perli v0.1.6
Contents
perli — introduction
perli is a multi-platform Perl REPL (read-eval-print-loop)
for interactive experimentation with Perl code, convenient documentation lookups, and quick computations.
On Unix-like platforms, perli makes use of the rlwrap utility to provide
command-line editing support, persistent command history, and tab-completion;
see the Installation chapter below.
See the examples below, concise usage information further below, or read the manual.
Examples
Startup and help
Once you enter perli, use ? for help.
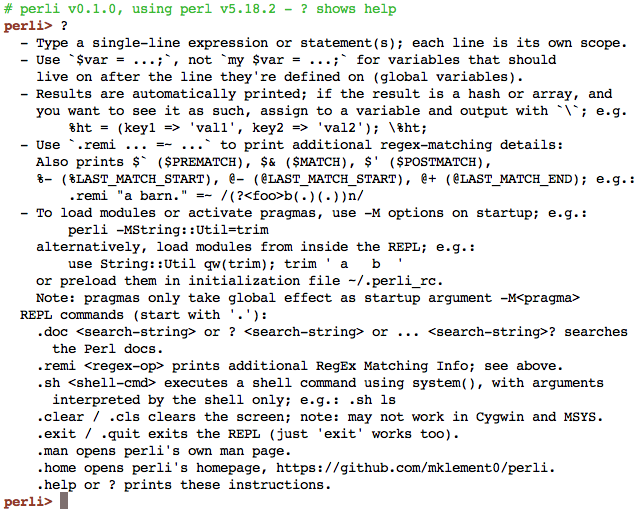
Automatic printing of results, use as a calculator
Results of expressions are automatically printed, which makes perli handy
as an interactive calculator:
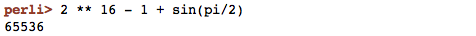
Results are printed with the Data::Dumper core Perl module, which means
that they are reusable as input.
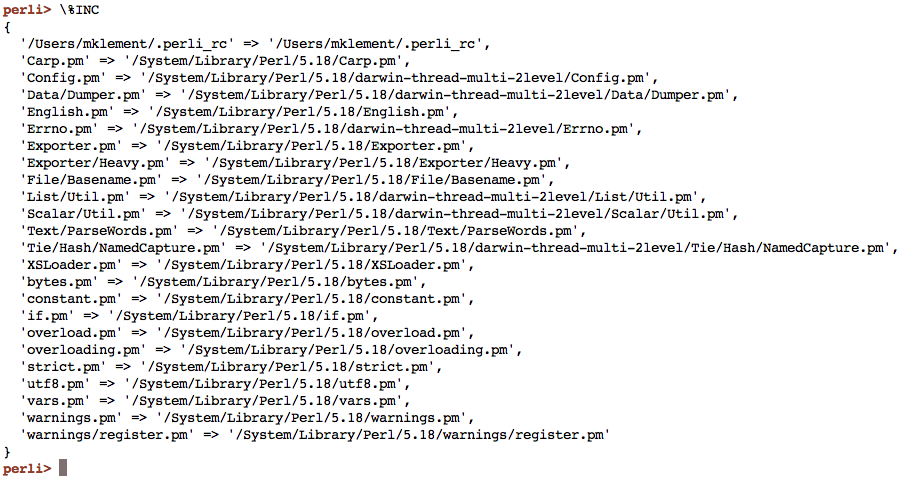
Inspecting a variable
The following example inspects the special %INC variable, which contains the
list of loaded modules. Note the first entry, which is perli's own (optional)
initialization file.
The \ prefix here is not strictly necessary, but ensures that the hashtable is
printed in prettier form.
Inspecting regular-expression matches
perli provides the .remi (for regular-expression match info)
command, which, in addition to an expression's own result, prints the values
of the special variables that Perl maintains about the most recent successful
regex match:

Looking up Perl documentation
Invoking documentation overlays the REPL temporarily, as a man page would
(not shown here).
By default, perli tries to guess the type of the element to look up, and
invokes perldoc behind the scenes accordingly.
- Prefix form
The following is the equivalent of perldoc perlrun:

- Postfix form
This form is handy for lookups while you're in the middle of typing an expression.
The following is the equivalen of perldoc -f split:

- Explicit-options form
If the "fuzzy" default lookup doesn't find anything, or shows the wrong page,
you can use the prefix form with explicit perldoc options.
The following example searches the FAQs (-q) for the term while (the default
lookup would have looked for the keyword).

