daisweb3.ts v0.4.0
Dais-Web3, is part of a suite of Node.js/TypeScript development tools. It is a command line tool that writes the necessary boilerplate to interface with DeFi's most popular platforms. Truffle is used as the Ethereum development environment and Solidity as the Smart Contract language.
Prerequisites
Use other verions at own risk
- truffle >=5.3.10
- node >=16.3.0
- npm >=7.15.1
- yarn >=1.22.10 (not required)
Installation
assuming node.js is installed on your machine
Install from NPM
npm i daisweb3.ts -gRecommend not using yarn global.
Install from source
git clone https://github.com/sntsabode/daisweb3.tscd daisweb3.tsassuming tsc command is available on your machine
tscnpm i -gRun tests
yarn run testRunning single test suite
yarn run mocha -r ts-node/register ./<file> --timeout (recommend above 20s if you plan on running the yarn/npm add tests)Test Coverage
yarn run test:coverageRunning this will run the mocha test suite using istanbul's nyc cli. Once the tests are complete a test coverage index.html file will be written into ./coverage. Open this file to examine the test suite's test coverage.
Usage
mkdir dais-demo-project
cd dais-demo-project
daisweb3 <options>Options:
-por--purge: Empties the current directory.-ior--init: Writes a template .daisconfig file.-aor--assemble: Writes the boilerplate.-yor--yes: Run without asking any questions (will still ask on--purge)-oor--offline: Runs yarn/npm add with the offline flag-cor--confirm: Confirm the command
Quick Start
daisweb3 -paicyRunning the daisweb3 command will generate the initial project structure and install the necessary dependencies:
*Paths marked with a question mark are optional (configured in the .daisconfig file).*
dais-demo-project
├── contracts
│ ├── interfaces
│ | ├── ${protocol}?
| | | └── ${file}?
│ ├── libraries
| | └── ${protocol}?
| | └── ${file}?
│ └── Migrations.sol
├── lib
| ├── __abis__?
| | ├── abis?
| | └── abis.ts?
| └── addresses.ts
├── migrations
| └── 1_initial_migration.js
├── node_modules
├── .eslintignore?
├── .eslintrc?
├── .gitattributes?
├── .gitignore?
├── fork-chain.js?
├── package.json
├── truffle-config.js
└── tsconfig.jsonThe generated boilerplate is as minimal as possible (for a truffle project). Once the installation is done boot the fork-chain (if any) and get to hacking!
QuickWrite
daisweb3 <PROTOCOL> <PACK> <abi | false> <omitNpmPack | false> <solver> <Supported Network | all> -ceg.
daisweb3 AAVE ILENDINGPOOL false omitNpmPack 0.8.6 MAINNET -c(Arguments have to be in the specified order)
Args
PROTOCOL: Any supported protocol.PACK: Any supported import for the entered protocol.abi: Any value other than false will be treated as true. If false isn't entered, the imported contract's abis are written into alib/__abis__/abis/directory in the directory the daisweb3 command was called from.omitNpmPack: Any value other than false will be treated as true. If false is entered the protocol's NPM packages are installed into the directory the daisweb3 command was called from.solver: Solidity version going to entered into the contract files.Supported Network: Any supported network or all. This is used to determine which contract addresses to return.
Philosophy
Eventually... I got tired of scouring DeFi Docs and God forbid Git repositories to find ABIs and addresses. So I made daisweb3, an all in one place for all of that.
