node-chrome-cordova-app v1.0.17
Node Chrome Cordova App (ncca)
Overview
Before continuing, please ensure you have a good understanding of:
- HTML5 development (Javascript/HTML/CSS)
- Node.js / NPM
Chrome Apps This is extremely important to fully understand. Make sure you download all the software needed. Take note of the mobile tools, MVC architecture, and application framework. Be sure to understand the components of a Chrome App (manifest, permissions, background.js, app life-cycle, etc...) as well as the
ccacommand line tool. It is a good idea to also install Android Debug Bridge as it will help you to properly connect your device
Chrome Apps offer device portability, Javascript as the base language, and hardware access via Cordova. Chrome Apps, as you have read, can be ported to any modern operating system and provide mechanisms for various common tasks (local/sync storage, OAuth, app life-cycle, etc...). Further, they provide javascript libraries, in companion with Cordova, to access device hardware information. By "wrapping" such apps in native code, iOS, Android, and future mobile operating systems are easily supported by the same code base. Secondly, a single style of coding and a single stack of technologies (rooted in HTML, CSS, and JS) can be used across all platforms. This makes it extremely easy to collaborate and include additional developers. The main drawback of such a technique is a limitation on the computational advantages that come with native language apps (intense graphics or computations). However, it is the main goal to provide a means of rapidly developing multi-platform, lightweight apps.
Chrome Apps fall short in two key areas: a clear method of dividing client-side logic and background logic (different than backend logic); and a standard method of file and Node package dependencies. Therefore, node-chrome-cordova-app (ncca) was created to provide a basic file structure template, Gruntfile, and build process for elegantly including Node modules into an organized chrome app.
Installation
npm install -g node-chrome-cordova-app
If you have not used ChromeCordovaApps (cca) in the past, it is a good idea to get your system set up before using ncca. First, install cca using npm install -g cca. Then follow these steps:
- Create a new project by running
cca create YourApp. - Change directories into your new project and run
cca prepare - Run
cca emulate [android/ios]to ensure you have working emulators Run
cca run android --devicewith a usb connected android device to install the app on physical hardware.
After completing each of these steps, cca may prompt you to fix/install something on your system. This process will ensure that your system is prepared to use ncca.
Usage
- Initialize the app with
ncca MyApp- This will run
cca create MyApp && cd MyApp && npm init
- This will run
- The
npm initwill prompt you for changes to the package.json.
name: (MyApp)
version: (1.0.0)
description:
entry point: (index.js)
test command:
git repository:
keywords:
author:
license: (ISC)
About to write to [path]/MyApp/package.json:
{
"name": "MyApp",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "",
"main": "index.js",
"scripts": {
"test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1"
},
"author": "",
"license": "ISC"
}
Is this ok? (yes)- After accepting your package.json configuration, ncca will update the file directories and package.json to include gruntfile dependencies.
- At this point you will be prompted with
Install Packages and Build? (y/n). If you choose 'no', then ncca will quit. If you choose yes, then ncca will runnpm install && grunt tasks && cca prepare && cca buildnpm installwill install the dependencies to a local node_modules folder.grunt taskswill run the template 'tasks' grunt tasks. This includes: jsbeautifier jshint browserify browserify docco uglify * NOTE: The most important task. It collects the dependencies for the client-side and background code, then it outputs the two included files in the www/bin/ folder for actually application use. Also, uglify is commented out by default and should be un-commented for production.cca prepareprepares the chrome-cordova-app for multi-device builds. * NOTE: If this fails, runcca checkingin the project root to ensure that your system is capable of building multi-device apps. Fix any issues here before manually runningcca prepare && cca buildagain.cca buildbuilds the application for iOS or Android depending on your current system setup.
- Now that the project has been created and built. Open Chrome Apps & Extensions Developer Tool and install your app via the www folder. Click launch to see how your app will run on a desktop OS.
- You can also run
cca run [ios/android] [--device]to test mobile functionality.
Be sure to read the template code to understand the app lifecycle. You can change the default window size via the background.js file.
Understand the Process
The diagram below illustrates the overall process of generating multi-platform applications using ncca.
