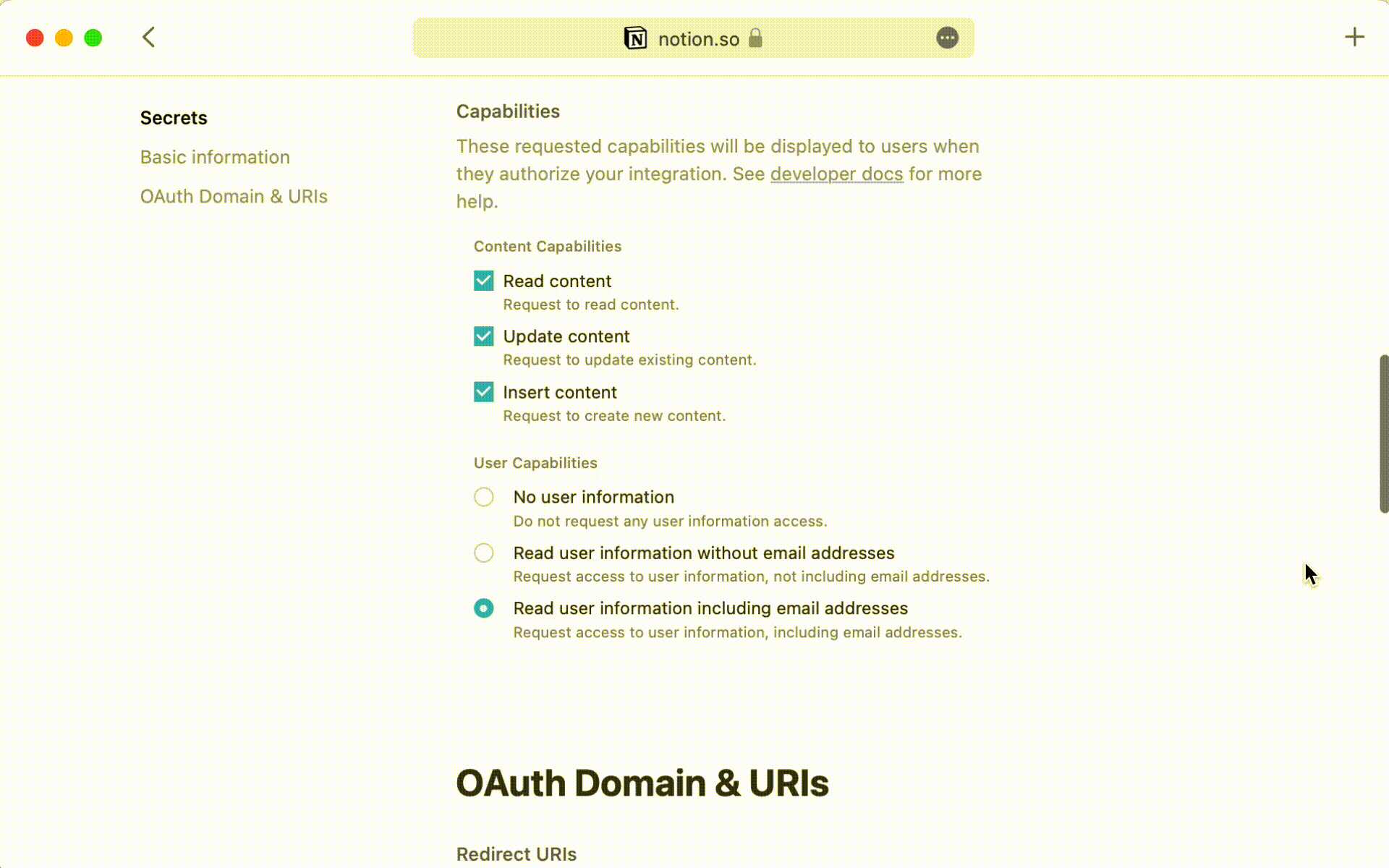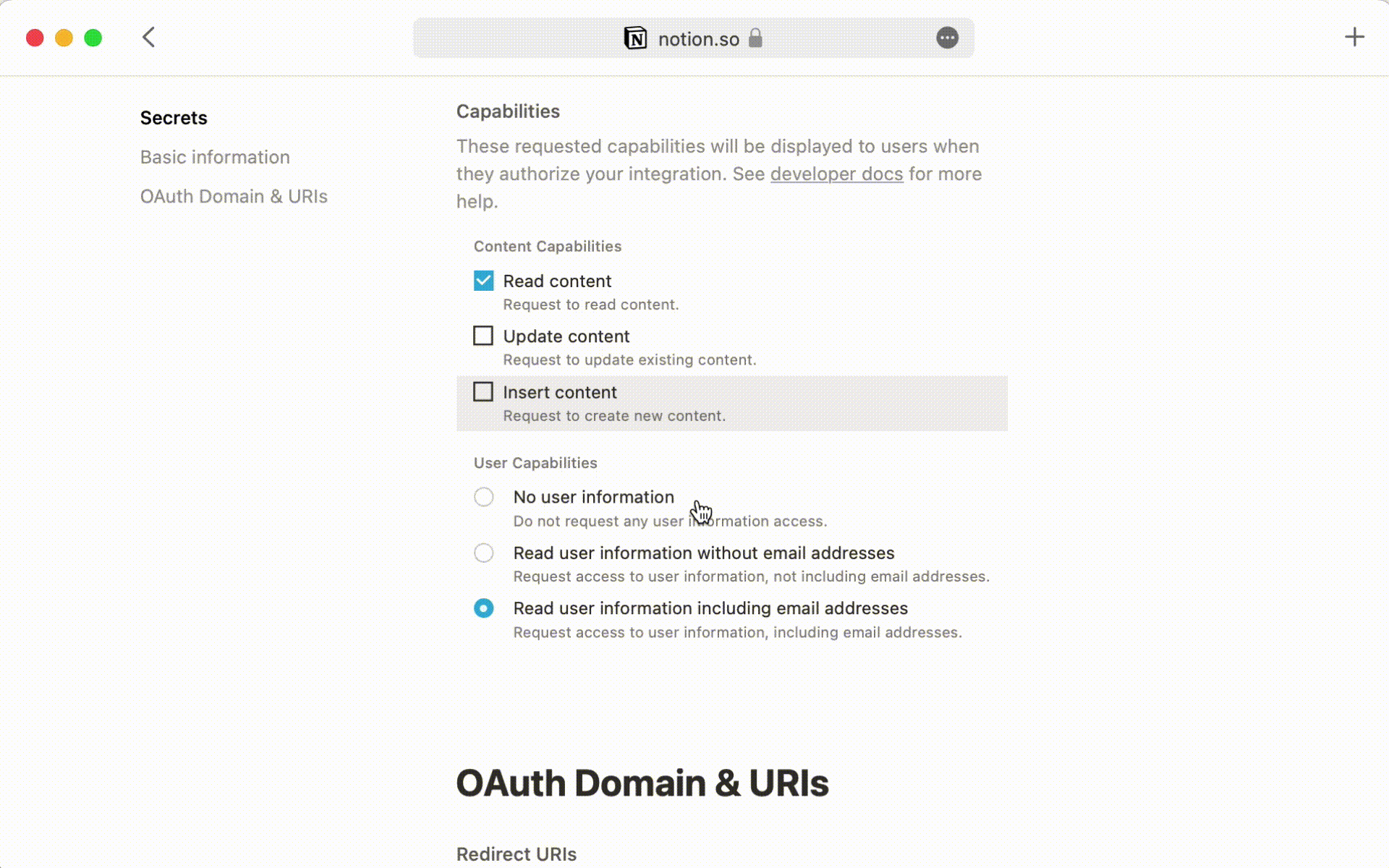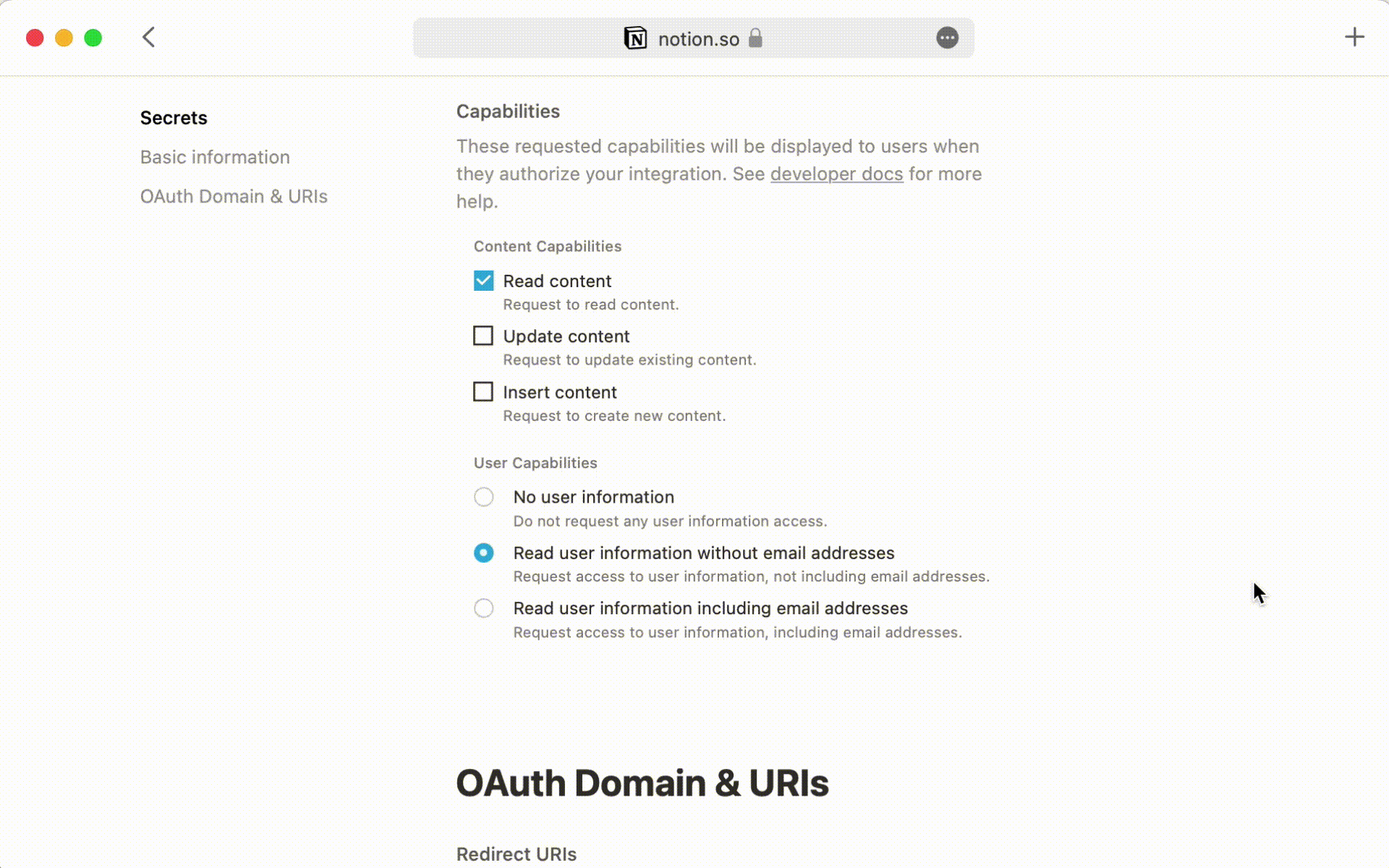
Add the integration to your databases
On each databases you want to query click on the ••• in the top right corner.
Click on Add connection and select your Integration. Your token should now have access to your database.