Installation
Supported platforms and prerequisites
perli runs on Linux, macOS, Windows, and - as @matheusfillipe assures me - on Android, with Perl v5.6.2 or higher installed.
Using the manual installation process detailed below, perli may work on other Unix-like platforms too.
On Unix-like platforms, perli makes use of the rlwrap utility, if present,
to provide command-line editing support, persistent command history,
and simple tab completion.
On Windows, rlwrap is not available, unfortunately, but you do get
in-session history and basic command-line editing out of the box (but no
tab-completion).
You can install rlwrap as follows:
Debian-based Linux distros such as Ubuntu:
sudo apt-get install rlwrapFedora:
sudo yum install rlwrapmacOS, via Homebrew:
brew install rlwrapUnix-emulation environments for Windows:
Cygwin (Windows):
Re-run Cygwin's
setup*.exeand installUtils>rlwrap and Base>libreadline*MSYS / MinGW / Git Bash (Windows):
Sadly,
rlwrapis not offered. The next best thing is to use a native Windows Perl version, with which you get at least basic command-line editing and in-session history: Deactivate the Unix Perl withmv /bin/perl /bin/perl.inactiveand install Strawberry Perl
All others: see
rlwrap's homepage
Installation from the npm registry
Note: Even if you don't use Node.js, its package manager, npm, works across platforms and is easy to install; try curl -L http://git.io/n-install | bash
With Node.js or io.js installed, install the package as follows:
[sudo] npm install perli -gNote:
- Whether you need
sudodepends on how you installed Node.js / io.js and whether you've changed permissions later; if you get anEACCESerror, try again withsudo. - The
-gensures global installation and is needed to putperliin your system's$PATH.
Manual installation
Unix-like platforms
- Download the CLI as
perli. - Make it executable with
chmod +x perli. - Move it or symlink it to a folder in your
$PATH, such as/usr/local/bin(macOS) or/usr/bin(Linux).
Windows
- Download the CLI as
perli.pl. - Either move
perli.plitself into a folder in your%PATH%, or write a wrapper batch file namedperli.cmdthat invokes it.
Usage
Find brief usage information below; for complete documentation, once installed, run man perli (perli --man on Windows and if installed manually), or read the manual online.
$ perli --help
A simple, convenient Perl REPL for interactive experimentation.
perli [<options>]
--norc skips loading of the initialization file
The following Perl options are also supported:
-M<name> (repeatable) load a module and import its defaults,
or activate a pragma (-M-<name> deactivates)
-m<module> (repeatable) load a module without importing
-I<dir> (repeatable) prepend <dir> to module search path (@INC)
Initialization file is ~/.perli_rc
Standard options: --help, --man, --version, --homeLicense
Copyright (c) 2015-2021 Michael Klement mklement0@gmail.com (http://same2u.net), released under the MIT license.
Acknowledgements
This project gratefully depends on the following open-source components, according to the terms of their respective licenses.
npm dependencies below have optional suffixes denoting the type of dependency; the absence of a suffix denotes a required run-time dependency: (D) denotes a development-time-only dependency, (O) an optional dependency, and (P) a peer dependency.
npm dependencies
Changelog
Versioning complies with semantic versioning (semver).
v0.1.6 (2021-04-30):
- enhancement Package is now installable on Android too, where @matheusfillipe assures me that
perliworks too (tip of the hat for the PR).
- enhancement Package is now installable on Android too, where @matheusfillipe assures me that
v0.1.5 (2021-02-23):
- fix Compatibility with
rlwrapversion 0.45, which in combination with Perl'sexecfunction caused a breaking change.
- fix Compatibility with
v0.1.4 (2019-02-11):
- fix Ammends v0.1.3 to auto-flush stderr too.
v0.1.3 (2019-02-11):
- enhancement Auto-flushing of stdout activated to support invocation from editors such as neovim - fixes #4
v0.1.2 (2015-09-30):
- fix Fixed inability to define global variables (without
my) in older Perl versions (e.g., v5.14).
- fix Fixed inability to define global variables (without
v0.1.1 (2015-09-24):
- Project-status corrected in read-me.
v0.1.0 (2015-09-24):
- Initial release.