Implemented Protocols
| Protocol | ID | Name | Support |
|---|---|---|---|
| AAVE | Aave | ||
| BANCOR | Bancor | ||
| DYDX | DyDx | ||
| KYBER | Kyber Network | ||
| ONEINCH | 1Inch Network | ||
| UNISWAP | Uniswap |
.daisconfig
template .daisconfig file
{
"solversion": "0.8.6",
"defaultNet": "MAINNET",
"eslint": true,
"git": true,
"contractWriteDir": "/lib/__abis__/artifacts",
"ganache": true,
"mocha": true,
"packman": "yarn",
"omitTruffleHdWalletProvider": false,
"ethNodeURL": "wss://mainnet.infura.io/ws/v3/INFURA_URL",
"contractImports": [
{
"protocol": "UNISWAP",
"pack": "V2Router02",
"omitNpmPack": true,
"abi": true
},
{
"protocol": "DYDX",
"pack": "Flashloan",
"omitNpmPack": true,
"abi": false
},
{
"protocol": "KYBER",
"pack": "IKyberNetworkProxy",
"omitNpmPack": true,
"abi": true
},
{
"protocol": "ONEINCH",
"pack": "OneSplit",
"omitNpmPack": true,
"abi": true
},
{
"protocol": "ONEINCH",
"pack": "OneSplitMulti",
"omitNpmPack": true,
"abi": true
},
{
"protocol": "BANCOR",
"pack": "IBancorNetwork",
"omitNpmPack": true,
"abi": true
}
],
"addedDependencies": [
"express"
],
"addedDevDependencies": [
"@types/express"
]
}Fields:
solversion: Solidity version being used
This is the Solidity verison that is going to be entered in all the boilerplate contracts:
pragma solidity ^{solversion};defaultNet: Network being used
This is the parameter that influences which Addresses are written into ./lib/addresses.ts.
Use all to print all the addresses for MAINNET and supported test nets.
export type SupportedNetwork =
| 'MAINNET'
| 'KOVAN'
| 'ROPSTEN'
| 'all'eslint: bool Whether or not eslint should be configured
If true eslint dependencies will be installed as dev-deps and template .eslintrc and .eslintignore files will be written in the root of the directory specified as the path
git: bool Whether or not git should be configured
If true git init will be called and template .gitignore and .gitattributes files will be written in the directory specified as the path
contractWriteDir: string The directory going to be entered into thecontracts_build_directoryin thetruffle-config.jsfile:
module.exports = {
contracts_build_directory: {contractWriteDir}
}ganache: bool Whether or not ganache-cli should be added as a dev-dep
If true ganache-cli will be installed and a fork-mainnet.js file will be written in the root of the directory the dais-web3 command was called from:
(snippet)
const server = ganache.server({
port: 7545,
default_balance_ether: 100,
fork: new Web3.providers.WebsocketProvider("ETH_NODE_URL"),
ws: true,
debug: true,
vmErrorsOnRPCResponse: true,
verbose: true,
logger: console
})
const PORT = 7545
server.listen(PORT, (err, blockchain) => { })mochabool Whether or not mocha and chai are installed as dev-deps.packmanyarn || npm The package manager going to be used to install said dependencies
Defaults to yarn, fallbacks to npm if yarn fails.
omitTruffleHdWalletProviderbool Whether or not @truffle/hdwallet-provider should be omitted
If false @truffle/hdwallet-provider is not installed so the truffle-config.js will need to be redone.
ethNodeURL: string The string going to be printed to an env variable in the.envfile. This env variable is the variable that will be used in ganache's fork chain (if it was enabled) and as Web3's WebSocket provider (make sure it's 'wss://' and not 'http://'/'https://'. If it's 'http://'/'https://', please make sure WebSocket connections are enabled on that endpoint)contractImportsArray
export type SupportedProtocol =
| 'AAVE'
| 'BANCOR'
| 'DYDX'
| 'KYBER'
| 'ONEINCH'
| 'UNISWAP'
export interface IContractImport {
readonly protocol: SupportedProtocol
readonly pack: string
readonly omitNpmPack: boolean
readonly abi: boolean
}protocolThe DeFi protocol you want to interface withpackThe specific import needed from the DeFi protocolomitNpmPackWhether or not the protocol's npm package should be installed
If true the protocol's npm package (if any) will be installed as a production dependency.
abi: Whether or not the contract's ABI should be included in the written boilerplate
| Logo | Support | Imports |
|---|---|---|
ILendingPoolAddressesProvider, ILendingPool |
Aave is a decentralised non-custodial liquidity protocol where users can participate as depositors or borrowers. Depositors provide liquidity to the market to earn a passive income, while borrowers are able to borrow in an over-collateralised (perpetually) or under-collateralised (one-block liquidity) fashion.
for more see Aave's docs
Supported Contract Imports
{
"protocol": "AAVE",
"pack": "ILendingPool",
"omitNpmPack": true,
"abi": false
}Writes ILendingPoolAddressesProvider and ILendingPool contract interfaces along with a DataTypes library.
