easy-text-update v1.0.7
easy-text-update
This library offers a simple way to update text in a React Application.
It provides a context provider that wraps your application and either hooks or an HOCs.
If active={true} is passed to the context provider, when you right click on a text element, a dialog will open to edit the text.
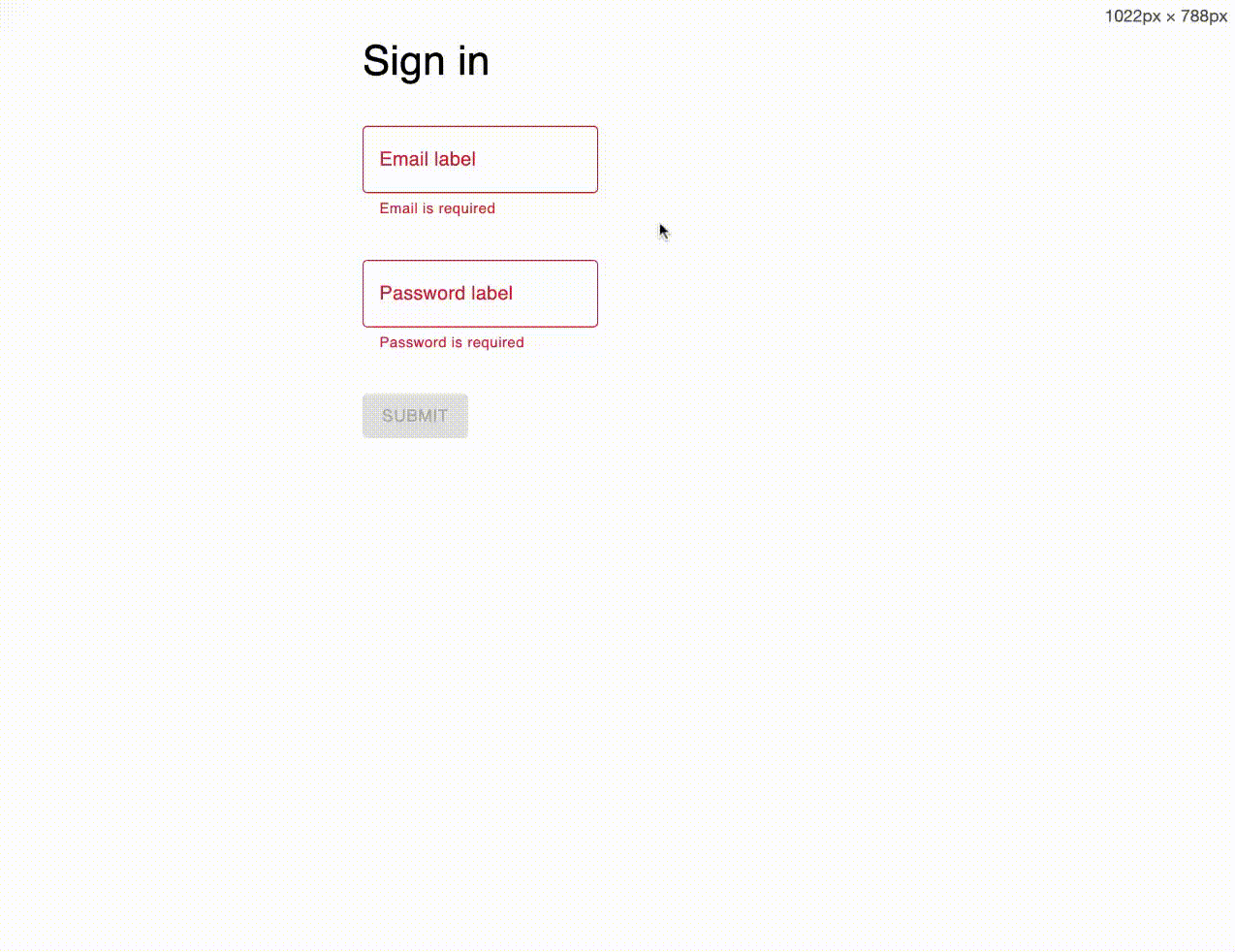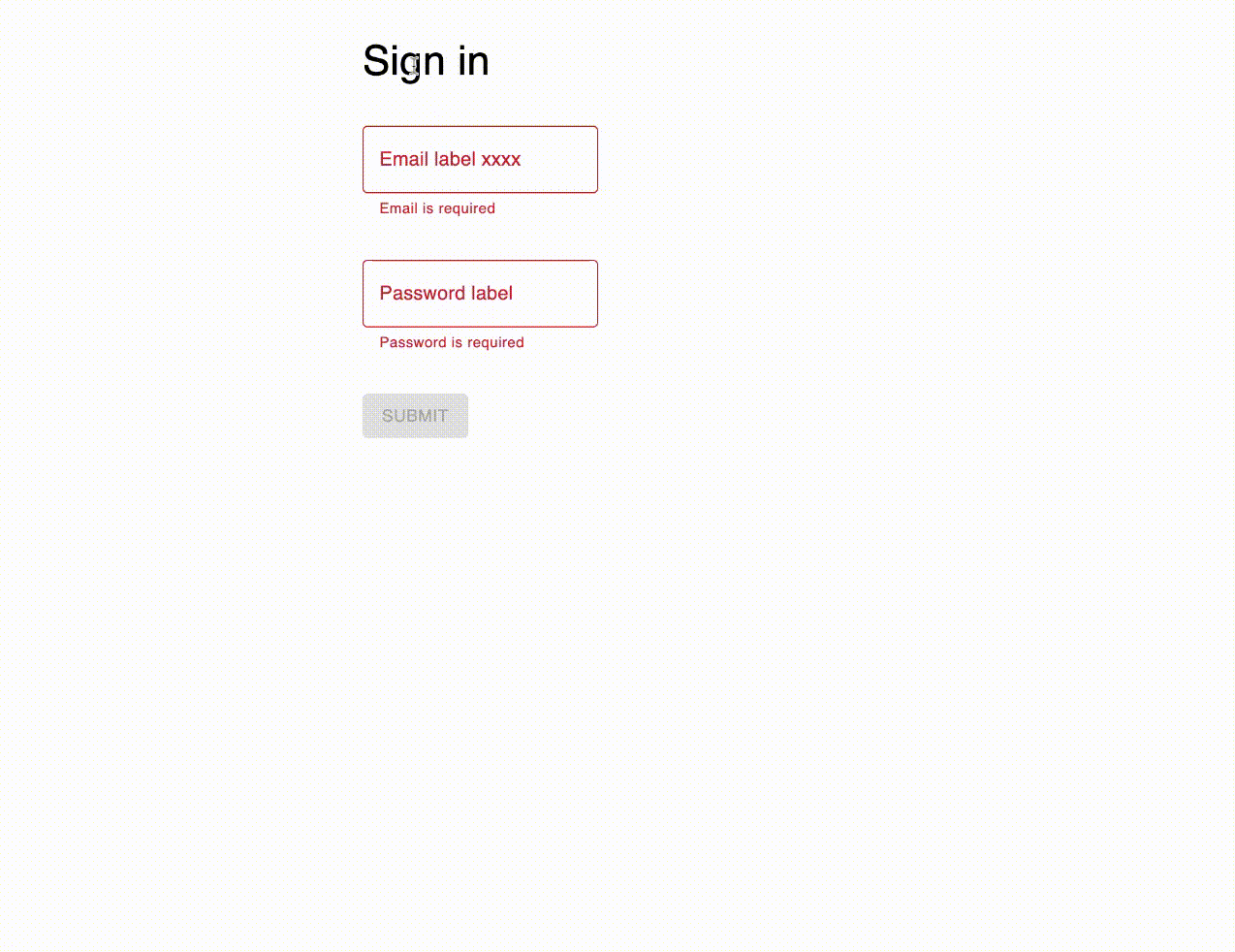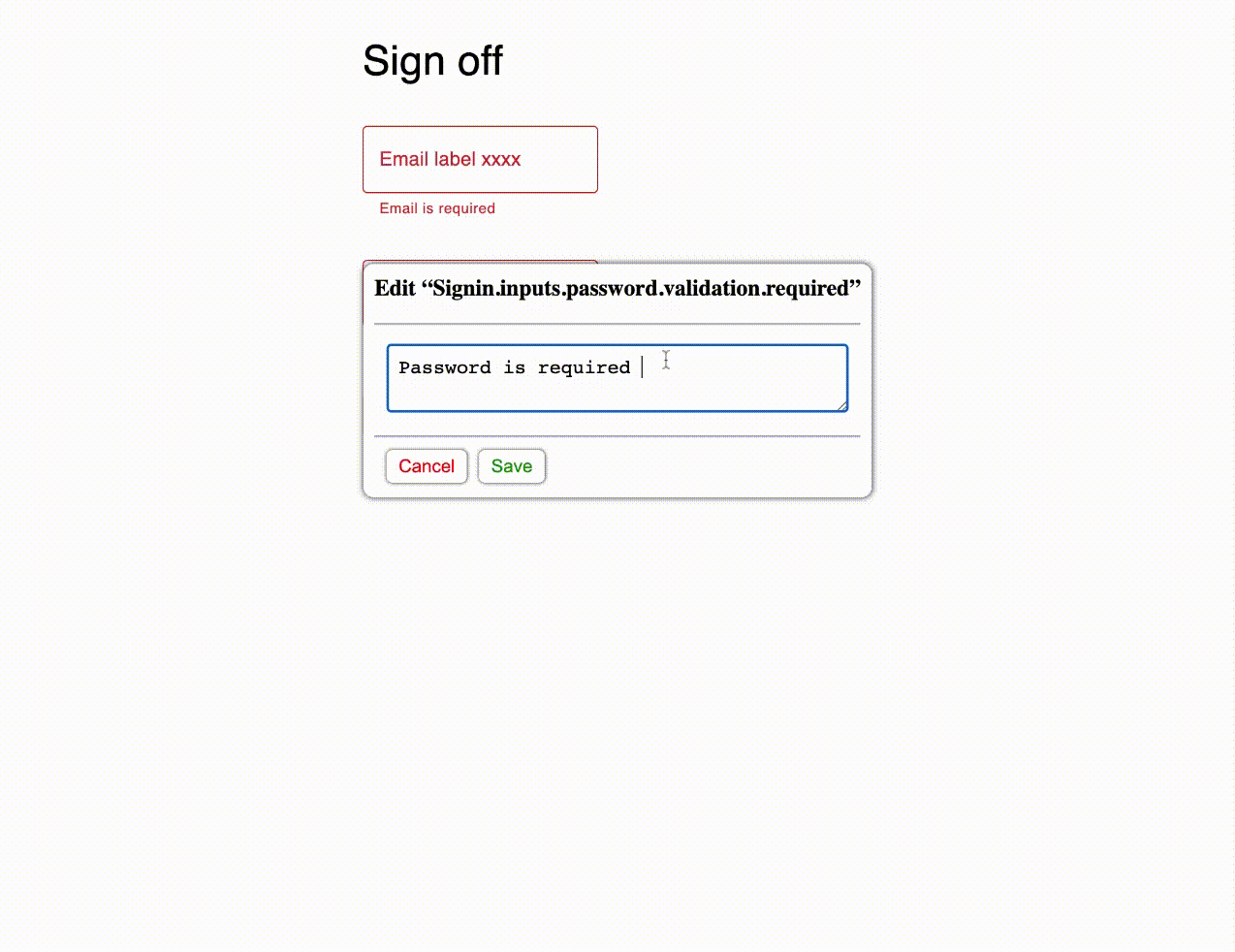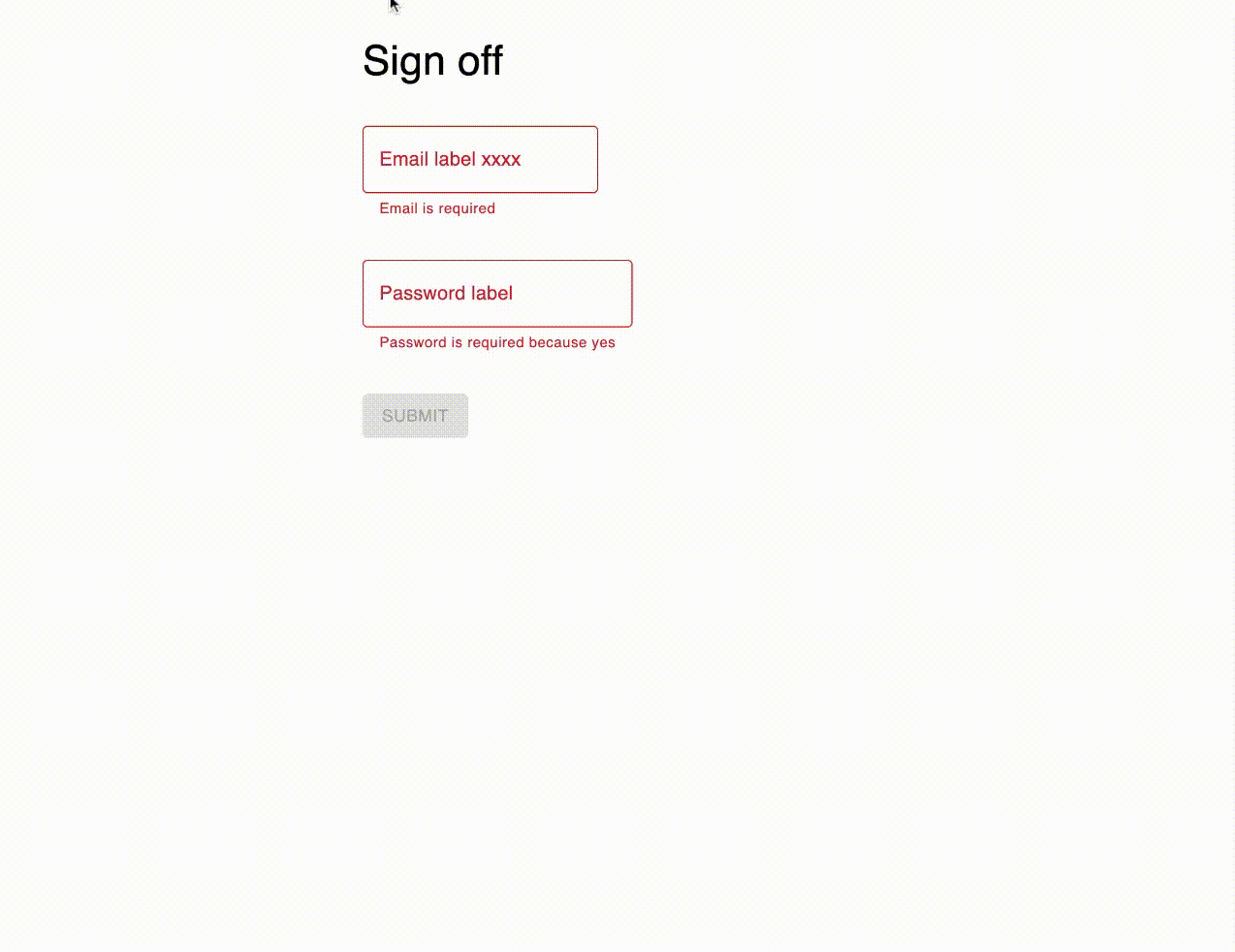
Installation
npm install easy-text-update
or
yarn add easy-text-updateSetup
import { TextUpdateProvider, TextObject, RevertFn } from "easy-text-update";
import axios from "axios";
const sendToApiEndpoint = (textObject: TextObject, revert: RevertFn) => {
axios
.post("/api/text-update", textObject)
.then(() => {
// Handle success
})
.catch(() => {
// Handle error
revert();
});
};
const App = ({ Component }) => {
const { data: textObject } = useSWR("/api/text", fetcher); // Fetch the text object from an API endpoint. Or import it from a file
return (
<TextUpdateProvider
text={textObject} // An object containing the text necessary in the UI
active={session.user.role === "Admin"} // A boolean value that determines if the text should be updatable
