front-components v0.0.5
front-components - compose different frontend microservices
Compose different microfrontend in a portal.
You can either instantiate a service as uncontrolled: it has access to browser url, and a global event bus provided by this package.
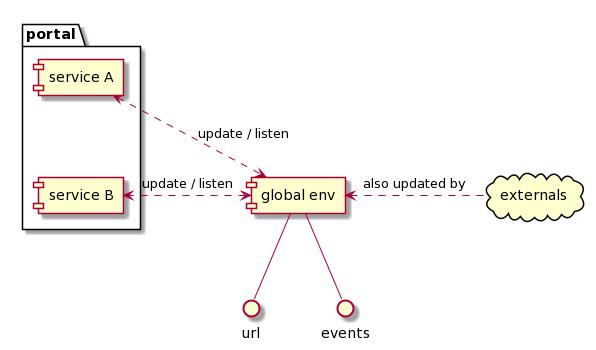
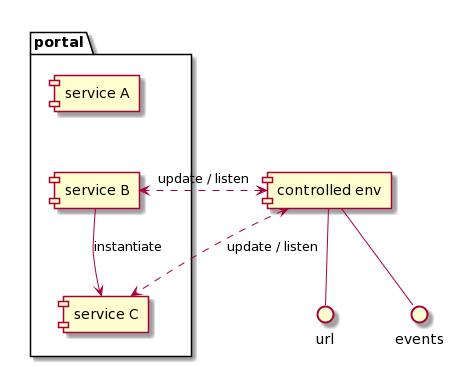
Or you can instantiate a service as controlled by another one: it has access to a scoped router, and a scoped event bus
Install
npm install --save front-components
Registering a service
Service A should register itself as soon as it can, and provide:
- a unique identifier
- a way to mount this service on DOM
- a way to unmount this service
import { registerInstance } from "front-components";
function mount(domElement) {
// ... For exemple: ReactDOM.render(..., domElement)
}
function unmount(domElement) {
// ... For exemple: ReactDOM.unmountComponentAtNode(domElement);
}
registerInstance({
serviceId: "service-A",
mount,
unmount,
});Instantiating a service
Load your service from you portal or another service, using its unique identifier.
If service is in a local file you can use require, if it's on remote file you can use <script> tag or even systemJs:
- instantiate an uncontrolled service with:
instantiateAt('service-A', domElement); - instantiate an controlled service with:
instantiateAt('service-A', domElement, { isControlled: true });
Events
To emit and listen to events from a service or portal:
import { emit, on } from "front-components";
emit("my-event");
on("my-event", (data) => console.log(data));Location
A service should not directly access window.location and other history related stuff.
Instead, it should gain access to navigation history using a plugin.
For example, for React-router, you can use history from our plugin:
import { getReactRouterHistory } from "front-components-history";
const history = getReactRouterHistory();
// uncontrolled service => history will be browser history
// controlled service => history will be memory historyBasic usage
Some exemple with React.
Portal instantiate uncontrolled service
An uncontrolled service emit and listen to events in global bus. Portal has access to global event bus.
// ... service-a/index.js
import { emit } from "front-components";
import { getReactRouterHistory } from "front-components-history";
function mount(domElement) {
// This will be browser history as service is uncontrolled
const history = getReactRouterHistory();
ReactDOM.render(<App history={history} />, domElement);
emit("hello", { foo: "bar" });
}
function unmount(domElement) {
ReactDOM.unmountComponentAtNode(domElement);
}
registerInstance({
serviceId: "service-A",
mount,
unmount,
});
// ... portal/index.js
import { instantiateAt, on } from "front-components";
// Listen to global events
on("mounted", (data) => {
console.log(data); // Once service-a will be mounted, this will be logged
});
// Instantiate service A
const div = document.getElementById("root");
instantiateAt("service-A", div).then(() => {
console.log("service A instantiated");
document.location = "new-url"; // will redirect service A
});Portal instantiate controlled service
An controlled service emit and listen to events in a scoped event bus. Portal has no direct access to this event bus. Portal can retrieve service event bus after service has been mounted.
// ... service-b/index.js
import { emit } from "front-components";
function mount(domElement) {
// This will be a memory history as service is controlled
const history = getReactRouterHistory();
ReactDOM.render(<App history={history} />, domElement);
emit("hello", { foo: "bar" });
}
function unmount(domElement) {
ReactDOM.unmountComponentAtNode(domElement);
}
registerInstance({
serviceId: "service-b",
mount,
unmount,
});
// ... portal/index.js
import { instantiateAt, on } from "front-components";
// Listen to global events
on("mounted", (data) => {
console.log(data); // This will never print, as service b is controlled
});
// Instantiate service B
const div = document.getElementById("root");
instantiateAt("service-B", div).then((controls) => {
controls.events.on("an-event-from-service-b", (data) => {
console.log(data); // This will print next time service b emit an event
});
// will move service B to a specific location, independant of browser url
controls.history.push("/service-b-specific-url");
});