dbscan v0.0.1
Clustering - DBScan algorithm
A node module, that uses DBScan unsupervised clustering algorithm, to return centroids and their cluster
This algorithm doesn't handle well the following:
- Large datasets computational complexity
- Number of dimensions ( > 16) - more computaitons, "curse of dimensionality"
about (2), given a fixed amount of points, the density of the points decreases exponentially. Meaning you won't be able to find cluster as you'll be wandering a lot. About "the curse", it means that Complexity: O(n^2) - space, O(n^2) - time
You'll find a pre-made 100 points 16-features vector sample file Uses stream, readline node modules
using jSHint, matchdep , stream, grunt.js
Use this with my permission only
ToC
Main app
points over map:
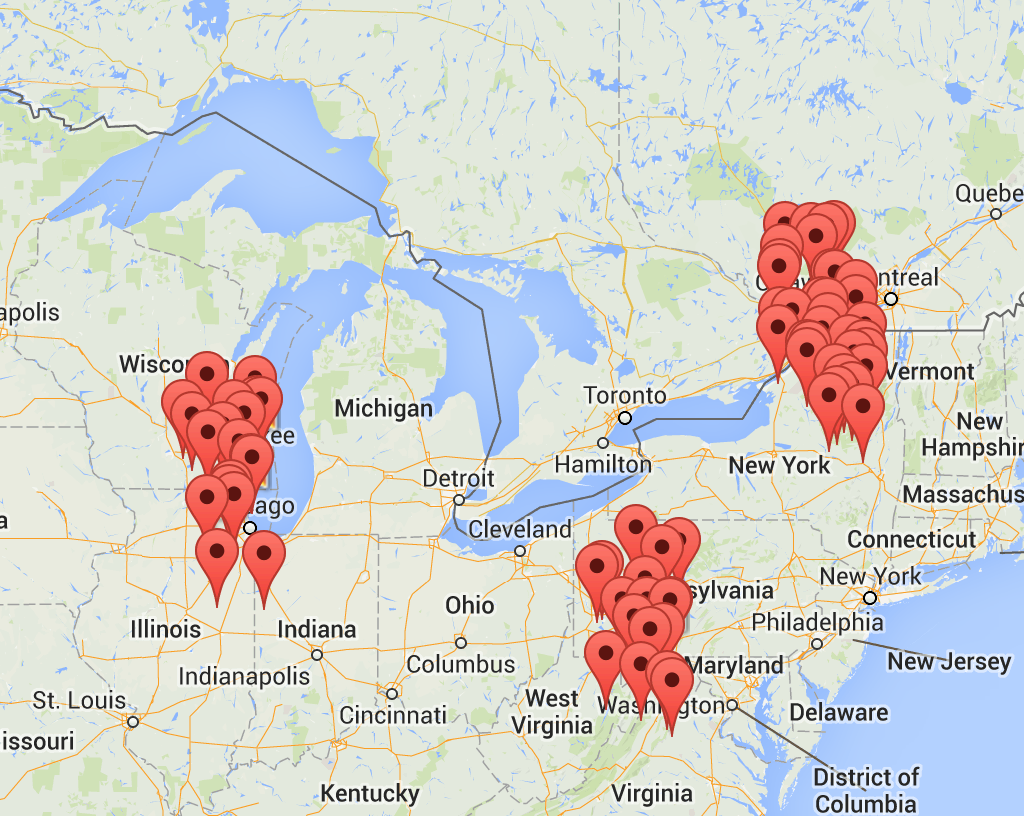
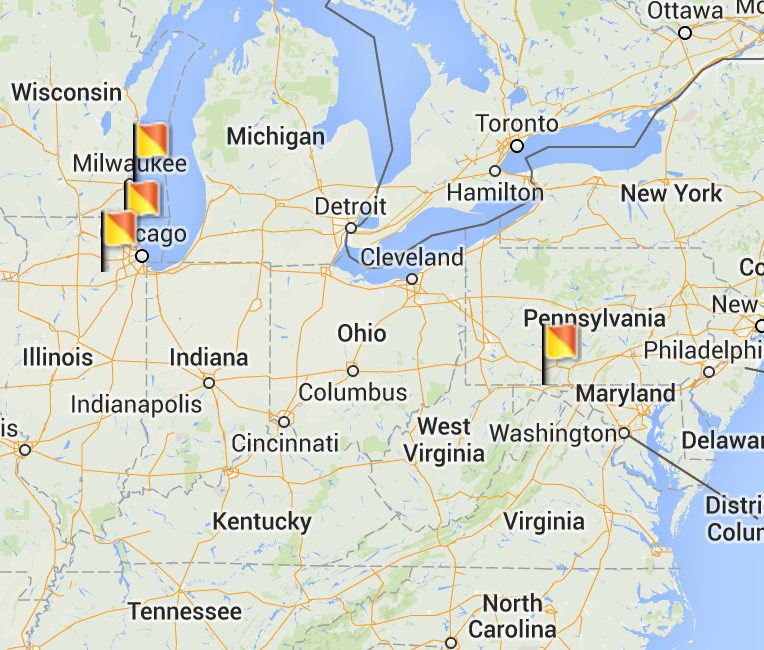
Initialization
we need to initialize the distance object, you can add any distance metric you wish to distance.js
var Distance = require("./lib/distance"),
distances = new Distance(),
// DBScan section
DBScan = require('./lib/dbscan.js'),
dbscan = new DBScan(distances)after initialization, you need to create a multi-dimensional vector, an array of arrays:
[[1,2],[1,4],[2,5],[5,9],...,[10,12]]
in code we grab it via stream from a line-by-line newline structured flat file so we won't have limit on memory space
readline = require('readline'), // using the UNSTABLE readline built-in node module
// Stream section
stream = require('stream'),
points = [],
rl, // read-line
in_stream;
in_stream = fs.createReadStream('./points.txt'),
rl = readline.createInterface({
input: in_stream,
terminal: false
})
rl.on('line', function(line) {
points.push(JSON.parse(line))
});finally we run the clustering:
var clustering_obj = dbscan.cluster(points,distanceFunction)
console.log('FINISHED reading ' + points.length + ' and clustering them');11 years ago