The LendingPool contract is the main contract of the protocol. It exposes all the user-oriented actions that can be invoked using either Solidity or web3 libraries. The source code can be found on Github here. If you need development support, join the #developers channel on the Aave community Discord server.
(snippet)
// SPDX-License-Identifier: NO-LICENSE
pragma solidity 0.6.12;
pragma experimental ABIEncoderV2;
import {ILendingPoolAddressesProvider} from './ILendingPoolAddressesProvider.sol';
import {DataTypes} from '../../libraries/Aave/DataTypes.sol';
interface ILendingPool {
...
event FlashLoan(
address indexed target,
address indexed initiator,
address indexed asset,
uint256 amount,
uint256 premium,
uint16 referralCode
);
event LiquidationCall(
address indexed collateralAsset,
address indexed debtAsset,
address indexed user,
uint256 debtToCover,
uint256 liquidatedCollateralAmount,
address liquidator,
bool receiveAToken
);
...
function liquidationCall(
address collateralAsset,
address debtAsset,
address user,
uint256 debtToCover,
bool receiveAToken
) external;
...
function flashLoan(
address receiverAddress,
address[] calldata assets,
uint256[] calldata amounts,
uint256[] calldata modes,
address onBehalfOf,
bytes calldata params,
uint16 referralCode
) external;
...
}{
"protocol": "AAVE",
"pack": "ILendingPoolAddressesProvider",
"omitNpmPack": true,
"abi": false
}Writes an ILendingPoolAddressesProvider contract interface.
Addresses register of the protocol for a particular market. This contract is immutable and the address will never change. Also see Deployed Contracts section.
(snippet)
// SPDX-License-Identifier: NO-LICENSE
pragma solidity ${solver};
/**
* @title LendingPoolAddressesProvider contract
* @dev Main registry of addresses part of or connected to the protocol, including permissioned roles
* - Acting also as factory of proxies and admin of those, so with right to change its implementations
* - Owned by the Aave Governance
* @author Aave
**/
interface ILendingPoolAddressesProvider {
event MarketIdSet(string newMarketId);
event LendingPoolUpdated(address indexed newAddress);
...
function getLendingPool() external view returns (address);
...
}| Logo | Support | Imports |
|---|---|---|
IBancorNetwork |
While many users benefit from the Bancor Network by using the Bancor App or a Bancor Widget, developers can also access Bancor's many features from their own smart contracts. The API reference section provides a detailed look into the full functionality of each contract in the system. This section will provide a quick look into some more common features and should contain sufficient information for most use cases.
Supported Contract Imports
{
"protocol": "BANCOR",
"pack": "IBancorNetwork",
"omitNpmPack": true,
"abi": true
}Writes IContractRegistry.sol and IBancorNetwork.sol files, Bancor's main trading proxy contract interface.
Trading With Bancor
path: Network path between sourceToken and toToken ThegetPathAndRatefunction on theBancor SDKwill generate the optimal path for this parameter
amount: Source token input amount
minReturn: To token minimum return
affiliateAccount: Address to direct affiliate fees
affiliateFee: Fee amount (1000 would be equal to 0.1%)
// SPDX-License-Identifier: UNLICENSED
pragma solidity 0.8.6;
import "../@OpenZeppelin/IERC20.sol";
interface IBancorNetwork {
function convertByPath(
address[] memory _path,
uint256 _amount,
uint256 _minReturn,
address _beneficiary,
address _affiliateAccount,
uint256 _affiliateFee
) external payable returns (uint256);
function rateByPath(
address[] memory _path,
uint256 _amount
) external view returns (uint256);
function conversionPath(
IERC20 _sourceToken,
IERC20 _targetToken
) external view returns (address[] memory);
}// SPDX-License-Identifier: UNLICENSED
pragma solidity 0.8.6;
interface IContractRegistry {
function addressOf(
bytes32 contractName
) external returns(address);
}| Logo | Support | Imports |
|---|---|---|
Flashloan |
Supported Contract Imports
{
"protocol": "DYDX",
"pack": "Flashloan",
"omitNpmPack": true,
"abi": false
}Writes the boilerplate contracts needed to perform a flashloan on DyDx. The boilerplate is adapted from money-legos' DyDx flash loan reference guide.