🔧 Configure
NotionCMS
NotionCMS is used to interact with a Notion Account.
import { NotionCMS } from '@syneki/notion-cms';
const cms = new NotionCMS({
auth: '<your-authentication-token>', // Your Notion Internal Integration Token
renderer: notionRenderer, // A NotionRenderer instance
parser: notionParser, // A NotionParser instance
});NotionDatabase
The NotionDatabase is used to interact with a specific Notion database.
import { NotionDatabse } from '@syneki/notion-cms';
const database = new NotionDatabase({
cms: notionCMS, // Your NotionCMS instance
databaseId: '<my-database-id>', // The ID of the Notion Database
mapping: {
title: {
// The property key of the final object
name: 'Title', // The name of the page Property
id: 'title', // The id of the page Property
},
shortDescription: {
name: 'Short description',
},
},
});The mapping is optionnal, if you do not specify it, the keys will be taken from the properties name.
Read more on how to query your pages.
ℹ You can find the Database ID from the URL on the page.
NotionRenderer
The NotionRenderer instance is used to transform properties and content into HTML. It accepts custom Blocks.
Read more on how to extend.
import { NotionRenderer } from '@syneki/notion-renderer';
const renderer = new NotionRenderer(ParagraphBlock, TaskBlock);🔍 Query
List pages of a database
import { NotionDatabase } from '@syneki/notion-cms';
const database = new NotionDatabse({ ... })
const posts = await database.list()
const posts = await database.list({
// Filtering
filter: {
property: 'Status', // The property name
type: 'status', // The property type
status: {
equals: 'Published' // What status you want to query
}
},
// Pagination
pageSize: 2, // The number of pages to query
cursor: '<cursor>', // At what page the list starts
// Sorting [WIP]
})Query a single page by ID
import { NotionDatabase } from '@syneki/notion-cms';
const database = new NotionDatabse({ ... })
const post = await database.get('<page-id>');Query a single page by property
import { NotionDatabase } from '@syneki/notion-cms';
const database = new NotionDatabse({ ... })
const post = await database.findFirst({
property: 'Slug',
rich_text: {
equals: 'my-super-post'
}
})Get the content of a page
When querying pages, you will only get the properties.
You must query the content with the getContent method.
The content is automatically rendered into HTML.
import { NotionDatabase } from '@syneki/notion-cms';
const database = new NotionDatabse({ ... })
const post = await database.findFirst({
property: 'Slug',
rich_text: {
equals: 'my-super-post'
}
})
const content = await database.getContent(post.id);🏗 Extend
Parsers
Parsers transform page properties sent by the Notion API.
For example, a date property in Notion results in a string but we parse it to transform it into a Date and make it directly accessible into the final object.
In the following examples we replace the first part of each email with fake data.
import { faker } from '@faker-js/faker';
import { NotionParser, NotionCMS, PropertyParser } from '@syneki/notion-cms';
const fakeEmailParser: PropertyParser<string, string> = (data) => {
const domain = data.email.split('@').at(-1);
return `${faker.internet.userName()}@${domain}`;
};
// Add it through the constructor
const parser = new NotionParser({
propertyParsers: {
email: fakeEmailParser,
},
});
// Or with the method addParser
parser.addParser('email', fakeEmailParser);
// Use it in NotionCMS
const cms = new NotionCMS({ parser });Renderers
Notion does not transform the rich content into HTML. It returns a JSON object with the configuration of each block.
You can add custom renderer to override the current Renderers or to handle more blocks.
import { createBlockRenderer, NotionRenderer } from '@syneki/notion-renderer';
const customParagraphRenderer = createBlockRenderer(
'paragraph',
(data, renderer) => {
return `<p class="custom-paragraph">${renderer.render(
...data.paragraph.rich_text
)}</p>`;
}
);
// Add it through the constructor
const renderer = new NotionRenderer(customParagraphRenderer);
// Or with the method addBlockRenderer
renderer.addBlockRenderer(customParagraphRenderer);
// Use it in NotionCMS
const cms = new NotionCMS({ renderer });As you can see we can render Blocks into blocks. In this case a Code Block contains Rich text, we call the renderer.render method to render it with the RichTextRenderer.
Contributing
Licence
Copyright © 2022 Syneki
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
3 years ago
3 years ago
3 years ago
3 years ago
3 years ago
3 years ago