save={sendToApiEndpoint} // A function that will be called when the text is updated. You can handle the saving of the text here
>
<Component />
</TextUpdateProvider>
);
};editMenuComponent
If you want a custom edit menu, you can pass it to the TextUpdateProvider as the editMenuComponent prop. The component will receive the following props:
initialText: string;
save: (updatedText: string) => void;
closeMenu: () => void;Example:
import { TextUpdateProvider, EditMenuComponentProps } from "easy-text-update";
import { useRef } from "react";
const Menu = ({ initialText, save, closeMenu }: EditMenuComponentProps) => {
const ref = useRef<HTMLInputElement>();
return (
<dialog open>
<input ref={ref} defaultValue={initialText} />
<button onClick={closeMenu}>Close</button>
<button onClick={() => save(ref.current.value)}>Save</button>
</dialog>
);
};
function App() {
return (
<TextUpdateProvider
text={text}
active={true}
save={console.log}
editMenuComponent={Menu}
>
<Component />
</TextUpdateProvider>
);
}Usage with HOC
import { UpdatableText } from "easy-text-update";
const Component = () => (
<>
{/*With child*/}
<UpdatableText path="Homepage.title">
<h1 style={{ color: "blue" }} />
{/*All props will be passed to the child
component. The text will be passed as the children prop*/}
</UpdatableText>