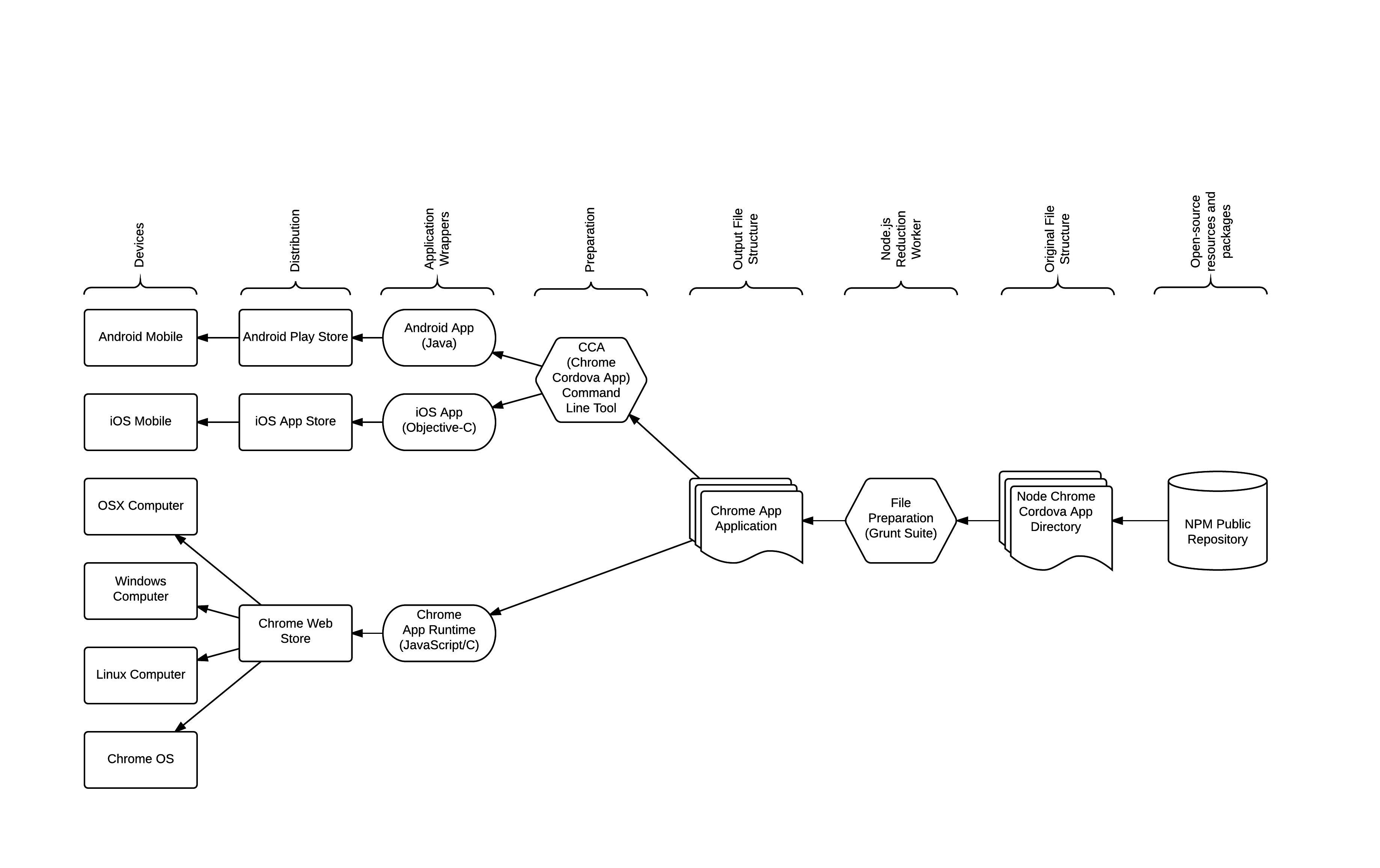
The diagram below illustrates the ncca file structure.
-/ROOT
|----/background [Place all files relating to the background process for the chrome app here.]
| |----background.js [Serves as a starting point for background execution and file dependency loading.]
|
|----/client [Place all files relating to the client process for the chrome app here.]
| |----client.js [Serves as a starting point for the client execution and file dependency loading.]
|
|----/docs [Created by ncca and populated each time grunt tasks completes]
|----/hooks [Created by cca, read google documentation for explanation]
|----/node_modules [Create by npm, used to store local dependencies.]
|----/platforms [Created by cca and updated each time cca build is ran]
|----/plugins [Created by cca and updated each time cca prepare is ran.]
|----/www [This is the main folder for the Chrome App]
| |----/assets [Holds application-specific assets]
| |----/bin [Holds the generated client.js and background.js files]
| |----index.css [Basic starting style sheet - edit accoridngly]
| |----index.html [Basic starting html file - edit accordingly, but ensure to include ./bin/client.js]
| |----manifest.json [Created by cca and used to describe the application. Edit accordingly, but ensure to use ./bin/background.js as the background script.]
| |----manifest.mobile.json [Created by cca and used for mobile settings.]
|
|----.gitignore [Created by cca and modified by ncca]
|----config.xml [Created and updated by cca prepare (do not edit directly, edit www/manifest.json)]
|----Gruntfile.js [Created by ncca to prepare files, edit accoridngly]
|----package.json [Created by npm to describe the 'package'. Relatively unused except for dependency tracking]
|----README.md [Created by ncca, but should be updated to match your app.]After the initial ncca MyApp runs, and you either automatically or manually run npm install && grunt tasks && cca prepare && cca build, you should run grunt in the project root. This will start a watcher that watches for file changes and automatically rebuilds the project upon changes. At any point, use ctrl-c to stop the watcher. Then run cca prepare && cca build to create the mobile-friendly builds.
