express-async-context v1.1.2
express-async-context
Zero-dependency context-provision for express-application based on the AsyncLocalStorage.
[](https://github.com/DScheglov/ express-async-context/actions/workflows/run-tests.yml)


Installation
npm install express-async-contextUsage
import express from 'express';
import createContext from 'express-async-context';
const Context = createContext(req => ({
traceId: req.headers['x-request-id'] ?? Math.random().toFixed(20).slice(2),
}));
const app = express();
app.use(Context.provider);
app.get('/trace-id', Context.consumer(
(req, res) => ({ traceId }) => res.json({ traceId }),
));
app.listen(8080, () => {
console.log('Server is listening on port: 8080');
console.log('Follow: http://localhost:8080/trace-id');
});curl -H "X-Request-Id: 58895124899023443277" http://localhost:8080/trace-idMotivation
The express-async-context library is designed to aproach context provision to the
chain of request handling in the express-application without mutation of the
request or/and response.
Under the hood library uses AsyncLocalStorage and is based on the thunk-idiom that means calculation postponed until it will be provided with the context.
The main benifit of context we can get when we use IoC-container as a context. To make such injection safe the static type-safe containers required, as instance: true-di.
See Live DI Demo on Sandbox
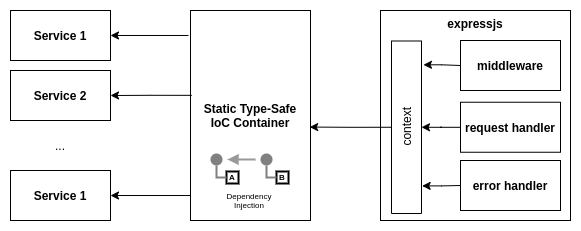
API Reference
- function
createContext - type
ContextFactory<T> - interface
ContextManager<T> - type
HandlerThunk<T> - type
ErrorHandlerThunk<T> - type
Thunk<T, R = void> - type
RunFn<T>
function createContext
<T>(contextFactory: ContextFactory<T>): ContextManager<T>;Accepts contextFactory function and creates a ContextManager.
type ContextFactory<T>
<T>(req: express.Request, res: express.Response) => T;The type describes function that accepts express.Request, express.Response and returns context data of any type T.
interface ContextManager<T>
interface ContextManager<T> {
provider: (req: express.Request, res: express.Response, next: express.NextFunction) => void;
consumer: {
(handler: express.RequestHandler | HandlerThunk<T>): express.RequestHandler;
(handler: express.ErrorRequestHandler | ErrorHandlerThunk<T>): express.ErrorRequestHandler;
}The interface contains two members:
provider - is an usual
expressmiddleware that creates context data for each request usingcontextFactoryand "binds" this data to the requestconsumer - is a decorator for
HandlerThunk<T>andErrorHandlerThunkthat converts them to usualexpress.RequestHandlerandexpress.ErrorRequestHandler.
type HandlerThunk<T>
(req: express.Request, res: express.Response, next: express.NextFunction) =>
(context: T, run: RunFn<T>) => void;The curried request handler that requires two-times application.
HandlerThunk could be considered as an express.RequestHandler
that returns a postponed handling of the request -- the Thunk
type ErrorHandlerThunk<T>
(err: any, req: express.Request, res: express.Response, next: express.NextFunction) =>
(context: T, run: RunFn<T>) => void;The curried handler of error trhown during the request processing.
ErrorHandlerThunk could be considered as an express.ErrorRequestHandler that
returns a postponed handling of the error -- the Thunk
type Thunk<T, R = void>
(context: T, run: RunFn<T>) => RThe postponed calculation, including handler of the request or an error.
The correspondent function receives context data and the run-function,
that runs any other Thunk.
type RunFn<T>
<R>(fn: Thunk<T, R>) => RRuns and injects the context data and itself to the postponed calculation that accepts as a single argument.
RunFn returns the result of execution of its argument-function.
