boundary-value-analytics v1.0.1
🎯 Boundary Value Analysis (BVA) Test Automation with Playwright
Overview
This package provides a helper function bvaTest to automate Boundary Value Analysis (BVA) testing using Playwright. The function simplifies testing minimum and maximum boundaries for both integer and floating-point input values in web applications. 🌍
📊 Boundary Value Analysis (BVA)
Boundary Value Analysis is a testing technique used to identify defects by focusing on edge cases at the boundaries of input ranges. These boundaries are more likely to have issues, as developers may overlook extreme values during coding.
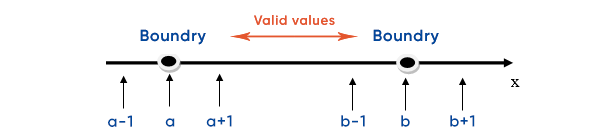
The key boundaries tested are:
- Lower Boundary: The minimum value the input field should accept.
- Upper Boundary: The maximum value the input field should accept.
- Just Below Lower Boundary: A value slightly smaller than the minimum boundary, which should be rejected.
- Just Above Lower Boundary: A value slightly greater than the minimum boundary, which should be accepted.
- Just Below Upper Boundary: A value slightly smaller than the maximum boundary, which should be accepted.
- Just Above Upper Boundary: A value slightly greater than the maximum boundary, which should be rejected.
🚀 Installation
To use this package, you need to install Playwright and this module.
Step 1: Install Playwright
First, if you haven't already, install Playwright:
npm install @playwright/testStep 2: Install the BVA Test Function
npm i boundary-value-analytics🛠️ Usage
Function: bvaTest
This function tests boundary values (both integers and floats) for form inputs using Playwright. It also allows for country-specific boundary increments.
Parameters
- minValue: (number) The minimum boundary value to test.
- maxValue: (number) The maximum boundary value to test.
- elementXPath: (string) The XPath of the input element where the test values will be entered.
- submitXPath: (string) The XPath of the submit button to trigger form submission.
- successXPath: (string or null) The optional XPath of the element that displays a success message. If the success message is not required, pass null.
- errorXPath: (string) The XPath of the element that displays an error message if validation fails.
- page: (object) The Playwright page object representing the browser page.
📊 Country-Specific Boundary Increment
The boundary increment (or "delta") adjusts based on the difference between the minimum and maximum values. This is useful in cases where boundaries vary by country or specific case ranges.
- If the boundary difference is greater than or equal to
1, the delta is1. - If the difference is less than or equal to
0.5, the delta is0.1. - If the difference is less than or equal to
0.1, the delta is0.01. - If the difference is less than or equal to
0.01, the delta is0.001.
These rules help accommodate different ranges for boundary values, which may differ in internationalized applications or based on country-specific increments.
Example
Below is an example of how to use the bvaTest function in your test suite:
const { test } = require('@playwright/test');
const { bvaTest } = require('boundary-value-analytics');
test('Boundary Value Analysis Test', async ({ page }) => {
const minValue = 1;
const maxValue = 10;
const elementXPath = '//input[@id="numberInput"]';
const submitXPath = '//button[@id="submit"]';
const successXPath = "//div[@class='success-message']"; // XPath of success message
// const successXPath = null; // Optional: Set to null if no success message element
const errorXPath = '//div[@id="errorMessage"]';
await bvaTest(minValue, maxValue, elementXPath, submitXPath, successXPath, errorXPath, page);
});🌟 How It Works
- Boundary Values: The
bvaTestfunction checks key boundary values, including:- Exact minimum and maximum values.
- Values just inside and outside these boundaries (with a delta).
- Delta Calculation: Based on the difference between
minValueandmaxValue, the function dynamically determines the appropriatedeltavalue for testing near-boundary cases. This is especially useful for country-specific or case-specific increments. - XPath Locators: You provide the XPath locators for the input element, submit button, and success/error messages. The function interacts with these elements during testing.
- Optional Success Message: If you do not need to check for a success message (e.g., in negative tests), simply pass
nullas the value forsuccessXPath. The function will still check for error messages if the input is invalid.
🧑🔧 Boundary Testing Scenarios
Here are the test scenarios the function runs for each boundary:
- Lower Boundary: Tests the exact minimum value (e.g.,
minValue). - Just Below Lower Boundary: Tests a value just below the minimum boundary
(minValue - delta), which should fail. - Just Above Lower Boundary: Tests a value just above the minimum boundary
(minValue + delta), which should pass. - Upper Boundary: Tests the exact maximum value
(e.g., maxValue). - Just Below Upper Boundary: Tests a value just below the maximum boundary
(maxValue - delta), which should pass. - Just Above Upper Boundary: Tests a value just above the maximum boundary
(maxValue + delta), which should fail.
🔥 Notes
- The function ensures that numeric values are tested. If the boundary values are not valid numbers, it will throw an error.
- The
pageobject must be an active instance of a Playwright page. - The
successXPathparameter is optional. Passnullif you don’t need to check for a success message after submission. - This function supports both integer and floating-point boundary values.
📜 License
MIT License