machinarium v0.0.4
Machinarium
Fluent, framework-agnostic, and type-safe state machine library, that aims for simplicity and great developer experience
Usage
To create a state machine using Machinarium, use the createMachine function. This function accepts generic type parameters for
the possible states and the events, and returns a chainable builder object that allows you to define the state machine.
Basic Usage
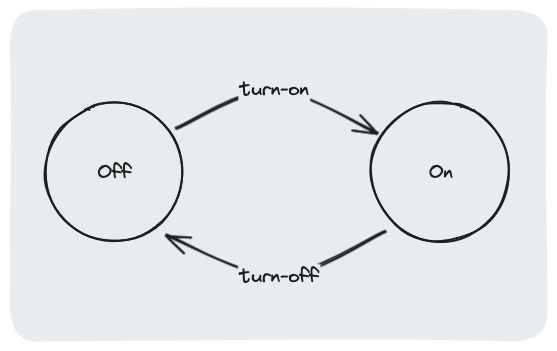
Let's start by building a state machine for a light bulb that can be either on or off, based on this simple state diagram:
import { createMachine } from 'machinarium';
type State = 'on' | 'off';
type Event = 'turn-on' | 'turn-off';
const bulbStateMachine = createMachine<State, Event>({
initialState: 'off',
})
.when('off', (b) => {
b.on('turn-on').transitionTo('on');
})
.when('on', (b) => {
b.on('turn-off').transitionTo('off');
});For each state, we need to define which events it'll respond to and what state it should transition to when that event is received.
To do that, we use the when method that accepts the state name and a callback. The callback receives a builder object that lets you
build the transitions for that state using the on and transitionTo methods.
Then, to actually transition between the states in the machine, use the send method and pass the event name to it:
bulbStateMachine.send('turn-on');
console.log(bulbStateMachine.getState()); // 'on'Multi-State Transitions
You can also define an array of states in the when method to easily support multiple states with the same transitions:
type State = 'on' | 'off' | 'broken';
type Event = 'turn-on' | 'turn-off' | 'break';
const bulbStateMachine = createMachine<State, Event>({
initialState: 'off',
})
.when('off', (b) => {
b.on('turn-on').transitionTo('on');
})
.when('on', (b) => {
b.on('turn-off').transitionTo('off');
})
.when(['off', 'on'], (b) => {
b.on('break').transitionTo('broken');
});In addition, you can pass a function to the transitionTo method to dynamically determine the next state based on the previous state:
type State = 'on' | 'off';
type Event = 'toggle';
const bulbStateMachine = createMachine<State, Event>({
initialState: 'off',
}).when(['on', 'off'], (b) => {
b.on('toggle').transitionTo((prev) => {
return prev === 'on' ? 'off' : 'on';
});
});Checking for Transitions
You might also want to check whether a transition can be performed on the current state. To do that, use the can method
and pass the event you want to check:
type State = 'on' | 'off';
type Event = 'turn-on' | 'turn-off';
const bulbStateMachine = createMachine<State, Event>({
initialState: 'off',
})
.when('off', (b) => {
b.on('turn-on').transitionTo('on');
})
.when('on', (b) => {
b.on('turn-off').transitionTo('off');
});
console.log(bulbStateMachine.can('turn-on')); // true
console.log(bulbStateMachine.can('turn-off')); // falseListening for Changes
To listen for state transitions, use the subscribe method:
const unsubscribe = bulbStateMachine.subscribe(() => {
console.log('New state:', bulbStateMachine.getState());
});
bulbStateMachine.send('turn-on'); // Logs 'New state: on'
unsubscribe();Usage with React
To use Machinarium with React, use the useMachine hook from machinarium/react. This hook will provide you with the
current state and a send function to transition between states:
import { createMachine } from 'machinarium';
import { useMachine } from 'machinarium/react';
type State = 'on' | 'off';
type Event = 'turn-on' | 'turn-off';
const bulbStateMachine = createMachine<State, Event>({
initialState: 'off',
})
.when('off', (b) => {
b.on('turn-on').transitionTo('on');
})
.when('on', (b) => {
b.on('turn-off').transitionTo('off');
});
function Bulb() {
const { state, send } = useMachine(bulbStateMachine);
return (
<div>
<p>The bulb is {state}</p>
<button onClick={() => send('turn-on')}>Turn on</button>
<button onClick={() => send('turn-off')}>Turn off</button>
</div>
);
}Each time the machine's state will change (either by using the send function from the hook, or by using the send method
from the machine itself), the component will re-render with the new state.
You can also determine reactively whether a transition can be performed using the canTransition function from the hook:
function Bulb() {
const { state, send, canTransition } = useMachine(bulbStateMachine);
return (
<div>
<p>The bulb is {state}</p>
<button
disabled={!canTransition('turn-on')}
onClick={() => send('turn-on')}
>
Turn on
</button>
<button
disabled={!canTransition('turn-off')}
onClick={() => send('turn-off')}
>
Turn off
</button>
</div>
);
}