Special thanks to kollateral for open sourcing their implementation. DyDx does not natively have a "flashloan" feature. However you can achieve a similar behavior by executing a series of operations on the SoloMargin contract. In order to mimic an Aave flashloan on DyDx, you would need to:
- Borrow x amount of tokens. (Withdraw)
- Call a function (i.e. Logic to handle flashloaned funds). (Call)
- Deposit back x (+2 wei) amount of tokens. (Deposit)
All within one transaction. The reason this works is because DyDx natively has this feature called operate which allows you to execute a series of operations without checking if the state is valid until the final step. That means that you can withdraw as much funds as you like, do anything with it, as long as you deposit back the funds (and have ~2 Wei of assets in your account) within the same transaction.
If the flashloan option is entered the following starter contract will be written into Flashloan.sol:
(snippet)
// SPDX-License-Identifier: UNLICENSED
pragma solidity ^0.8.6;
pragma experimental ABIEncoderV2;
import "./interfaces/@OpenZeppelin/IERC20.sol";
import "./interfaces/DyDx/ISoloMargin.sol";
import "./interfaces/DyDx/ICallee.sol";
import "./libraries/DyDx/Actions.sol";
import "./libraries/DyDx/Account.sol";
contract FlashLoan is ICallee {
mapping(address => uint) public DyDxCurrencyMarketIDs;
address immutable SoloAddress;
constructor(
address ISoloMarginAddress, address USDC,
address WETH, address DAI, address SAI
) { }
struct CallFuncParam {
uint256 amount;
address currency;
}
function callFunction(
address _sender,
Account.Info calldata _accountInfo,
bytes calldata _data
) external override {
CallFuncParam memory data = abi.decode(_data, (CallFuncParam));
}
function flashloan(
CallFuncParam calldata param
) external {
Actions.ActionArgs[] memory operations = new Actions.ActionArgs[](3);
...
this.SoloFac().operate(accountInfos, operations);
}
function SoloFac() external view returns(ISoloMargin solo) {
return ISoloMargin(SoloAddress);
}
}| Logo | Support | Imports |
|---|---|---|
IKyberNetworkProxy |
Supported Contract Imports
{
"protocol": "KYBER",
"pack": "IKyberNetworkProxy",
"omitNpmPack": true,
"abi": true
}Writes an IKyberNetworkProxy.sol file, Kyber main proxy contract interface.
contract
KyberNetworkProxyis
IKyberNetworkProxy,ISimpleKyberProxy,WithdrawableNoModifiers,Utils5importsWithdrawableNoModifiers,Utils5,SafeERC20,IKyberNetwork,IKyberNetworkProxy,ISimpleKyberProxy,IKyberHintSource:
KyberNetworkProxy.sol
// SPDX-License-Identifier: UNLICENSED
pragma solidity 0.8.6;
import "../@OpenZeppelin/IERC20.sol";
interface IKyberNetworkProxy {
event ExecuteTrade(
address indexed trader,
IERC20 src,
IERC20 dest,
address destAddress,
uint256 actualSrcAmount,
uint256 actualDestAmount,
address platformWallet,
