future-proof v0.1.0
future-proof
Write data migration logic in code so you can change the shape of your data confidently as your app evolves.
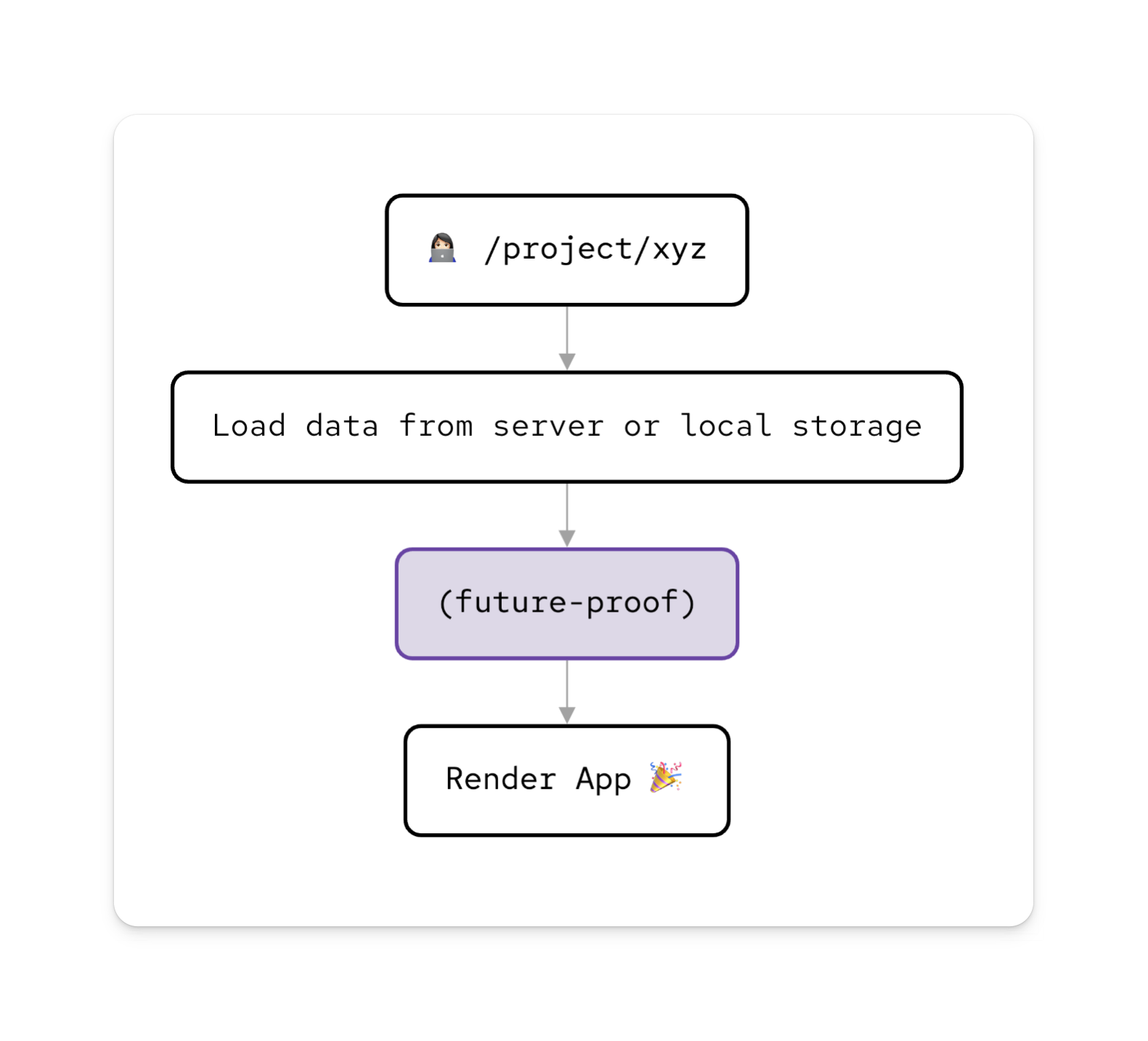
Motivation
Usually an app begins with one data shape but over time the shape of data changes. In most apps I've written, the parts which ensure the data is up to data are a tangled mess. I wanted something that ensured my data was up-to-date, was easy to read, and was lightweight enough to run on the client when loading data.
I'm also a frequent user of Zustand persisted stores, so I wrote the API with that in mind. However, it can be used with any data.
Installation
pnpm add future-proofnpm install future-proofyarn add future-proofHow to Use
Define Migration Steps
Pass your initial state to the from function. Don't use a variable.
To complete the definition, call the init function with the initial state (do use a variable!).
// In the beginning
const initialState = { x: 0, y: 0 };
const { version, migrate } = from({ x: 0, y: 0 }).init(initialState);As your data changes, chain to functions to define migration steps.
// Later on
const initialState = { x: 0, y: 0, z: 0 };
const { version, migrate } = from({ x: 0, y: 0 })
.to((state) => ({ ...state, z: 0 }))
.init(initialState);Each to function takes a callback function that receives the current state object and returns a new state object with the desired changes. You can add as many to functions as necessary to transform your data.
Here's a longer example:
// In this example we begin with x and y properties.
// Later on we added z
// Even later we added θ
const { version, migrate } = from({
x: 100,
y: 100,
})
.to((state) => ({
...state,
z: 100,
}))
.to((state) => ({
...state,
θ: 0,
}))
.init({
x: 100,
y: 100,
z: 100,
θ: 0,
});The init function returns the current version number and a migrate function we can use to ensure our data is up to date.
Apply Migrations
To apply the migration to your data, you can call the migrate function with the data object and it's version. The migrate function will return the migrated data object.
Here's an example of applying migration:
const data = migrate(
{
x: 200,
y: 200,
},
0
);In this example, we pass the data object with x and y properties, along with the version number 0. The migrate function will return the migrated data object, which includes the properties x, y, z, and θ.
Usage with Zustand
import { create } from "zustand";
import { persist } from "zustand/middleware";
import { from } from "future-proof";
type State = { x: number; y: number; z: number; θ: number };
const initialState: State = {
x: 100,
y: 100,
z: 100,
θ: 0,
};
const { version, migrate } = from({
x: 100,
y: 100,
})
.to((data) => ({ ...data, z: 100 }))
.to((data) => ({ ...data, θ: 0 }))
.init(initialState);
const useStore = create<State>()(
persist((set) => initialState, {
name: "my-persisted-store",
version,
migrate,
})
);Contributions
Contributions are welcome! Please open an issue or submit a PR.
2 years ago