dcx-protocol v0.0.5
Decentralized Credential Exchange (DCX)
DCX is a new Decentralized Web Nodes (DWN) protocol that facilitates the decentralized exchange of borrower data for lender money seurely and privately and a npm package that implements the protocol as a one-click server solution.
As an open, permissionless, "credentials in, credentials out" asynchronous web server, DCX leverages the strongest Web5 primitives: DWNs, Verifiable Credentials (VCs), Credential Manifests, Verifiable Presentations and Presentation Exchange amongst other important Web5 primitives. DCX facilitates decentralized credential exchange by performing CRUD operations on both applicant and issuer DWNs. Different DWN record schemas represent various messages sent between actors, detailing the VCs required as inputs and outputs for the DCX server.
Credential Manifests are a big part of what makes DCX work. These documents outline key pieces of information: 1. The input credentials required by the issuer 2. The output credential(s) the applicant can expect 3. Data formatting preferences
Credential Manifests are a resource format that defines preconditional requirements, Issuer style preferences, and other facets. User Agents utilize to help articulate and select the inputs necessary for processing and issuance of a specified credential.
A Credential Manifest is a document, hosted by an Issuer and consumed by User Agents, codifying the credentials that it issues in terms of pre-requisites and inputs. These can be static or dynamic, but their form and usage are detailed in this specification.
Applicants pull these manifest records from the issuer's DWN, so they can understand what VCs are required on their side of the exchange. For more details on protocol interactions between issuers and applicants, see the Architecture Diagram and Sequence Diagram sections below.
src/protocol/credential-issuer.tsdefines credential issuer protocolsrc/protocol/credential-applicant.tsdefines credential applicant protocol
src/schemas/invoice.tsdefines the schema for invoice recordssrc/schemas/manifest.tsdefines schema for manifest recordssrc/schemas/application.tsdefines schema for application recordssrc/schemas/response.tsdefines schema for response records
EXAMPLE-MANIFEST.jsondefines an example manifest- NOTE: Manifests do not ship with the DCX package. Developers are required to provide their own manifests when building their DCX issuer server
