javascript-algorithms-and-data-structures v0.0.4
JavaScript Algorithms and Data Structures
This repository contains JavaScript based examples of many popular algorithms and data structures.
Each algorithm and data structure has its own separate README with related explanations and links for further reading (including ones to YouTube videos).
Read this in other languages: 简体中文, 繁體中文
Data Structures
A data structure is a particular way of organizing and storing data in a computer so that it can be accessed and modified efficiently. More precisely, a data structure is a collection of data values, the relationships among them, and the functions or operations that can be applied to the data.
- Linked List
- Queue
- Stack
- Hash Table
- Heap
- Priority Queue
- Trie
- Tree
- Graph (both directed and undirected)
- Disjoint Set
Algorithms
An algorithm is an unambiguous specification of how to solve a class of problems. It is a set of rules that precisely define a sequence of operations.
Algorithms by Topic
- Math
- Factorial
- Fibonacci Number
- Primality Test (trial division method)
- Euclidean Algorithm - calculate the Greatest Common Divisor (GCD)
- Least Common Multiple (LCM)
- Integer Partition
- Sets
- Cartesian Product - product of multiple sets
- Power Set - all subsets of a set
- Permutations (with and without repetitions)
- Combinations (with and without repetitions)
- Fisher–Yates Shuffle - random permutation of a finite sequence
- Longest Common Subsequence (LCS)
- Longest Increasing subsequence
- Shortest Common Supersequence (SCS)
- Knapsack Problem - "0/1" and "Unbound" ones
- Maximum Subarray - "Brute Force" and "Dynamic Programming" (Kadane's) versions
- Strings
- Levenshtein Distance - minimum edit distance between two sequences
- Hamming Distance - number of positions at which the symbols are different
- Knuth–Morris–Pratt Algorithm - substring search
- Rabin Karp Algorithm - substring search
- Longest Common Substring
- Searches
- Sorting
- Bubble Sort
- Selection Sort
- Insertion Sort
- Heap Sort
- Merge Sort
- Quicksort - in-place and non-in-place implementations
- Shellsort
- Counting Sort
- Radix Sort
- Trees
- Depth-First Search (DFS)
- Breadth-First Search (BFS)
- Graphs
- Depth-First Search (DFS)
- Breadth-First Search (BFS)
- Dijkstra Algorithm - finding shortest path to all graph vertices
- Bellman-Ford Algorithm - finding shortest path to all graph vertices
- Detect Cycle - for both directed and undirected graphs (DFS and Disjoint Set based versions)
- Prim’s Algorithm - finding Minimum Spanning Tree (MST) for weighted undirected graph
- Kruskal’s Algorithm - finding Minimum Spanning Tree (MST) for weighted undirected graph
- Topological Sorting - DFS method
- Articulation Points - Tarjan's algorithm (DFS based)
- Bridges - DFS based algorithm
- Eulerian Path and Eulerian Circuit - Fleury's algorithm - Visit every edge exactly once
- Hamiltonian Cycle - Visit every vertex exactly once
- Strongly Connected Components - Kosaraju's algorithm
- Travelling Salesman Problem - shortest possible route that visits each city and returns to the origin city
Uncategorized
Algorithms by Paradigm
An algorithmic paradigm is a generic method or approach which underlies the design of a class of algorithms. It is an abstraction higher than the notion of an algorithm, just as an algorithm is an abstraction higher than a computer program.