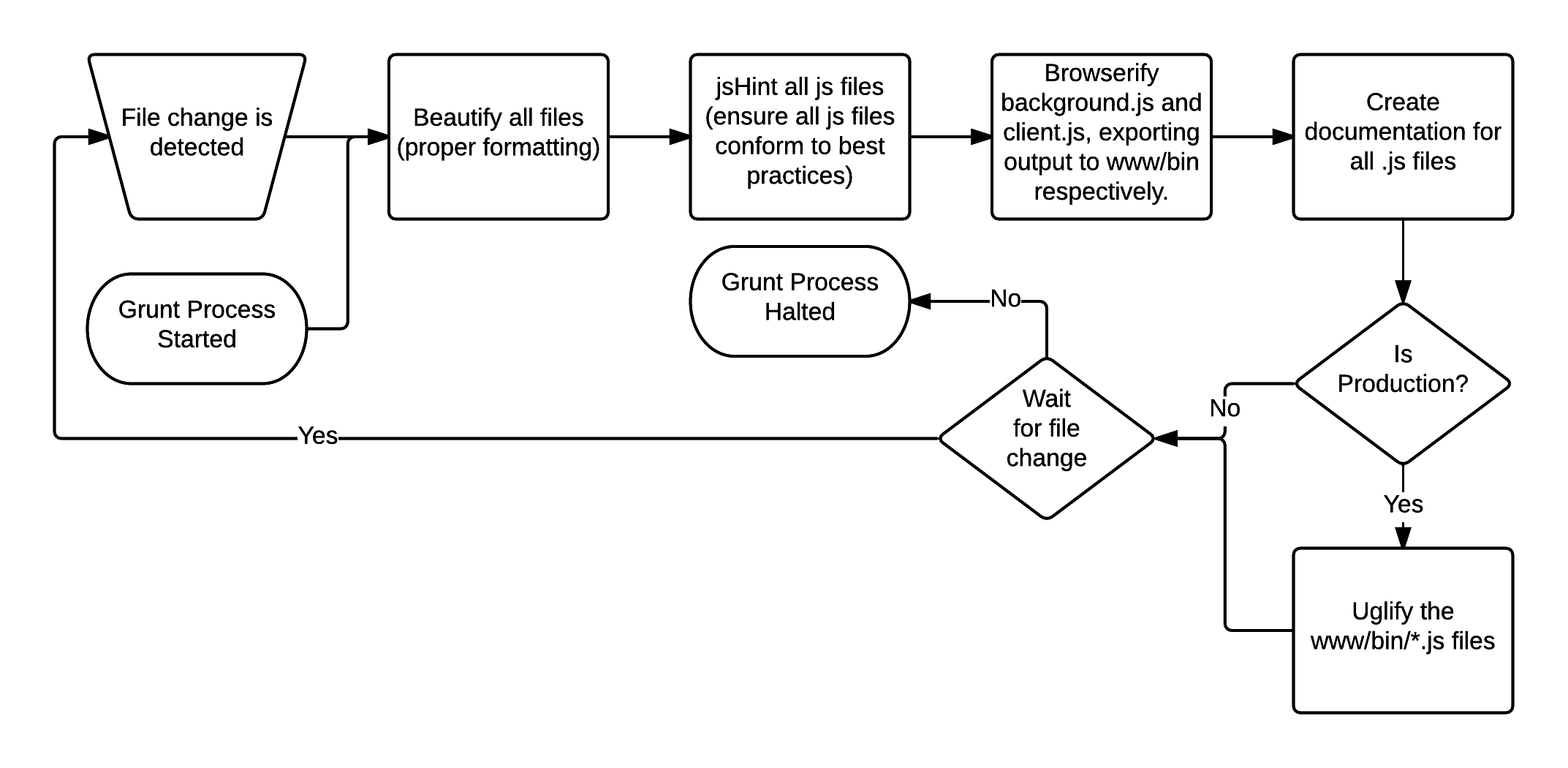
Below is a process flow of the Gruntfile.js process:
11 years ago
11 years ago
11 years ago
11 years ago
11 years ago
11 years ago
11 years ago
11 years ago
11 years ago
11 years ago
11 years ago
11 years ago
11 years ago
11 years ago
11 years ago
11 years ago
11 years ago
11 years ago