uint256 platformFeeBps
);
/// @notice backward compatible
function tradeWithHint(
ERC20 src,
uint256 srcAmount,
ERC20 dest,
address payable destAddress,
uint256 maxDestAmount,
uint256 minConversionRate,
address payable walletId,
bytes calldata hint
) external payable returns (uint256);
function tradeWithHintAndFee(
IERC20 src,
uint256 srcAmount,
IERC20 dest,
address payable destAddress,
uint256 maxDestAmount,
uint256 minConversionRate,
address payable platformWallet,
uint256 platformFeeBps,
bytes calldata hint
) external payable returns (uint256 destAmount);
function trade(
IERC20 src,
uint256 srcAmount,
IERC20 dest,
address payable destAddress,
uint256 maxDestAmount,
uint256 minConversionRate,
address payable platformWallet
) external payable returns (uint256);
/// @notice backward compatible
/// @notice Rate units (10 ** 18) => destQty (twei) / srcQty (twei) * 10 ** 18
function getExpectedRate(
ERC20 src,
ERC20 dest,
uint256 srcQty
) external view returns (uint256 expectedRate, uint256 worstRate);
function getExpectedRateAfterFee(
IERC20 src,
IERC20 dest,
uint256 srcQty,
uint256 platformFeeBps,
bytes calldata hint
) external view returns (uint256 expectedRate);
}| Logo | Support | Imports |
|---|---|---|
OneSplit, OneSplitMulti |
To use this service you have to call methods at
OneSplitAudit
How to use it
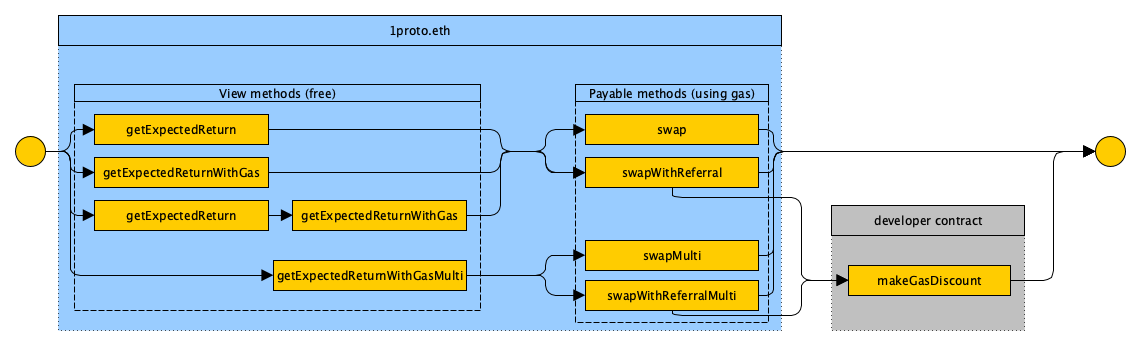
To swap tokens you have to figure out way from left to right points by one of paths on scheme above.
For example, first of all call method getExpectedReturn (see methods section), it returns distribution array. Each element of this array matches element of splitExchanges (see above) and represents fraction of trading volume. Then call getExpectedReturnWithGas to take into account gas when splitting. This method returns more profitable distribution array for exchange. Then call method swap or swapWithReferral (see methods section) with param distribution which was recieved earlier from method getExpectedReturn.
Swap may be customized by flags (see flags section). There are 2 types of swap: direct swap and swap over transitional token.
In case of direct swap each element of distribution array matches element of splitExchanges and represents fraction of trading off token as alerady described above.
In case of swap with transitional token each element of distribution (256 bits) matches 2 swaps: second bytes are equal to swap to transitional token, lowest bytes are equal to swap to the desired token.
Supported Contract Imports
{
"protocol": "ONEINCH",
"pack": "OneSplit",
"omitNpmPack": true,
"abi": true
}Writes an IOneSplit.sol contract interface, OneInch's main trading interface (for token to token) see IOneSplitMulti.sol.
(snippet)
// SPDX-License-Identifier: UNLICENSED
pragma solidity 0.8.6;
import "../@OpenZeppelin/IERC20.sol";
...
