naturally v1.4.1
Naturally
Naturally allows to write Flowed specs using natural language instead of JSON.
TOC
Example
Define a flow named testFlow that has the following tasks:
A task named firstTask
that requires the following inputs: someInput, someOtherInput
that provides the following outputs: someOutput
using a resolver named testResolver
with the following mapped inputs:
param p1 mapped from someInput
param p2 mapped from someOtherInput
param p3 transformed with "{{someInput.property}}";
param p4 transformed with {
"a1": "{{someInput.property}}",
"a2": "{{someOtherInput.propertyB}}"
};
param p5 with value 123
param p6 with value 456.789
param p7 with value "sample string"
param p8 with a null value
param p9 with a true value
param p10 with a false value
param p11 with value ["a", "b", "c"];
param p12 with value {
"a1": "123",
"a2": true
};
with the following mapped outputs:
param taskResult mapped to someOutputOnce parsed will return the following javascript object:
{
code: 'testFlow',
tasks: {
firstTask: {
requires: [ 'someInput', 'someOtherInput' ],
provides: [ 'someOutput' ],
resolver: {
name: 'testResolver',
params: {
p1: 'someInput',
p2: 'someOtherInput',
p3: { transform: '{{someInput.property}}' },
p4: {
transform: {
a1: '{{someInput.property}}',
a2: '{{someOtherInput.propertyB}}'
}
},
p5: { value: 123 },
p6: { value: 456.789 },
p7: { value: 'sample string' },
p8: { value: null },
p9: { value: true },
p10: { value: false },
p11: { value: [ 'a', 'b', 'c' ] },
p12: { value: { a1: '123', a2: true } }
},
results: { taskResult: 'someOutput' }
}
}
}
}Grammar
naturally follows the following grammar:
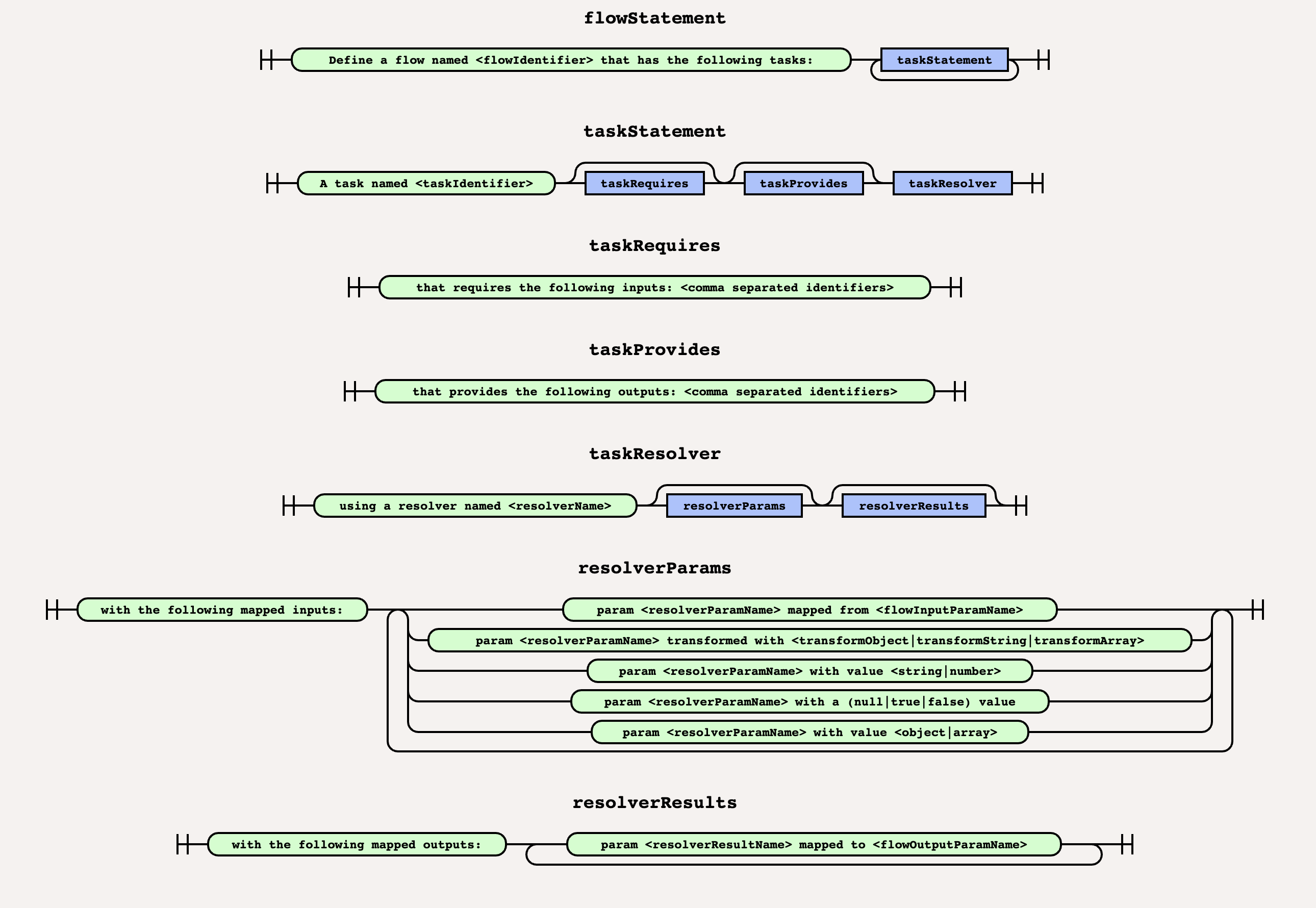
Let's see each section in detail.
