damp v1.0.12

DAMP
(verb) - /dæmp/ - to check or retard the energy, action, etc., of; deaden; dampen; to stifle or suffocate; extinguishThis is a utility to control the responses from APIs via a proxy through various configuration mechanisms. You can force errors or delays on specific API invocations. Also known as the Dynamically Arranged Mocking Proxy
Prerequisites
You will need Node.js >= v0.12
For RHEL machines, just run yum install npm.
If you need to upgrade or install Node.js on your workstation, the easiest way is to use an installer for your platform. Download the .msi for Windows or .pkg for Mac from the NodeJS website.
Running from NPM
Run the following to install from NPM:
npm install -g dampThen you can execute with damp
Running from Docker
Here's an example of running as a Docker container:
docker run -d -p 8000 -name "damp" \
-v /host/path/to/damp_routesets:/opt/damp/routesets \
-e PORT=8000 \
-e DEFAULT_TARGET=https://localhost:8080 \
-e APP_CONFIG_PATH=/opt/damp/routesets \
docker.vsp.com:443/gts-ea/dampRunning from source
Alternatively, if you want to run from the source then clone the repo locally and then from within the local directory run npm install and sudo npm link
Then you can execute with damp
Runtime Options
Start the proxy by running damp. Configuration can be provided by environment variables or command options:
| Command Option | Environment Variable | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| -c, --config | CONFIG_PATH | .damp.yml | Path to proxy config |
| -a, --appconfig | APP_CONFIG_PATH | $(os.tmpdir)/damp/ | Path to app proxy configs |
| -X, --appheader | APP_HEADER | X-TransactionId | Header to use for app routesets |
| -t, --target | DEFAULT_TARGET | http://localhost:8080 | Proxy target |
| -d, --delay | DEFAULT_DELAY | 0 | Delay in milliseconds |
| -p, --port | PORT | 8000 | Port to listen on |
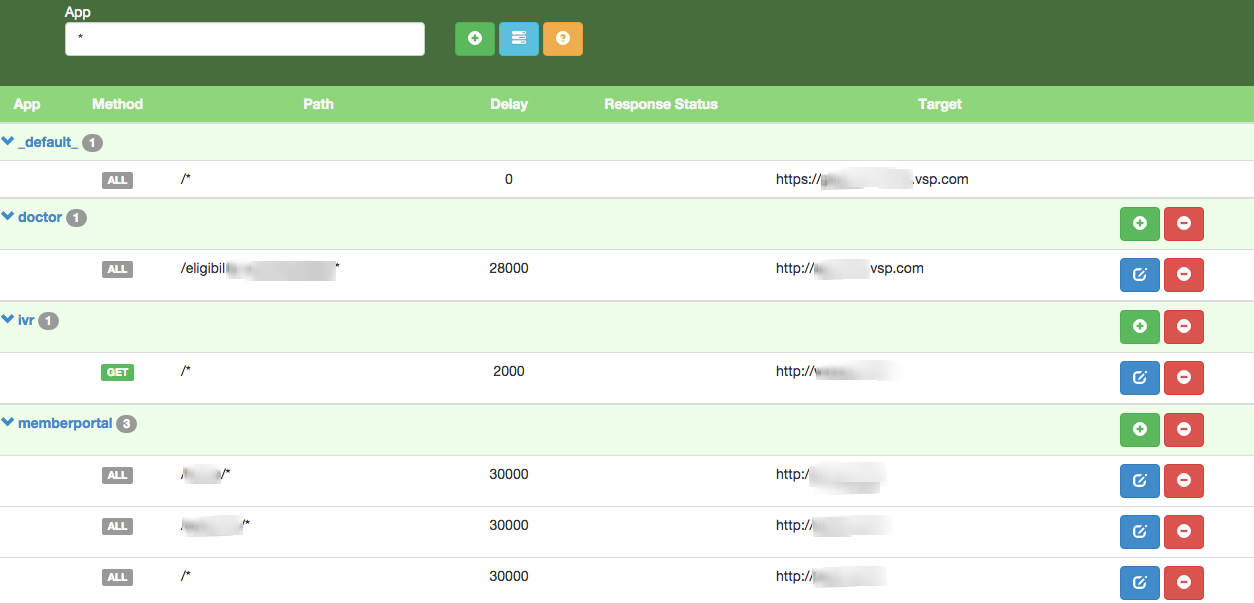
Configuration via UI
A user interface exists for managing application specific configuration. DAMP can be run as a shared service in your testing environment. For example inside VSP we have a shared instance available at http://damp.vspglobal.com. When running locally, you can access it at http://localhost:8000.
Configuration via YAML
You can configure specific paths in a YAML file. By default, it looks for a file named .damp.yml in the current directory. Here's a sample file with a couple paths, one with a custom delay and another with a custom status code:
## 30 second delay and custom target for '/home'
- path: /home
delay: 30000
target: http://gtssbxlb-0002.vsp.com
## 1 second delay with custom status (401) for '/as/*' with wildcard
- path: /as/*
delay: 1000
status: 401Configuration via API
The API consists fo the following resources:
| Method | Path | Input | Output |
|---|---|---|---|
| GET | /_api | none | Map of resources (key: resource name, value: URL) |
| GET | /_api/routesets?all | all - load all routesets from disk (Default: false) | Array of routesets JSON |
| POST | /_api/routesets | body - Routeset JSON to create | none |
| GET | /_api/routesets/:name | :name - name of routeset to get | Routeset JSON |
| PUT | /_api/routesets/:name | :name - name of routeset to update body - Routeset JSON to update | Routeset JSON |
| DELETE | /_api/routesets/:name | :name - name of routeset to delete | none |
The routeset data model looks like:
{
"name": "foo",
"routes": [
{
"path": "/bar/*",
"status": 500,
"target": "http://www.baz.com",
"delay": 0
}
]
}Choose either a status or a target for whether you intend to return a static response or proxy the request respectively.
Runtime Routing
Every request that arrives at the proxy runs through a series of routes and applies ALL routes that match the path (in order of most specific path to least specific) until either a status or target route is found.
Routesets are loaded in the following order:
Request Routeset - The request is interrogated to determine if a specific routeset is configured. This is done in the follow order and once a routeset is matched, it is used and the subsequent steps are skipped:
appheaderwithdamp-appname- if the request has a header with name matching theappheaderconfigured and the value matchesdamp-appname:<myapp>then a routeset named myapp is loaded (ie. /_api/routesets/myapp). If it exists, it will be used.appheaderwithdamp-routeset- if the request has a header with name matching theappheaderconfigured and the value matchesdamp-routeset:<base64>then a routeset is decoded from the Base64 encoded JSON in base64 and will then be used.Hostheader - if the request has aHostheader with name matchingmyapp.damp.vspglobal.com(which resolved from the *.damp.vspglobal.com wildcard DNS), then a routeset named myapp is loaded. If it exists, it will be used.
Static Routeset - After all the routes in the Request Routeset resolve, if no
targetorstatusroutes are found, then the static routeset is loaded from theconfigoption provided at runtime.Default Routeset - After all the routes in the Request Routeset resolve and the routes in the Static Routeset resolve, if no
targetorstatusroutes are found, then the defalut route is resolved based on thedelayandtargetprovided at runtime.
Support
Please create an issue for any bugs you come across or feature requests.
Contributing
Pull requests are welcome; see the contributor guidelines for details.
License
IP is licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0.
For additional information, see the LICENSE file.


