micro-app-graph-dashboard v1.0.0
micro-app-graph-dashboard - MQTT/Node based graphing dashboard
Micro app to display one or more graphs based on data received through MQTT. In my case MQTT data is fed by home sensors throughout the house. The dashboard is updated in realtime using socket.io.
The dashboards listens on a number of mqtt topics for updates and then forwards the updates to clients using socket.io. It provides a simple way to display graphjs of sensor data (of course it can display any data fed through MQTT regardless of how it is generated).
This is an example display:
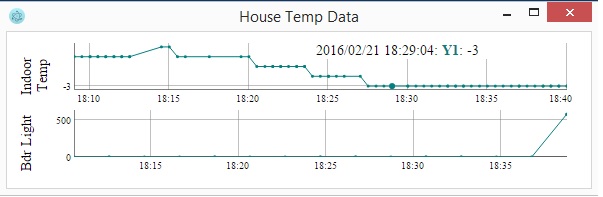
The following project can be used to connect a variety of sensors including temperature, power, humidity and power sensors.
Usage
After installation modify ../lib/config.json to match your configuration.
The configuration entries that must be updated include:
- mqttServerUrl - url of the mqtt server to connect to. This can either start with tcp:// or mqtts://. If it starts with mqtts:// there must be a subdirectory in the lib directory called mqttclient which contains ca.cert, client.cert, client.key which contain the key and associated certificates for a client which is authorized to connect to the mqtt server.
- graphEntries - array in which each entry contains a name, topic field, rentionSeconds(optional), and yPixelsPerLabel(optional). One graph will be included on the page for the app for each entry configured. The name is what will be displayed as the label for the graph and the topic is the topic on which the dashboard will listen for updates. Updates on the topic should be in the form of yyyyy,xxxx:value were yyyyy is generally a timestamp and the dasboard will extract the value after the ':' character and display it as the value for the corresponding label. The retentionSeconds specifies the maximum time in seconds a particular data point will be displayed (ie after a data point is retentionSeconds old it will no longer be included in the graph display), and yPixelsPerLabel controls the minimum number of pixels between each yAxis label.
- serverPort - port on which the dashboard listens for connections
- title - title for the dashbaord page (optional)
As a micro-app the dashboard also supports other options like authentication and tls for the dashboard connection. See the documentation for the micro-app-framework for additional details.
The following is an example configuration file with the IP for my server masked out:
Installation
Simply run:
Running
To run the graph-dashboard app, add node.js to your path (currently requires 4.x or better) and then run:
from the directory in which the micro-app-graph-dashboard was installed.
Once the server is started. Point your browser at the host/port for the server (or now use the micro-app-electron-launcher). If you have configured your browser to allow javascript to close the current page the original window will be closed and one with the correct size of the simple-dashboard app page will be created.
This micro-app allows resizing and the graphs will change to fit the available space in the window.
Example
The following is the page shown for a sample configuration:

Key Depdencies
micro-app-framework
As a micro-app the graph-dashboard app depends on the micro-app-framework:
See the documentation on the micro-app-framework for more information on general configuration options that are availble (ex using tls, authentication, serverPort, etc).
10 years ago