- See Usage for how to provide manifests
Docs & Diagrams
Additional docs & diagram files can be found in the /docs folder.
- DEVELOPMENT.md Lists current issues and PRs
- SUMMARY.md Shorter summary about DCX
Architecture Diagram
Actors
- DCX: Protocol boundary within which actors communicate
- DCX Issuer: Web server running @web5/dcx and web5-js
- Issuer DWN: DCX Issuer's DWN server running dwn-sdk-js
- DCX Applicant: User client application running @web5/dcx and web5-js
- Applicant DWN: DCX Applicant's DWN server running dwn-sdk-js

Sequence Diagram
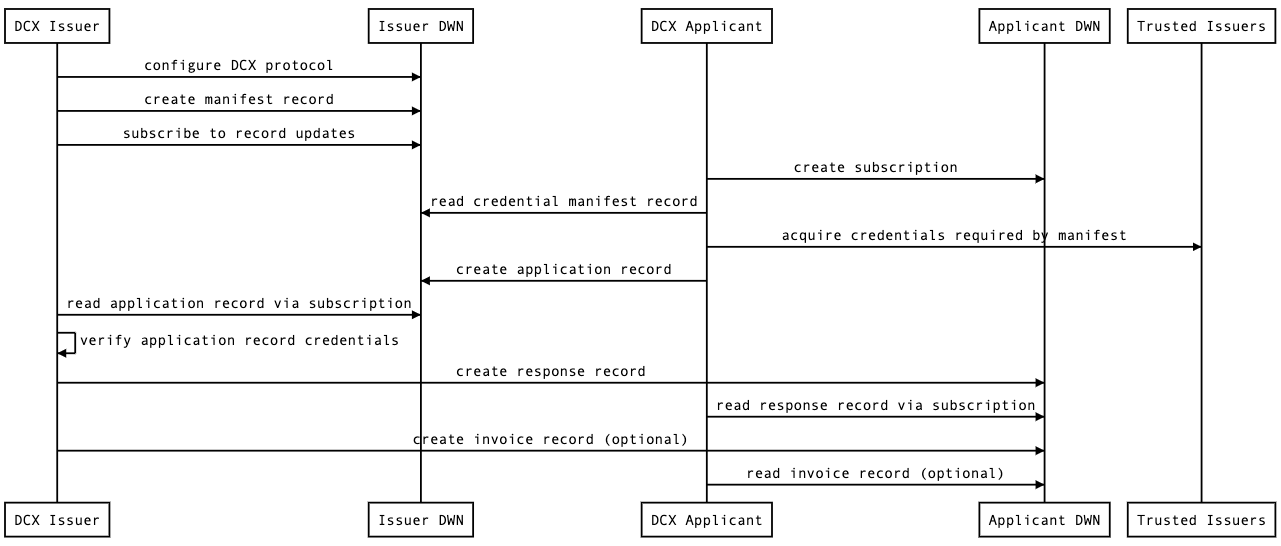
Full Protocol
- DCX Issuer configures Issuer DWN with dcx protocol
- DCX Issuer creates credential manifest record in Issuer DWN
- DCX Issuer creates subscription to Issuer DWN
- DCX Applicant creates subscription to Applicant DWN
- DCX Applicant reads credential manifest record from Issuer DWN
- DCX Applicant acquires required credentials from issuers listed in manifest
- DCX Applicant creates application record in Issuer DWN
- DCX Issuer reads application record via Issuer DWN subscription
- DCX Issuer uses @web5/dcx to verify application record credentials against credential manifest
- DCX Issuer creates response record in Applicant DWN
- DCX Applicant reads response record via Applicant DWN subscription
- DCX Issuer creates invoice record in Applicant DWN
- DCX Applicant reads invoice record via Applicant DWN subscription
- Credential-issuer and credential-applicant protocols defines DWN record CRUD actions between Issuer and Applicant
- under the credential-issuer manifest route
- Subscription to receive incoming application records
- Subscription to receive incoming response records
- Defines required "credentials in" to receive desired "credentials out"
- Credentials are acquired separately, outside of DCX protocol, from listed trusted issuers
- Application record includes credentials that satisfy credential manifest mentioned in step 5
- DCX Issuer validates credentials against credential manifest using DCX software handlers
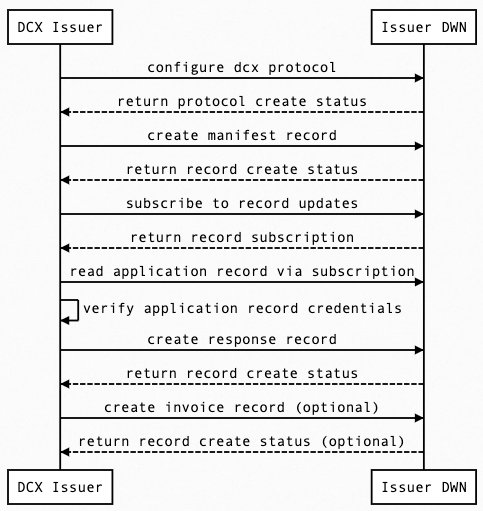
Issuer Protocol
- DCX Issuer configures Issuer DWN with dcx protocol (issuer & applicant)
- DCX Issuer creates credential manifest record in Issuer DWN