- Brute Force - look at all the possibilities and selects the best solution
- Maximum Subarray
- Travelling Salesman Problem - shortest possible route that visits each city and returns to the origin city
- Greedy - choose the best option at the current time, without any consideration for the future
- Unbound Knapsack Problem
- Dijkstra Algorithm - finding shortest path to all graph vertices
- Prim’s Algorithm - finding Minimum Spanning Tree (MST) for weighted undirected graph
- Kruskal’s Algorithm - finding Minimum Spanning Tree (MST) for weighted undirected graph
- Divide and Conquer - divide the problem into smaller parts and then solve those parts
- Binary Search
- Tower of Hanoi
- Euclidean Algorithm - calculate the Greatest Common Divisor (GCD)
- Permutations (with and without repetitions)
- Combinations (with and without repetitions)
- Merge Sort
- Quicksort
- Tree Depth-First Search (DFS)
- Graph Depth-First Search (DFS)
- Dynamic Programming - build up a solution using previously found sub-solutions
- Fibonacci Number
- Levenshtein Distance - minimum edit distance between two sequences
- Longest Common Subsequence (LCS)
- Longest Common Substring
- Longest Increasing subsequence
- Shortest Common Supersequence
- 0/1 Knapsack Problem
- Integer Partition
- Maximum Subarray
- Bellman-Ford Algorithm - finding shortest path to all graph vertices
- Backtracking - similarly to brute force, try to generate all possible solutions, but each time you generate next solution you test
if it satisfies all conditions, and only then continue generating subsequent solutions. Otherwise, backtrack, and go on a
different path of finding a solution. Normally the DFS traversal of state-space is being used.
- Hamiltonian Cycle - Visit every vertex exactly once
- N-Queens Problem
- Knight's Tour
- Branch & Bound - remember the lowest-cost solution found at each stage of the backtracking search, and use the cost of the lowest-cost solution found so far as a lower bound on the cost of a least-cost solution to the problem, in order to discard partial solutions with costs larger than the lowest-cost solution found so far. Normally BFS traversal in combination with DFS traversal of state-space tree is being used.
How to use this repository
Install all dependencies
npm installRun all tests
npm testRun tests by name