{/*With function as child*/}
<UpdatableText path="Homepage.title">
{(title, editProps) => <h1 {...editProps}>{title}</h1>}
</UpdatableText>
{/*With component prop*/}
<UpdatableText
path="Homepage.title"
component={<h1 style={{ color: "blue" }} />}
/>
{/*With component function*/}
<UpdatableText
path="Homepage.title"
component={(text, editProps) => <h1 {...editProps}>{text}</h1>}
/>
{/*With JSX element as component prop*/}
<UpdatableText
path="Homepage.title"
component={<h1 style={{ color: "blue" }} />}
/>
{/*Without child (a span will be used)*/}
<UpdatableText path="Homepage.title" />
</>
);Usage with hook
import { useUpdatableText } from "easy-text-update";
const Component = () => {
const { text, props } = useUpdatableText("Homepage.title");
return (
<>
<h1>{title}</h1>{" "}
{/*You can access the text this way, but no editing will be possible*/}
<h1 {...props} /> {/*When you right click the h1 element, a dialog will open to edit the text*/}
</>
);
};Usage with hooks to get access to an object within the text object passed to the TextUpdateProvider
import { useUpdatableTextContainer } from "easy-text-update";
const Component = () => {
const { getText, getProps } = useUpdatableTextContainer("Login.form");
return (
<>
<label {...getProps("email.label")} />