interface IOneSplit {
function getExpectedReturn(
IERC20 fromToken,
IERC20 destToken,
uint256 amount,
uint256 parts,
uint256 flags // See constants in IOneSplit.sol
) external view returns(
uint256 returnAmount,
uint256[] memory distribution
);
function getExpectedReturnWithGas(
IERC20 fromToken,
IERC20 destToken,
uint256 amount,
uint256 parts,
uint256 flags, // See constants in IOneSplit.sol
uint256 destTokenEthPriceTimesGasPrice
) external view returns(
uint256 returnAmount,
uint256 estimateGasAmount,
uint256[] memory distribution
);
function swap(
IERC20 fromToken,
IERC20 destToken,
uint256 amount,
uint256 minReturn,
uint256[] memory distribution,
uint256 flags
) external payable returns(uint256 returnAmount);
}{
"protocol": "ONEINCH",
"pack": "OneSplitMulti",
"omitNpmPack": true,
"abi": true
}Writes an IOneSplitMulti contract interface and an IOneSplit contract interface. (If IOneSplit is not imported an IOneSplit contract will be written anyway).
// SPDX-License-Identifier: UNLICENSED
pragma solidity ^0.8.6;
import "../@OpenZeppelin/IERC20.sol";
import "./IOneSplit.sol";
interface IOneSplitMulti is IOneSplit {
function getExpectedReturnWithGasMulti(
IERC20[] memory tokens,
uint256 amount,
uint256[] memory parts,
uint256[] memory flags,
uint256[] memory destTokenEthPriceTimesGasPrices
)
external view returns(
uint256[] memory returnAmounts,
uint256 estimateGasAmount,
uint256[] memory distribution
);
function swapMulti(
IERC20[] memory tokens,
uint256 amount,
uint256 minReturn,
uint256[] memory distribution,
uint256[] memory flags
)
external payable returns(uint256 returnAmount);
}| Logo | Support | Imports |
|---|---|---|
V2Router |
Supported Contract Imports
{
"protocol": "UNISWAP",
"pack": "V2Router",
"omitNpmPack": true,
"abi": true
}Writes IUniswapV2Router01.sol and IUniswapV2Router02.sol files, Uniswap's main trading contract interfaces.
Because routers are stateless and do not hold token balances, they can be replaced safely and trustlessly, if necessary. This may happen if more efficient smart contract patterns are discovered, or if additional functionality is desired. For this reason, routers have release numbers, starting at
01. This is currently recommended release,02.
For more visit V2Router02
(snippet)
// SPDX-License-Identifier: UNLICENSED
pragma solidity >=0.6.2;
interface IUniswapV2Router01 {
function factory() external pure returns (address);
function WETH() external pure returns (address);
function addLiquidity(
address tokenA,
address tokenB,
uint256 amountADesired,
uint256 amountBDesired,
uint256 amountAMin,
uint256 amountBMin,
address to,
uint256 deadline
)
external
returns (
uint256 amountA,
uint256 amountB,
uint256 liquidity
);
...
function removeLiquidity(
address tokenA,
address tokenB,
uint256 liquidity,
uint256 amountAMin,
uint256 amountBMin,
address to,
uint256 deadline
) external returns (uint256 amountA, uint256 amountB);
...
function swapExactTokensForTokens(
uint256 amountIn,
uint256 amountOutMin,
address[] calldata path,
address to,
uint256 deadline
) external returns (uint256[] memory amounts);
...
function swapExactETHForTokens(
uint256 amountOutMin,
address[] calldata path,
address to,
uint256 deadline
) external payable returns (uint256[] memory amounts);
...
function getAmountsOut(uint256 amountIn, address[] calldata path)
external
view
returns (uint256[] memory amounts);
}(snippet)
// SPDX-License-Identifier: UNLICENSED
pragma solidity >=0.6.2;
import "./IUniswapV2Router01.sol";
interface IUniswapV2Router02 is IUniswapV2Router01 {
function removeLiquidityETHSupportingFeeOnTransferTokens(
address token,
uint256 liquidity,
uint256 amountTokenMin,
uint256 amountETHMin,
address to,
uint256 deadline
) external returns (uint256 amountETH);
...
function swapExactTokensForTokensSupportingFeeOnTransferTokens(
uint256 amountIn,
uint256 amountOutMin,
address[] calldata path,
address to,
uint256 deadline
) external;
}Author
👤 Sihle Masebuku snts.abode@gmail.com
Show your support
Give a ⭐️ if this project helped you!
This README was generated with ❤️ by readme-md-generator