npm test -- -t 'LinkedList'Playground
You may play with data-structures and algorithms in ./src/playground/playground.js file and write
tests for it in ./src/playground/__test__/playground.test.js.
Then just simply run the following command to test if your playground code works as expected:
npm test -- -t 'playground'Useful Information
References
▶ Data Structures and Algorithms on YouTube
Big O Notation
Order of growth of algorithms specified in Big O notation.
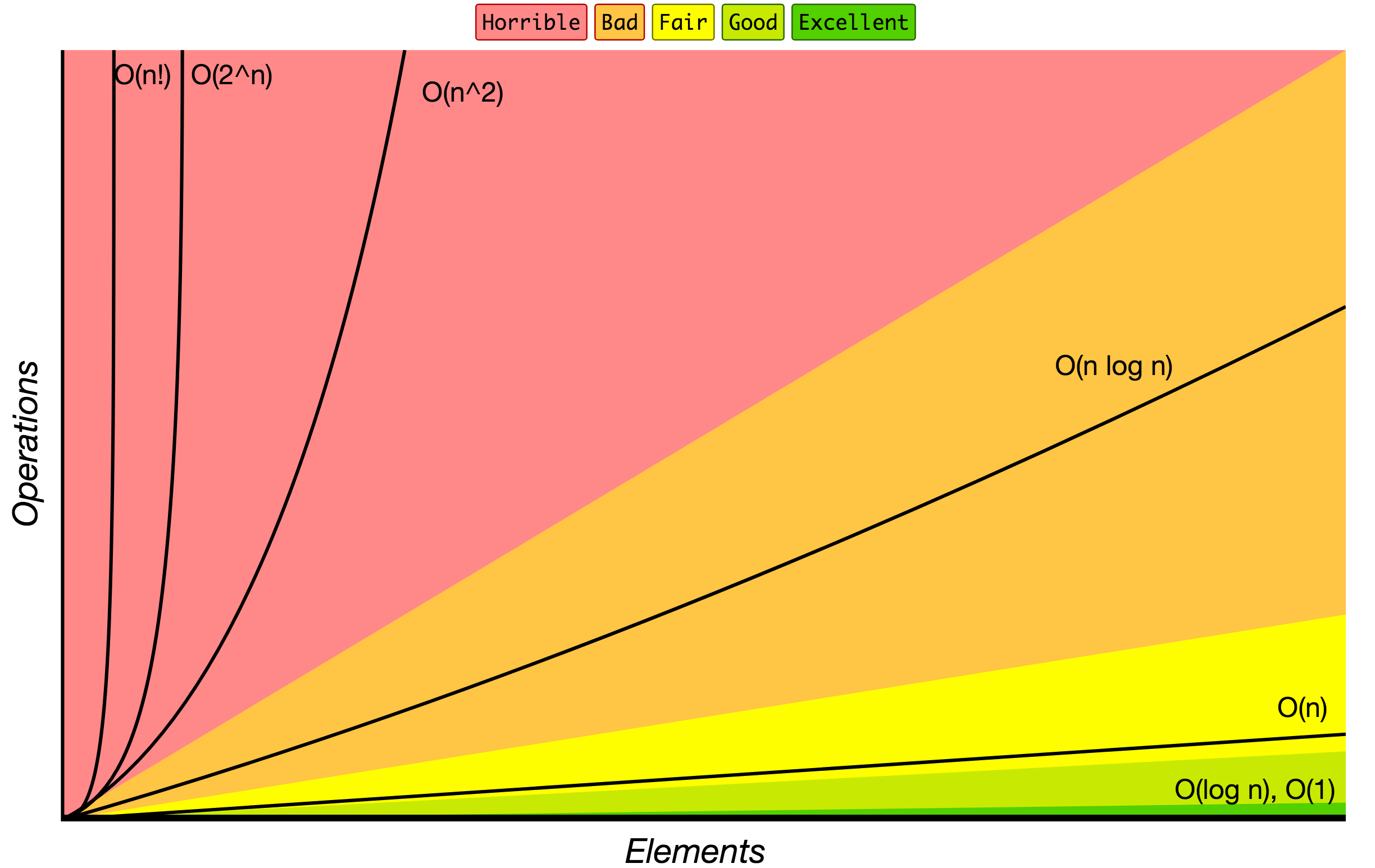
Source: Big O Cheat Sheet.
Below is the list of some of the most used Big O notations and their performance comparisons against different sizes of the input data.
| Big O Notation | Computations for 10 elements | Computations for 100 elements | Computations for 1000 elements |
|---|---|---|---|
| O(1) | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| O(log N) | 3 | 6 | 9 |
| O(N) | 10 | 100 | 1000 |
| O(N log N) | 30 | 600 | 9000 |
| O(N^2) | 100 | 10000 | 1000000 |
| O(2^N) | 1024 | 1.26e+29 | 1.07e+301 |
| O(N!) | 3628800 | 9.3e+157 | 4.02e+2567 |
Data Structure Operations Complexity
| Data Structure | Access | Search | Insertion | Deletion | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Array | 1 | n | n | n | |
| Stack | n | n | 1 | 1 | |
| Queue | n | n | 1 | 1 | |
| Linked List | n | n | 1 | 1 | |
| Hash Table | - | n | n | n | In case of perfect hash function costs would be O(1) |
| Binary Search Tree | n | n | n | n | In case of balanced tree costs would be O(log(n)) |
| B-Tree | log(n) | log(n) | log(n) | log(n) | |
| Red-Black Tree | log(n) | log(n) | log(n) | log(n) | |
| AVL Tree | log(n) | log(n) | log(n) | log(n) |
Array Sorting Algorithms Complexity
| Name | Best | Average | Worst | Memory | Stable | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bubble sort | n | n^2 | n^2 | 1 | Yes | |
| Insertion sort | n | n^2 | n^2 | 1 | Yes | |
| Selection sort | n^2 | n^2 | n^2 | 1 | No | |
| Heap sort | n log(n) | n log(n) | n log(n) | 1 | No | |
| Merge sort | n log(n) | n log(n) | n log(n) | n | Yes | |
| Quick sort | n log(n) | n log(n) | n^2 | log(n) | No | |
| Shell sort | n log(n) | depends on gap sequence | n (log(n))^2 | 1 | No | |
| Counting sort | n + r | n + r | n + r | n + r | Yes | r - biggest number in array |
| Radix sort | n * k | n * k | n * k | n + k | Yes | k - length of longest key |