<input
placeholder={getText("email.placeholder")}
{...getProps("email.placeholder", {
returnChildren: false,
})}
/>
</>
);
};In the example above, the getProps function accepts a second parameter of type UseUpdatableTextConfig which has the following properties:
returnChildren: A boolean value that determines if the children prop should be added to the element. Defaults to true. For input and textarea elements, this prop will always be false, therefore it can be omitted.innerHtml: A boolean value that determines if the innerHtml prop should be added to the element. Defaults to false.triggerEvent: A string value that determines which event should trigger the dialog. Defaults to "onContextMenu". Accepted events are:onClick, onContextMenu, onDoubleClick, onMouseEnter, onMouseOver
Both useUpdatableText and useUpdatableTextContainer, as well as the getProps function returned by useUpdatableTextContainer accept a second parameter of type UseUpdatableTextConfig.
If the config object is not passed, it will be inherited.
For example, if you pass the config object to useUpdatableTextContainer, all the getProps functions returned by it will inherit the config object.
Example with Material UI Input
/*
Text object example:
{
Signup: {
title: "Sign up",
inputs: {
email: {
label: "Email label",
placeholder: "johndoe@mail.com",
validation: {
email: "Email is invalid",
required: "Email is required",
},
},
}
}
*/
import { useUpdatableTextContainer } from "easy-text-update";
import { useFormContext } from "react-hook-form";
const Input = ({ name, tPath, ...rest }: Props) => {
const { getText, getProps } = useUpdatableTextContainer(tPath);
const { formState } = useFormContext(); // react-hook-form, but you can use any form library
const error = formState.errors[name];
return (
<TextField
error={!!error}
label={<span {...getProps("label")} />}
placeholder={getText("placeholder")} // pass this as a string
helperText={
// this accepts a string or a JSX element
// if you want the label to be editable, you can pass it as a child
error ? <span {...getProps(`validation.${error.type}`)} /> : undefined
}
{...rest} // pass the rest of the props
inputProps={{
...rest?.inputProps, // copy over any inputProps
...getProps("placeholder", {
// this enables editing the placeholder
returnChildren: false,
}),
}}
/>
);
};
const Page = () => {
return <Input name="email" tPath="Signup.inputs.email" />;
};One admin page for all the texts
The EditTextPage component can be used as a central page where you can edit your text object.