- DCX Issuer creates subscription to Issuer DWN
- DCX Issuer reads application record via Issuer DWN subscription
- DCX Issuer uses DCX software handlers to verify credentials against credential manifest
- DCX Issuer configures DWN with DCX Issuer protocol
- DCX Issuer creates DWN manifest record in own DWN to define required credentials to obtain other credentials
- DCX Issuer subscribes to own DWN to listen for application records
- DCX Issuer reads an incoming application record and validates against respective credential manifest
- DCX Issuer creates application response or denial record and sends to applicant DWN
- DCX Issuer creates invoice response record and sends to applicant DWN
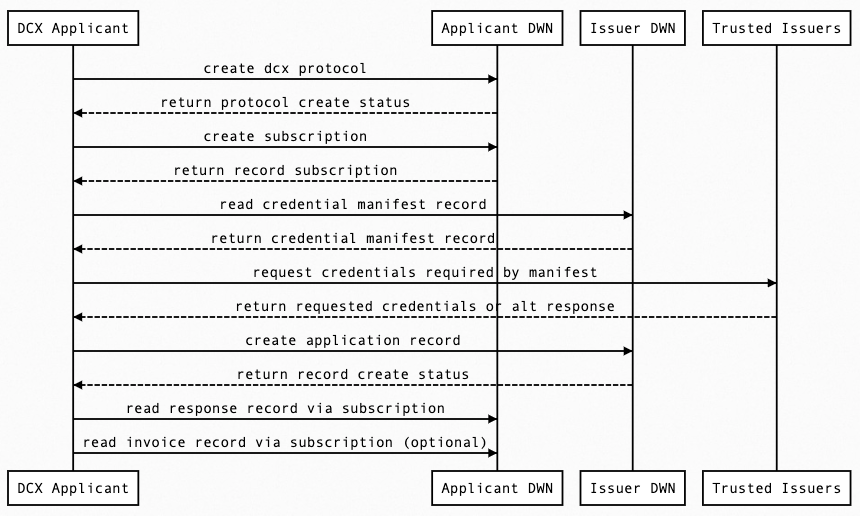
Applicant Protocol
- DCX Applicant configures Applicant DWN with dcx protocol (issuer & applicant)
- DCX Applicant creates subscription to Applicant DWN
- DCX Applicant reads credential manifest record from Issuer DWN
- DCX Applicant acquires required credentials from issuers listed in manifest
- DCX Applicant creates application record in Issuer DWN
- DCX Applicant reads response record via Applicant DWN subscription
- DCX Applicant reads invoice record via Applicant DWN subscription (optional)
Package Versions
| Name | Latest Version | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| @formfree/dcx |  | ||
| <!-- | @formfree/dcx |  | --> |
| <!-- | @formfree/dcx |  | --> |
Usage
Import the server from @formfree/dcx and run .start() to simply run the server as-is.
import { server } from '@formfree/dcx';
await server.start();You can also import the DcxServer class and pass options to customize the server
import DcxServer, ExampleManifest from "@formfree/dcx";
const server = new DcxServer();
const server = new DcxServer({
manifests: [ExampleManifest],
providers: [{
id: ExampleManifest.output_descriptors[0].id,
method: 'POST',
endpoint: 'http://localhost:4000/api/v1/vc/data'
}],
dwns: ['http://localhost:3000/']
});
await server.start();However, using the server this was alone is limited to local development.
To customize local dev and/or prepare for prod, you must provide your own credential manifest(s).
You can leverate the .use() method on the server to define custom server options like custom manifests.
Use Manifest
To define your own manifests, you can leverage server.use('manifest' ... ) to pass in your own.
