ngxs-firestore v0.0.0
NGXS Firestore
Demo
Description
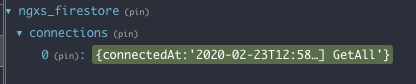
NGXS Firestore plugin helps you integrate Firestore and NGXS. It uses @angular/fire under the hood and provides a wrapper service with handful CRUD operations methods and easy integration with NGXS actions. In addition it provides useful data for debugging purposes, such as Active Connections, Reads, Updates, Creates and Deletes.
Quick start
Install the plugin:
- npm
npm install --save @ngxs-labs/firestore-plugin- yarn
yarn add @ngxs-labs/firestore-pluginIn your app.module.ts include the plugin, note that we also include AngularFireModule and NgxsModule, as they are peer dependencies for the plugin.
//...
import { AngularFireModule } from '@angular/fire';
import { NgxsModule } from '@ngxs/store';
import { NgxsFirestoreModule } from '@ngxs-labs/firestore-plugin';
import { NgxsReduxDevtoolsPluginModule } from '@ngxs/devtools-plugin';
@NgModule({
declarations: [AppComponent, ListComponent],
imports: [
//...
AngularFireModule.initializeApp(environment.firebase),
NgxsModule.forRoot(//...),
NgxsReduxDevtoolsPluginModule.forRoot()
NgxsFirestoreModule.forRoot()
],
//...
})
export class AppModule { }Next create a service (i.e races.firestore.ts) to execute Firestore operations. This service extends the plugin FirestoreService, which is generic service, and takes the type <T> of the Firestore document. We also need to provide the path of the collection.
//...
import { FirestoreService } from '@ngxs-labs/firestore-plugin';
@Injectable({
providedIn: 'root'
})
export class RacesFirestore extends FirestoreService<Race> {
protected path = 'races';
}Finally we create the @State. The state will contain actions to execute the Firestore CRUD operations via the service created previously. When getting data from Firestore, we have two options:
- Get data once
- Connect to a document or collection and receive changes as they occur on the Firestore server.
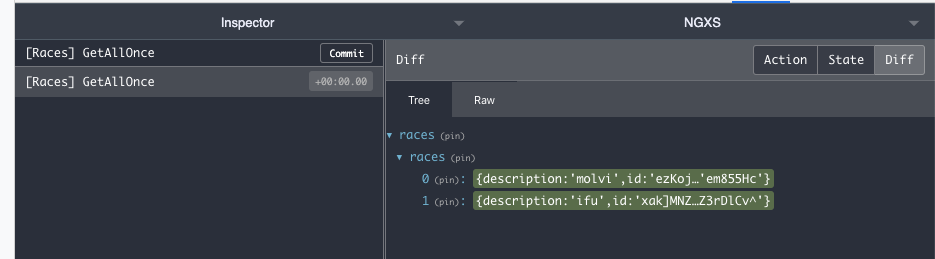
For the first scenario the plugin FirestoreService provides the methods docOnce$() and collectionOnce$(), which will get the first emission and unsubscribe immediately after. NGXS handles subscribing to the Observable and the action is done once the first data is emmited.
//...