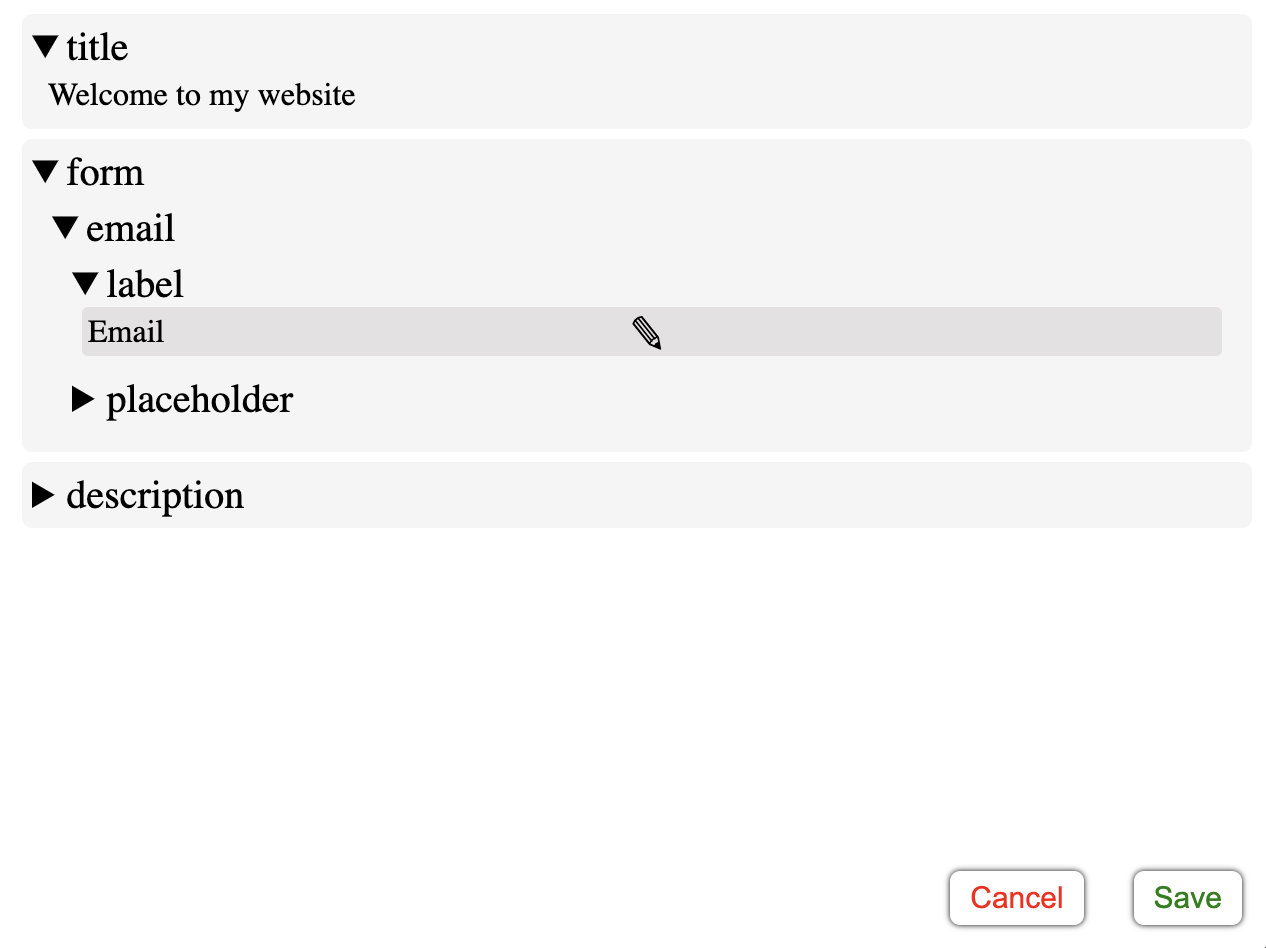 Example with React Router:
Example with React Router:
import { TextUpdateProvider, EditTextPage } from "easy-text-update";
import { BrowserRouter, Routes, Route } from "react-router-dom";
// Better to import this from a JSON file or from a database
const text = {
title: "Hello World",
form: {
email: {
label: "Email",
placeholder: "Enter your email",
},
},
description: "A lot of amazing stuff in here!!!",
};
function App() {
return (
<BrowserRouter>
<TextUpdateProvider text={text} active save={console.log}>
<Routes>
<Route path="edit" element={<EditTextPage title="Text Admin" />} />
{/* Your other routes */}
</Routes>
</TextUpdateProvider>
</BrowserRouter>
);
}
export default App;You can pass onInactive and onSave props to EditTextPage to handle the inactive state and the save action. By default, on inactive, null will be returned. For the save action, the save function passed to TextUpdateProvider will be called.
Or build your own text admin page
Use the useEditTextPageContext to get access to the text object, the active value and the save function.
import { useEditTextPageContext } from "easy-text-update";
import { useEffect } from "react";
const EditTextPage = () => {
const { textObject, active, save } = useEditTextPageContext();
useEffect(() => {
if (!active) {
// Redirect or whatever
}
}, [active]);
return <>Amazing stuff here</>;
};Saving the text
When you click "Save" the text is updated in the UI, and the save function provided to TextUpdateProvider is called with the updated text object.
In the save function you can handle the saving of the text the way you want. Since the text object is a plain javascript object, you can send it to the backend and save it to a database or a file.
If the update fails, you can call the revert callback provided to your save function as the second parameter. This will revert the text to the previous state in the UI.