0.2.6 • Published 8 years ago
decision-tree-builder v0.2.6
decision-tree-builder 

A tool to build data classification rules using visual flowchart-style decision tree. Uses d3.js v4 for SVG drawing.
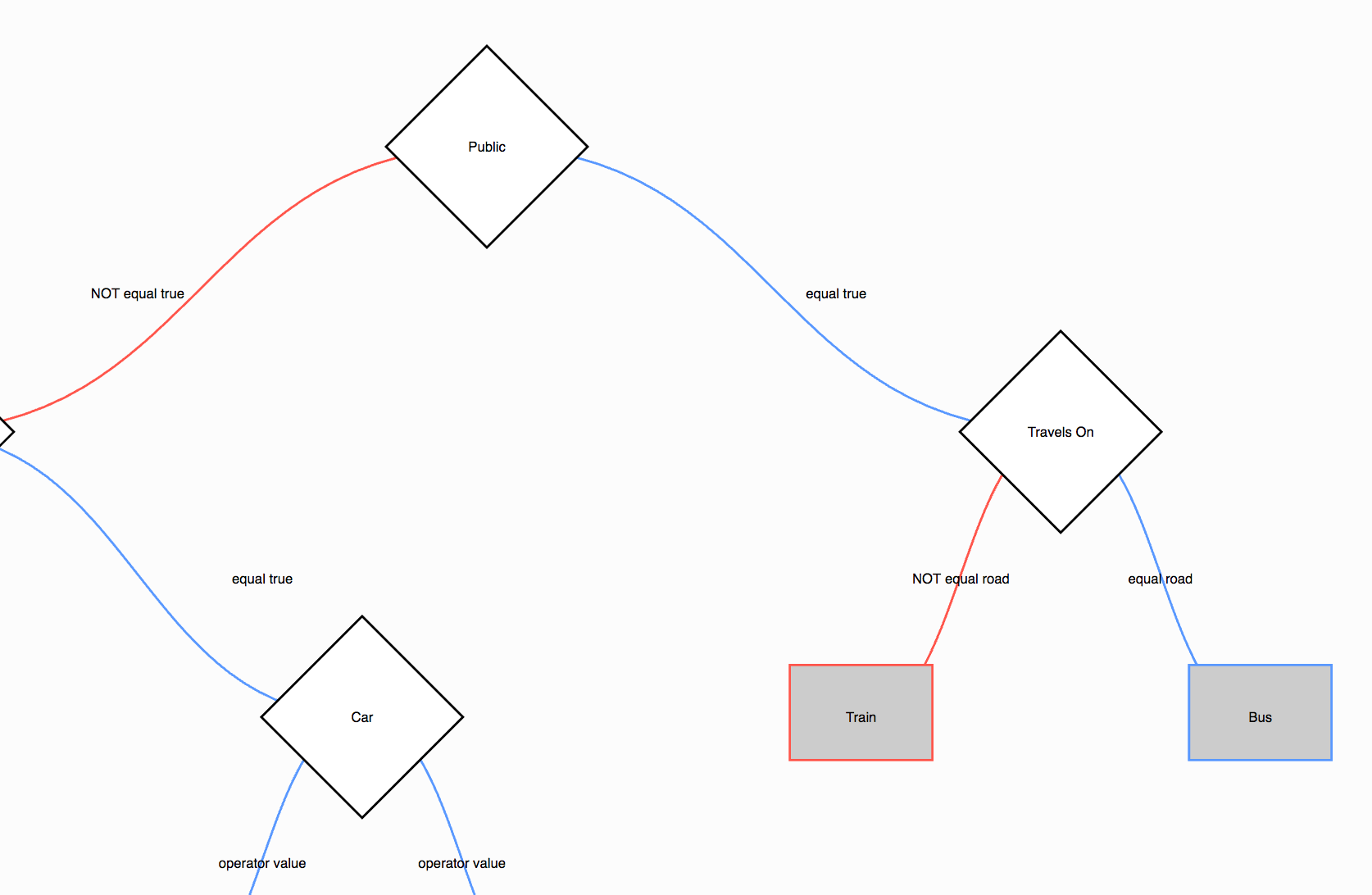
terminology / concepts
- Property: a (data) attribute being evaluated as part a decision (e.g. Property: "animal")
- Value: a value being used in a conditional statement to evaluate a property (e.g. does Property "animal" equal the Value "cat")
- Operator: the logical operator used to evaluate a properties value (e.g. "equals", "less than" etc.)
- Condition: the logical operator (AND/OR) used to evaluate decisions that have more than one rule, e.g.
rule1 AND rule2. - Decision: a conditional operation determining which of two paths the program will take
- Result Node: aka a leaf node, represents the final result when an input is evaluated by the decision tree
- TreeSchema: the JSON serialised representation of a decision tree
- DataSchema: the actual things/options that may be used to define a tree (the Properties, Values, and Operators that are available - this is not handled by this tool, user defined).
notes
- You should not directly modify the
nodeobject that is broadcast with thenodeClickevent as this may cause issues with d3's internal data structure. You should instead usecloneAndStripNodeor similar to get a distinct copy of the nodes values. - Decision nodes are if/else binary decision only, the data is structured such that the two children of a decision 0,1,
are in a meaningful array order, i.e.
the child at
0index represents afalsedecision outcome the child at1index represents atruedecision outcome so; when we query the tree as well as getting a result/leaf node, we also get a binary representation of the path, i.e.0110indicates four decisions were taken to reach a result =>false, true, true, false - We do not provide any validation of decision tree conditional logic (it is distinct from the tree data structure... well more accurately the decision logic is simply stored as tree node metadata). * for example; you could make a change to a parent node which renders its children completely redundant, and it will still be valid (children won't be auto pruned, do it yourself man).
example use
Initialise with data and options:
let options = {
layout: {
divId: "tree-panel",
svgWidth: 1200,
svgHeight: 1000,
svgMargin: {
top: 20,
right: 90,
bottom: 30,
left: 90
},
nodeWidth: 250,
nodeHeight: 250,
nodeMargin: {
x: 100,
y: 250
},
zoomScale: [-1, 100],
transitionDuration: 750
},
// defined for use with `queryDecisionTree` example
operatorFunctions: {
equal: function(a, b){
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve(a == b);
});
}
}
};
let myBuilder = new DecisionTreeBuilder(treeData, options); // see demo for expected data formatThen listen for nodeClick events, you will be passed the target node in the event detail:
window.addEventListener('nodeClick', function (e) {
var node = e.detail;
// perform action with the node..
});You can optionally color stroke of nodes and links based on their truthy/falsey status, see demo.css for example.
core methods
addChildNodes(node, newNodesData)updateDecisionNodeData(node, newData)pruneNode(node)serialiseTreeToJSON()queryDecisionTree(target)// returns the value of resulting leaf node, and a binary path to the result.setHighlighted(node, ignoreToggleState)fitBounds(paddingPercent, transitionDuration)adjustBounds(offset)destroy()
See demo.js for example.
shout outs / other tools
- Mike Bostock
- d3noob
- Adam Feuer's d3js Tree Editor found it too late to use it, but looks relevant.
license
The MIT License (MIT)