import { NgxsFirestore } from '@ngxs-labs/firestore-plugin';
@State<RacesStateModel>({
name: 'races',
defaults: {
races: []
}
})
export class RacesState {
@Action(RacesActions.GetAllOnce)
getAllOnce({ getState, patchState }: StateContext<RacesStateModel>) {
return this.racesFS.collectionOnce$().pipe(
tap(races => {
patchState({ races: races });
})
);
}
}
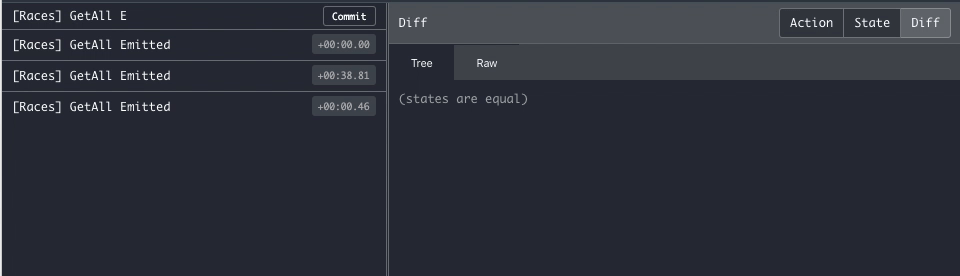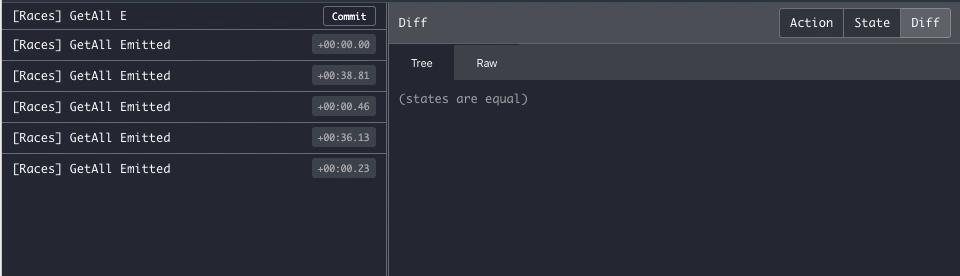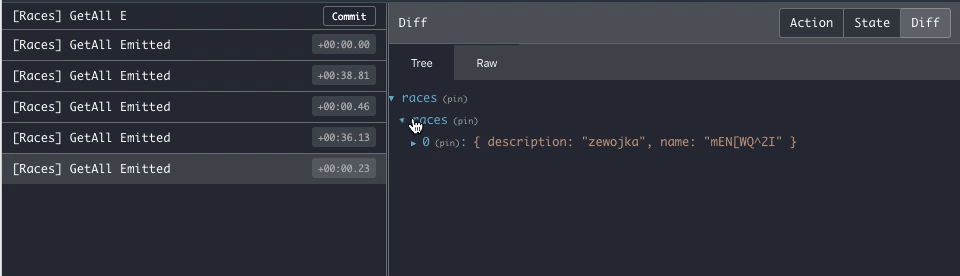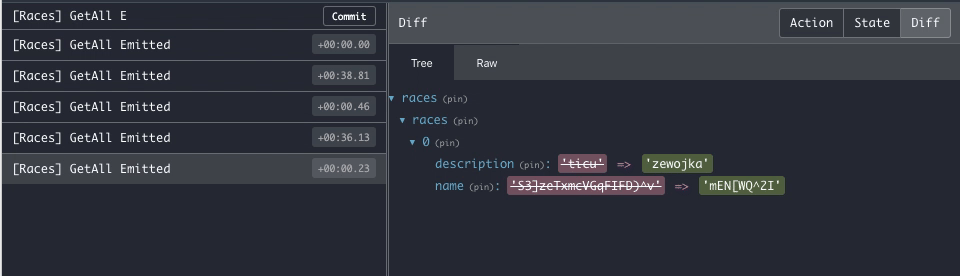
In the second scenario, the plugin provides the @NgxsFirestoreConnect decorator, which will connect to Firestore and emit every new change as a separate Emit action.
The decorator takes the Action that will trigger the connection and a function that receives the Action result and return the patched state value.
//...
import { NgxsFirestore } from '@ngxs-labs/firestore-plugin';
export class RacesState {
//...
@NgxsFirestore(
RacesActions.GetAll,
(payload): Partial<RacesStateModel> => ({ races: payload })
)
@Action(RacesActions.GetAll)
getAll({ patchState }: StateContext<RacesStateModel>) {
return this.racesFS.collectionOnce$();
}
}Once you connect to the Firestore stream you'll keep receiving every server update on a new Emit action, making it easier to debug.
6 years ago