npm-benchmark-ts v1.1.6
Benchmark and Data Visualization
This project was created to measure the execution time of algorithms. It's worth mentioning that shorter execution times don't necessarily is the best solution, however they provide a valuable metric for our projects. With this package, I aim to demonstrate how we can effectively measure execution time using minimal external libraries.
Installation
To install all the dependencies, use the package manager npm and use the follow:
npm i npm-benchmark-tsThe unique external library in this project is the ChartJsImage. This library provides a ChartJsImage object. Import it, instantiate it, and set the necessary config.
Usage
First need to import :
import { benchMark, BenchmarkFunctions } from "npm-benchmark-ts";For example, this method uses a for loop to sum an array of numbers:
function sumNumberUsingFor(numbers: number[]): number {
let result: number = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < numbers.length; i++) {
result += numbers[i];
}
return result;
}And this method sums an array of numbers using the reduce built-in method in TypeScript:
function sumNumberUsingReduce(numbers: number[]): number {
return numbers.reduce((acc, current) => acc + current, 0);
}To compare the execution time, run the test to generate the image and JSON files as follows:
const arrayLength = 1000000;
const numberArray = generateArray(arrayLength);
const benchmark1: BenchmarkFunctions<number, number> = {
functionDescription: "forLoop",
functionUnderTest: () => SumMethods.sumNumberUsingFor(numberArray),
detail: "Sum numbers using for",
};
const benchmark2: BenchmarkFunctions<number, number> = {
functionDescription: "reduce",
functionUnderTest: () => SumMethods.sumNumberUsingReduce(numberArray),
detail: "Sum numbers using reduce",
};
await benchMark<number, number>("comparison_sum_methods", [
benchmark1,
benchmark2,
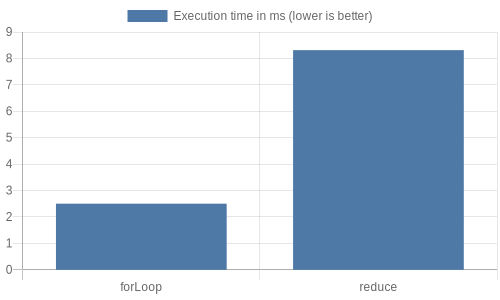
]);Chart Image Benchmark Result
If you want to generate a chart and json response you can pass the option parameter.
const options: Options = {
dirPath: "TMP",
};
const benchMarkResult = await benchMark<number, number>(
"comparison_sum_methods",
[benchmark1, benchmark2],
options
);Chart Data Result
JSON Data Result
{
"forLoop": {
"name": "forLoop",
"duration": 4.217916999012232
},
"reduce": {
"name": "reduce",
"duration": 14.500208999961615
}
}Conclusion
Based on the benchmark results, it's evident that in this specific scenario, the method sumNumberUsingFor, which utilizes a for loop, is better than sumNumberUsingReduce, which use the built-in reduce method, in terms of execution time. The for loop method completes the task in approximately 4.218 milliseconds, while the reduce method takes around 14.500 milliseconds.
However, it's important to note that the superiority of the for loop in this scenario may vary depending on different factors such as the size of the input array, the complexity of the operations within the methods, and the specific environment in which the code is executed. Therefore, while these benchmark results provide valuable insights into the performance of these methods under certain conditions, it's crucial to consider various scenarios and factors when determining the optimal approach for a given task.
Contributing
Pull requests are welcome <3. Please make sure to update tests as appropriate.