aichatjs v1.1.0
AIchat.js
Aichat.js is an open-source chatbot writen in javascript that uses classifiers and a response template to respond to user messages and questions. It is particularly useful for situational conversations such as customer support and sales of products.
You can see a live version in the following links:
For a complete Chabot Solution for websites CMSs, and CRMs you can see this other project:
Chat Compose - Create your own intelligent chatbot.
Screenshot
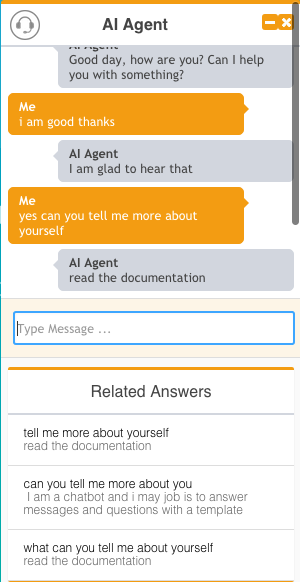
Installation
To install AIchat in your site, you need to download the files on the AIchat.v1 folder and upload them into your server or hosting. Then you need to reference the files in your html or php code before the closing body tag (</body>).
<link rel="stylesheet" href="AIchat.v1.min.css" type="text/css" media="screen" />
<script type="text/javascript" src="dependencies.v1.min.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="AIchat.v1.min.js"></script>You will also need to upload a response template file named faqen.csv to the same folder where your site is in order for it to work. You can check the example template in the AIchat.v1 folder to learn the format and to add your own messages and questions. You can also choose your own response template by setting it's path as the csv variable (see below).
Customizations
You can customize some of the parameters of AIchat by defining the following variables inside a <script> tag in your code (also before the closing body tag).
var reg = /\, |\. | and /g; // list of words and characters to omit, if you use weights do not set a score for that word
var csv = "faqen.csv"; // file with the response template
var decider=0.6; // decides if the classification was successful or not (Jacobian)
var lengthmax=12; // max sentence length before being divided
var memory=0; // 1 takes the last message sent into account for classification. 0 does not.
var coef=0.7; // coefficient that allows typing errors and associates words with similar stems
var weights=0; // 1 assigns weights to words from the csv field, 0 ignores weights.
var train=0; // 1 enables manual traning on the current bot, 0 disables it.
var nameagent="AI Agent"; // Name of the bot.(Default values)
An example of custom implemention of AIchat would look something like this:
<link rel="stylesheet" href="AIchat.v1.min.css" type="text/css" media="screen" />
<script type="text/javascript" src="dependencies.v1.min.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="AIchat.v1.min.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
var reg = /\, |\. | and /g; // list of words and characters to omit, if you use weights do not set a score for that word
var csv = "responsetemplate.csv"; // file with the response template
var decider=0.4; // decides if the classification was successful or not (Jacobian)
var lengthmax=8; // max sentence length before being divided
var memory=1; // 1 takes the last message sent into account for classification. 0 does not.
var coef=0.7; // coefficient that allows typing errors and associates words with similar stems
var weights=1; // 1 assigns weights to words from the csv field, 0 ignores weights.
var train=1; // 1 enables manual traning on the current bot, 0 disables it.
var nameagent="Peter"; // Name of the bot.
</script>Technical Documentation
Aichat uses template-based matching with a modified Naive Bayes classifier, allowing to identify the most likely class of a message in a csv document with template questions and returning the associated response.
It includes additional parameters such as a coefficient that tolerates typing errors and associates word stems, and the optional function to add weights to different words on a string (language modeling).
You can also omit certain words from the classification (low discriminating power) and to take context into account. The context is defined as the accumulated probability from the current and previous message.
AIchat uses a csv file containing the text strings to be classified against and the response to them, if activated it also can model language through the use of weights on the words on the text string. The files faqen.csv and faqes.csv provide example datasets for the chatbot.
A decision on the success of the classification can be set through the use of a jacobian estimator that calculates the success through word matches and sentences length.
A maximum length for the messages can also be set, allowing the bot to divide long strings for multiple classifications, and responses.
You can test a running version for english (simple conversation) and spanish (flower shop support). You can also upload your own csv and test the classification of certain sentences.
The success of the chatbot and the classification is highly dependent on the design of the csv with the questions/mesages and the related responses. Check the example faqs FAQENweighted.csv and FAQESnw.csv as points of reference on how to create a good data source for the chatbot.
AIchat is particularly useful in cases of situational conversations, such as giving information on products and how to buy them and deliver them, but it can also be used as a general purpose chatbot.
The most important parameters are the following:
var reg = /\, |\. | and /g; // list of words to omit, if you use weights do not set a score for that word
var csv = "faqen.csv"; // file with questions and answers
var decider=0.6; // decides if the classification was successful or not (Jacobian)
var lengthmax=12; // max sentence length before being divided
var memory=0; // 1 takes the last message sent into account for classification. 0 does not.
var coef=0.7; // coefficient that allows typing errors and associates words with similar stems
var weights=1; // 1 assigns weights to words from the csv field, 0 ignores weights.The decider variable can be a number from 0 to 1. Likewise for the coef variable that assigns the value of the association of words through the use of the levenshtein distance.
You can customize the variable number values to tune the classification and the responses of your bot.
Calculating weights for your document
A python script is included with a scoring function that will calculate a weight for each word on a question based on its frequency in all the questions and on its discriminating power. After designing a csv faq with the headers Question and Answer and running the script, it will create a new csv document called Weighted.csv with an additional column named Weights. To run the script do as follow in the command line:
python addweights.py <csv-file>The weight will be calculated based on the frequency of that word on the document and a lower bound or base.
The lower bound is composed of a base number base=1/length(question).
The partial weight is then defined as as the inverse frequency of that word plus the base partialweight=base+1.0/freq[word].
Finally the weights are normalized as the individual weights divided by the total weights of that sentence weight=partialweight/sum(partialweights), alowing their sum to be 1 for each sentence.
You can also set a constant lower bound for all words by setting a second argument on the script.
python addweights.py <csv-file> lowbound(optional)
ex: python addweights.py faqen.csv 0.18 years ago