nsolid-command-gc v1.0.0
nsolid-command-gc - an N|Solid custom command to request garbage collection
This package provides an N|Solid custom command to request garbage
collection for an N|Solid process. After installing the custom command as an
npm package, you can then register the command in your app - when running
your app with the N|Solid Runtime, you'll be able to request garbage collection
with the nsolid-cli tool.
For more information on N|Solid, visit the N|Solid product page.
Installation
npm install nsolid-command-gcUsage
Once you have installed the package, you can register the gc custom command within
your apps in one of two ways:
Add
require('nsolid-command-gc')somewhere in your application codeAdd the arguments
--require nsolid-command-gcto yournsolidcommand invocation; the--requireoption is standard in modern versions of Node.js, including the N|Solid Runtime
The second option requires no changes to your code, so it obviously wins!
You will also need to use the Node.js --expose-gc option, which will add
a gc() function to the global object. This package uses this function to
request the garbage collection.
Once the gc custom command has been registered, garbage collection can be
requested for these apps with the nsolid-cli command, using the custom
subcommand with the --name gc option.
Putting this all together:
Run your app with the gc custom command registered:
nsolid --require nsolid-command-gc --expose-gc [other Node.js parameters]Request garbage collection for that process, where $AGENT_ID is the agent id
for that process:
nsolid-cli custom --id $AGENT_ID --name gcBy default, a 'full' garbage collection is requested. For a 'minor' garbage
collection, use the arguments --data minor, as in:
nsolid-cli custom --id $AGENT_ID --name gc --data minorThe result of the nsolid-cli custom command is a line of JSON, that has a
result property as a top-level property. The value of that property contains
two properties: status and type. The status property indicates whether
the garbage collection was able to be requested. The type property returns
full or minor depending on which type of garbage collection was requested.
For example:
{
"result": {
"status": "OK",
"type": "full"
},
"id": "<agent id>",
"app": "<your app name>",
"hostname": "<hostname>",
"tags": ['<process tag', ...],
"time": <time command was run>
}When the gc command is registered, and when it is invoked, the process it is
registered with will output messages to stderr via
process.emitWarning()†. You can use Node.js
command-line options and event emitters on process to customize the behavior
of this method call.
† process.emitWarning is only available in N|Solid based on Node.js LTS 6.x Boron
and newer. Argon-based N|Solid releases will simply use process.stderr.
Example Usage
A sample is shipped with this package, in the test directory, named
generate-garbage.js. This application generates and then orphans a lot of
references that need to be garbage collected. After letting it run for a few
seconds, and then using the gc custom command, you should see a drop in the
process's rss memory value. Hint: use the N|Solid Console to watch the
rss value drop in the process graphs.
Note that for this example, you will need to have the N|Solid Storage server already running, and will probably want the N|Solid Console running as well. For more information on installing and using the N|Solid Storage and Console servers, see the N|Solid documentation site.
We'll assume you've already run npm install nsolid-command-gc for your
application, and that the package is available in
node_modules/nsolid-command-gc.
First, let's set some environment variables for N|Solid:
export NSOLID_APPNAME=generate-garbage # the name of the N|Solid application
export NSOLID_COMMAND=9001 # the command port of N|Solid StorageNow run the test app with the gc custom command enabled:
nsolid --require nsolid-command-gc --expose-gc node_modules/nsolid-command-gc/test/generate-garbage.jsYou should see the following message in the output of the process, indicating the custom command has been installed:
(nsolid:$PID) nsolid-command-gc: installing nsolid custom command "gc"By monitoring this process in the N|Solid Console, you can see memory usage increasing.
To request a garbage collection, we first need to know the agent id of the
process. You can see it in the URL from the N|Solid Console when viewing the
process details - it's a 40 character hex string that is a path element of the
page's URL. Alternatively, you can get it from with the nsolid-cli ls command.