An example manifest can be found here to use for accepting and issuing VCs
import ExampleManifest from '../EXAMPLE-MANIFEST.json';
import { server } from '@formfree/dcx';
// Define manifest in local json file, import and pass into server
server.use('manifest', ExampleManifest);
// Or define manifest directly into .use method
server.use('manifest', {
"id": "dcx-credential-manifest-example",
"name": "DCX Credential Manifest Example",
"description": "This is an example of a credential manifest used by DCX. This document should be replaced with your own version to satify the requirements of the credentials your DCX server expects as inputs and the desired output credential.",
"spec_version": "https://identity.foundation/credential-manifest/spec/v1.0.0/",
"issuer": {
"id": "[replaced dynamically]",
"name": "example-issuer"
},
"output_descriptors": [
{
"id": "example-output-descriptor-id",
"name": "Example Output Descriptor Name",
"schema": "https://example.com/schemas/ExampleOutputDescriptorSchema"
}
],
"format": {
"jwt_vc": {
"alg": [
"EdDSA"
]
}
},
"presentation_definition": {
"id": "example-presentation-definition-id",
"input_descriptors": [
{
"id": "example-presentation-definition-input-descriptor-id",
"purpose": "Meant as an example to developers",
"constraints": {
"fields": [
{
"path": [
"$.type[*]"
],
"filter": {
"type": "string",
"pattern": "^*$"
}
},
{
"path": [
"$.credentialSubject.some.unique.field1",
"$.credentialSubject.some.unique.field2",
"$.credentialSubject.some.unique.fieldn"
]
}
]
}
}
]
}
});
// Define provider that your DCX will make API calls to for VC data
server.use('provider',
{
id: ExampleManifest.output_descriptors[0].id,
method: 'POST',
endpoint: 'http://localhost:4000/api/v1/vc/data'
}
);
// Define a list of DWN Endpoints
server.use('dwn', 'http://localhost:3000/');
await server.start();Use Issuer
You can define your own set of trusted issuers using server.use('issuer' .... The list of issuers defined will be used
when an application is processed. The issuers of the input VCs will be compared to this list.
DCX defined 1 default issuer if none are provided. See Config or below example for details.
import { server } from './src/index';
server.use('issuer',
{
name: 'MX Technologies',
id: 'did:dht:sa713dw7jyg44ejwcdf8iqcseh7jcz51wj6fjxbooj41ipeg76eo'
}
);
await server.start();Use Provider
You can define your own VC data providers using server.use('provider' .... Ideally, you only define 1 provider, but
the server can handle multiple for different development contexts (i.e. development, testing, production).
import { server } from './src/index';
// development
server.use('provider',
{
method: 'POST',
endpoint: 'http://localhost:4000/api/v1/vc/data'
}
);
// production
server.use('provider',
{
name: "Some Third Party Provider",
method: 'POST',
endpoint: 'http://api.provider.com/v1/vc/data',
headers: { 'Authorization': `Bearer ${process.env.PROVIDER_AUTHORIZATION_BEARER_TOKEN}`, }
}
);
await server.start();Use Handler
You can define your own set of protocol handlers using server.use('handler' .... The custom handlers you define should
either overwrite and/or work with the existing default ones. See handlers.ts for the inputs/outputs
expected by the default handlers. Default handler names are: selectCredentials, verifyCredentials, requestCredential, issueCredential.
import { server } from './src/index';
async function requestCredentialCustom(){
return await fetch('http://api.example.com/v1/vc-data', /* ... */)
};
server.use('handler', 'requestCredential', requestCredentialCustom);
await server.start();Use Gateway
You can define your own DHT Gateway using server.use('gateway' .... At the moment, this has no impact.
DCX defaults to using TBD or FormFree DHT gateways. This can be used to easily toggle between dev envs.
import { server } from './src/index';
// development
server.use('gateway', 'http://localhost:8305');
await server.start();Putting it all together into 1 example
import ExampleManifest from './EXAMPLE-MANIFEST.json';
import { server } from '@formfree/dcx';
server.use('manifest', ExampleManifest);
server.use('issuer', { name: 'MX Technologies', id: 'did:dht:sa713dw7jyg44ejwcdf8iqcseh7jcz51wj6fjxbooj41ipeg76eo' });
async function requestCredentialCustom(){
return await fetch('http://api.example.com/v1/vc-data', /* ... */)
};
server.use('handler', 'requestCredential', requestCredentialCustom);
server.use('gateway', 'http://localhost:8305');
await server.start();
process.on('SIGTERM', () => {
server.stop();
});Project Resources
| Resource | Description |
|---|---|
| CODEOWNERS | Outlines the project lead(s) |
| CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md | Expected behavior for project contributors, promoting a welcoming environment |
| CONTRIBUTING.md | Developer guide to build, test, run, access CI, chat, discuss, file issues |
| GOVERNANCE.md | Project governance |
| LICENSE |  |
2 years ago