flowStatement
The flow statement is a string that matches the following RegEx:
/Define a flow named ([._a-zA-Z][.\-_a-zA-Z0-9]+) that has the following tasks:/itaskStatement
The flow statement is a string that matches the following RegEx:
/A task named ([._a-zA-Z][.\-_a-zA-Z0-9]+)/itaskRequires
The task requires statement is a string that matches the following RegEx:
/that requires the following inputs: (([._a-zA-Z][.\-_a-zA-Z]+,\s?)*[._a-zA-Z][.\-_a-zA-Z]+)/itaskProvides
The task provides statement is a string that matches the following RegEx:
/that provides the following outputs: (([._a-zA-Z][.\-_a-zA-Z]+,\s?)*[._a-zA-Z][.\-_a-zA-Z]+)/itaskResolver
The task resolver statement is a string that matches the following RegEx:
/using a resolver named ([._a-zA-Z][.:\-_a-zA-Z0-9]+)/iresolverParams
Resolver params are basically two types of statements:
One statement that matches
/with the following mapped inputs:/ifollowed by one or more of the statements:
Mapped values
A string that matches the following RegEx:
/param ([._a-zA-Z][.\-_a-zA-Z0-9]+) mapped from ([._a-zA-Z][.\-_a-zA-Z0-9]+)/iString or number values
String or number values statements are strings that matches the following RegEx:
/param ([._a-zA-Z][.\-_a-zA-Z0-9]+) with value ((?<string>"(.*)")|(?<number>[\+\-]?\d*\.?\d+(?:[Ee][\+\-]?\d+)?))/iObject or array values
Object or array values are a special construct that allows to define a JSON object (object or array) as param value. It's a string that matches the following RegEx:
/param ([._a-zA-Z][.\-_a-zA-Z0-9]+) with value ((?<object>\{(.+)\});|(?<array>\[(.*)\]);)/siNote the s modifier, that allows to write the object in multiple lines.
Also note that both object and array values should end with }; or ]; respectively.
Null or boolean values
Null value is a special value and thus it have its own statement: a string that matches the following RegEx:
/param ([._a-zA-Z][.\-_a-zA-Z0-9]+) with a (null|true|false) value/iTransformed Values
Transformations values are strings that matches then follwoing RegEx:
/param ([._a-zA-Z][.\-_a-zA-Z0-9]+) transformed with ((?<object>\{(.+)\});|(?<array>\[(.*)\]);|(?<string>"(.+)");)/siNote the s modifier in the second RegEx, that allows to write the object in multiple lines.
Note that the expression support three types of transformations: object, array and string, each one should end with ; or ]; or "; respectively.
resolverResults
Resolver results are two types of statements.
One statement that matches the following RegEx:
/with the following mapped outputs:/ifollowed by one or more statements matching the folloging RegEx:
/param ([._a-zA-Z][.\-_a-zA-Z0-9]+) mapped to ([._a-zA-Z][.\-_a-zA-Z0-9]+)/iNOTE: All regex have the i modifier in order to be case insensitive.
Usage
const { NaturallyParser } = require('naturally');
const naturallyFlowedExpression = `
Define a flow named testFlow that has the following tasks:
A task named firstTask
that requires the following inputs: someInput, someOtherInput
that provides the following outputs: someOutput
using a resolver named testResolver
with the following mapped inputs:
param p1 mapped from someInput
param p2 mapped from someOtherInput
param p3 transformed with "{{someInput.property}}";
param p4 transformed with {
"a1": "{{someInput.property}}",
"a2": "{{someOtherInput.propertyB}}"
};
param p5 with value 123
param p6 with value 456.789
param p7 with value "sample string"
param p8 with a null value
param p9 with a true value
param p10 with a false value
param p11 with value ["a", "b", "c"];
param p12 with value {
"a1": "123",
"a2": true
};
with the following mapped outputs:
param taskResult mapped to someOutput
`;
const parser = new NaturallyParser();
const jsonFlow = parser.parse(naturallyFlowedExpression);
console.log(jsonFlow);Installation
npm install naturally