Since the nsolid-cli ls command outputs a line of JSON for every N|Solid process,
you probably want to have a nice JSON swiss army knife utility like jq handy to
produce more readable output. Using jq and grep as filters, the following
command will print out the agent id of the generate-garbage application:
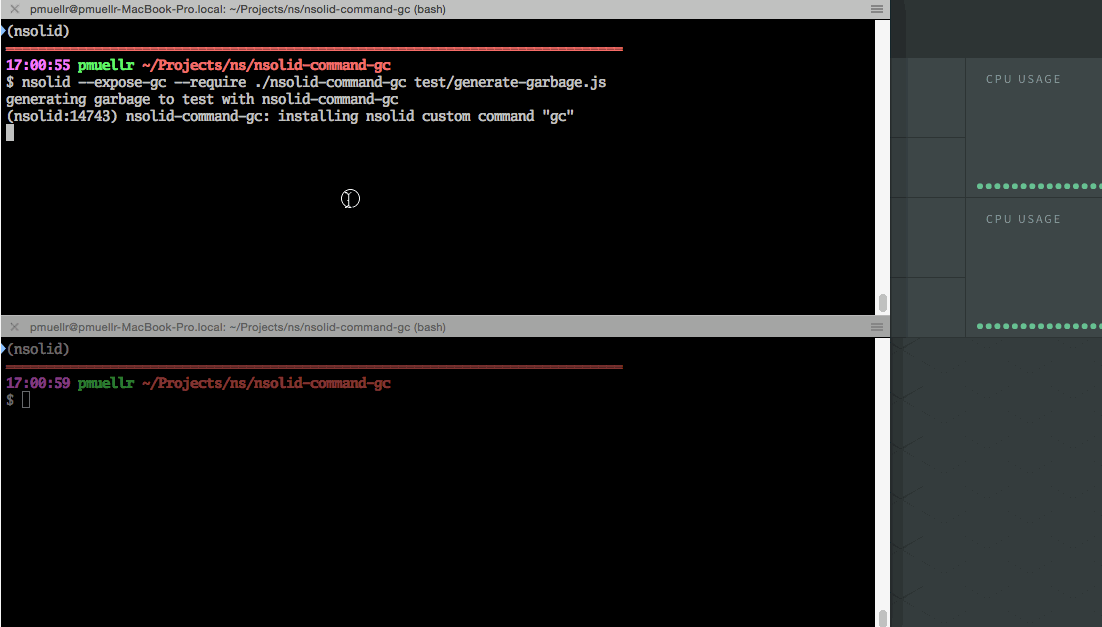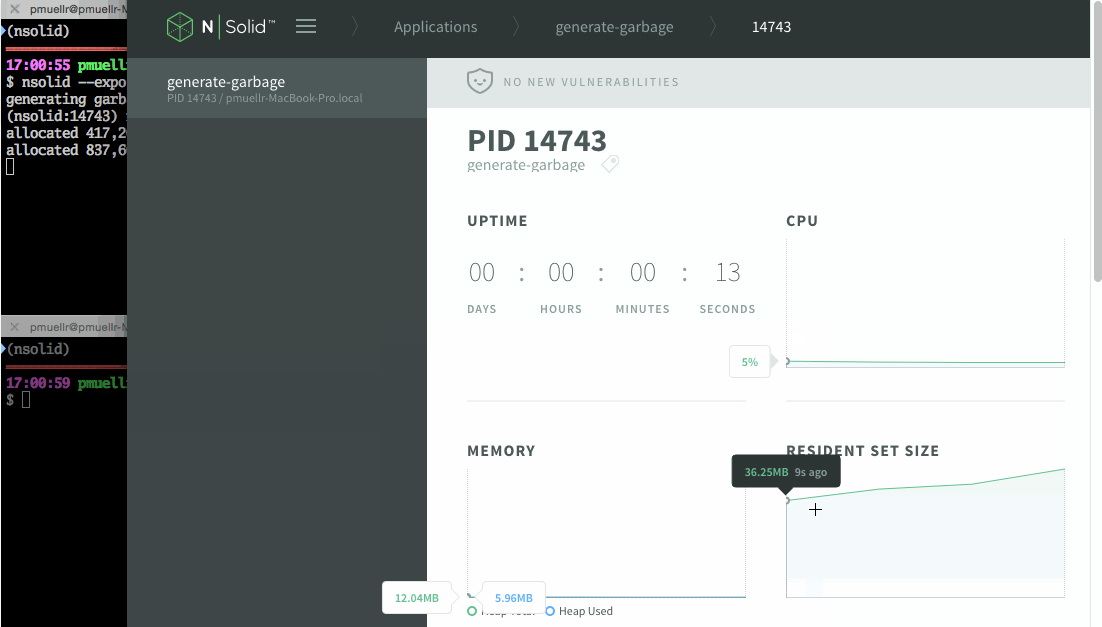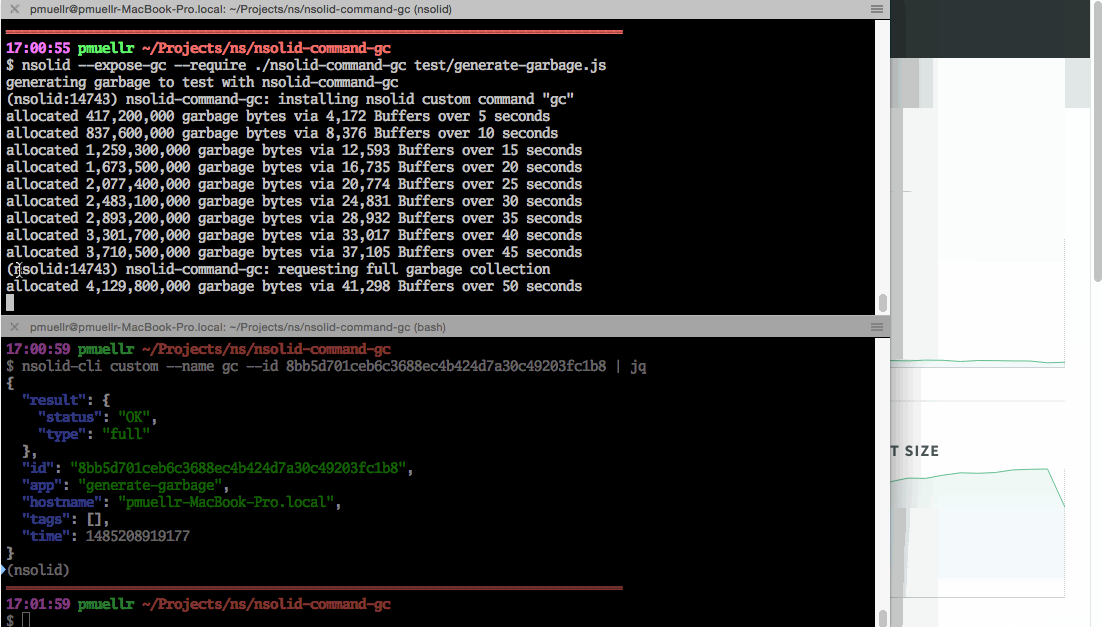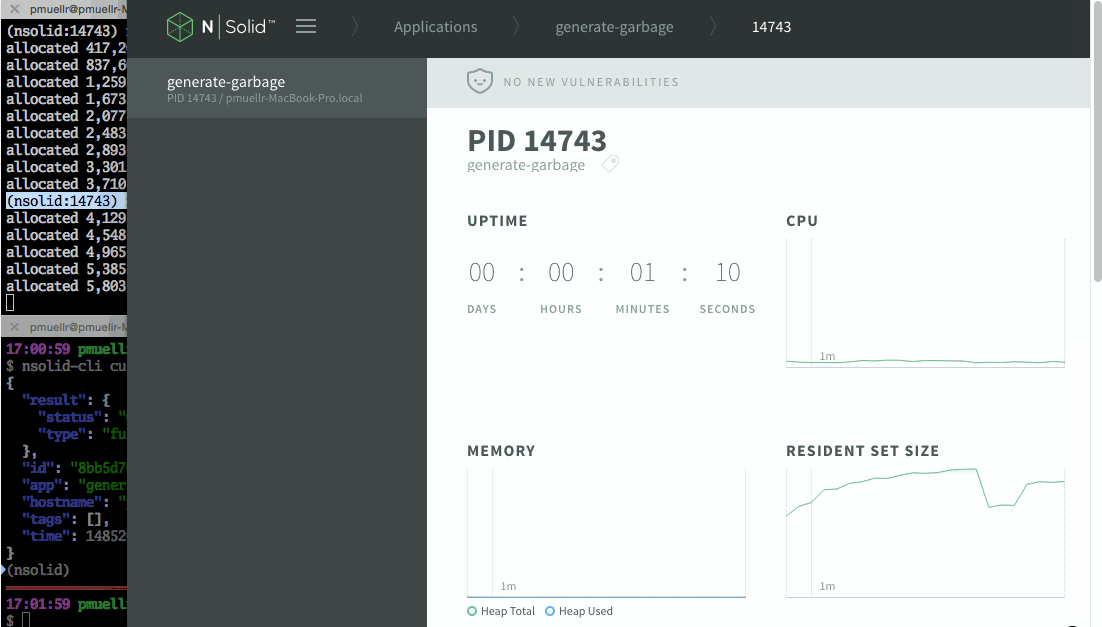
nsolid-cli ls | grep generate-garbage | jq .idNow, given the agent id, you can request garbage collection with the
command, where you would replace $AGENT_ID below with the actual agent id:
nsolid-cli custom --id $AGENT_ID --name gc | jqThe nice looking output formated from jq will look like this:
{
"result": {
"status": "OK",
"type": "full"
},
"id": "a2827de4011e0b683c101aae7db5c37e9c62c5c7",
"app": "generate-garbage",
"hostname": "your-hostname-here",
"tags": [],
"time": 1484957897813
}The process the command is sent to should also print the following message:
(nsolid:$PID) nsolid-command-gc: requesting full garbage collectionYou should notice the garbage collection visually in N|Solid Console, by a drop in memory measurements in the graphs.
Contributing
To submit a bug report, please create an issue at GitHub.
If you'd like to contribute code to this project, please read the CONTRIBUTING.md document.
Authors and Contributors
License & Copyright
nsolid-command-gc is Copyright (c) 2017 NodeSource and licensed under the MIT license. All rights not explicitly granted in the MIT license are reserved. See the included LICENSE.md file for more details.
9 years ago