playwright-structure-ts v1.0.8
Playwright TS Boiler Plate
A brief description of what this project does and who it's for
Quick Start
To create a project, simply run:
npx playwright-structure-ts <project-name>Or
npm init playwright-structure-ts <project-name>Installation
Clone the repo:
git clone --depth 1 https://github.com/erenkorkmazemre/playwright-structure-ts
cd playwright-structure-tsInstall the dependencies:
npm installSet the environment variables:
cp .env.example .env
# open .env and modify the environment variables (Talk to Eren Emre Korkmaz for local tests(you need franchise username and password) !!!!!!!)Technologies
- Node.js (10.16.3)
- Faker-js (7.6.0)
- Playwright/test (1.35.1)
- Eslint (8.44.0)
- Dotenv (16.0.3)
- Prettier (2.8.8)
- Docker
- Jenkins
- Winston (3.8.2)
Structure
project/ # Source code.
├── tests/ # This folder contains your tests.
│ ├── e2e/ # This folder contains E2E (end-to-end) tests. Tests that simulate user interactions using browser automation tools are placed here.
│ │ ├── login.spec.ts
│ │ ├── home.spec.ts
│ │ └── ...
│ ├── integration/ # This folder contains integration tests. It is used to test the interaction between components, services, and other pieces of source code.
│ │ ├── footer.spec.ts
│ │ ├── header.spec.ts
│ │ └── ...
│ ├── unit/ #
│ │ ├── utils.spec.ts
│ │ ├── services.spec.ts
│ │ └── ...
│ ├── types/ #
│ │ ├── utils.spec.ts
│ │ ├── services.spec.ts
│ │ └── ...
│ └── ...
├── actions/ # This directory contains page object files that define the elements and actions on specific pages of your application. Each page object file represents a different page or a component of your application.
│ ├── pages/
│ │ ├── LoginPage.ts
│ │ ├── HomePage.ts
│ │ └── ...
│ └── ...
├── locators/ # This directory contains locator files that define the selectors or locators for specific elements on the pages of your application. Each locator file corresponds to a particular page or component and contains variables or functions that return the selectors for elements on that page.
│ ├── loginLocators.ts
│ ├── homeLocators.ts
│ └── ...
├── utils/ # This directory houses utility files, such as helper functions, configuration files, or custom modules that provide commonly used functionalities across your tests.
│ ├── endpoints/ #
│ │ ├── asdasd.ts
│ │ └── ...
│ ├── urls/ #
│ │ ├── asdasd.ts
│ │ └── ...
│ ├── helpers.ts #
│ ├── configurations.ts #
│ ├── logger.ts #
│ └── ...
├── data/ #
│ ├── mocks/ #
│ │ ├── dynamic/ #
│ │ │ ├── endpoint-1.ts
│ │ │ ├── endpoint-2.ts
│ │ │ └── ...
│ │ ├── static/ #
│ │ │ ├── endpoint-1.json
│ │ │ ├── endpoint-2.json
│ │ │ └── ...
│ │ └── ...
│ └── ...
├── playwright-report/ #
│ ├── index.html #
│ └── ...
├── test-results/ #
│ ├── index.html #
│ └── ...
├── scripts/ #
│ ├── cron-slack.sh #
│ ├── trigger-slack.sh #
│ ├── trigger-jenkins.sh #
│ └── ...
├── playwright.config.ts #
├── .env #
├── .env.example #
├── bitbucket-pipelines.yml #
├── Jenkinsfile #
├── package.json #
├── tsconfig.json #
└── README.md #Deployment Process
The deployment process also includes the pipeline processes involved in the project.
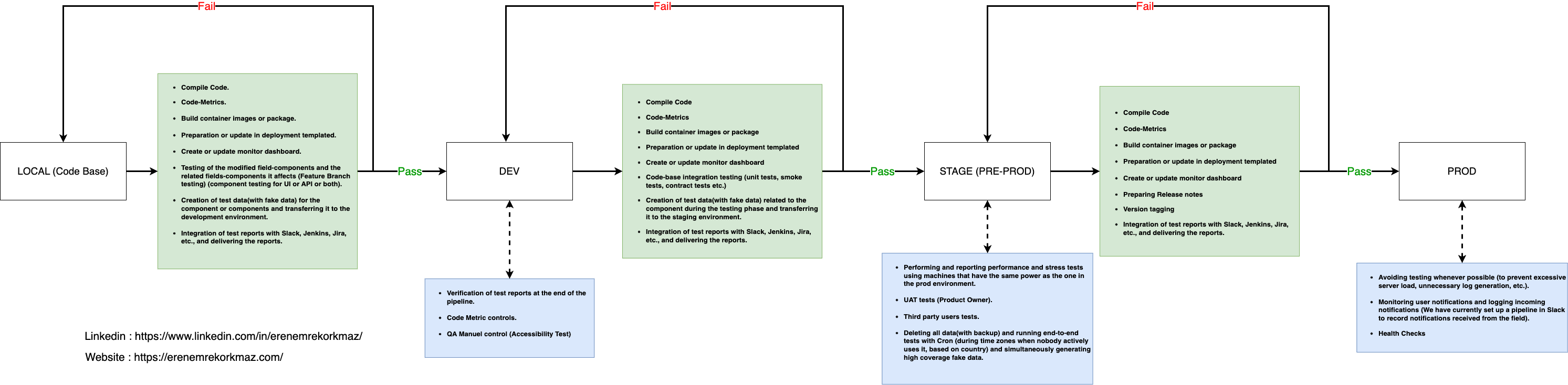
The steps when the pipeline is triggered
LOCAL(CODE-BASE) => DEV
- Compile Code.
- Code-Metrics.
- Build container images or package.
- Preparation or update in deployment templated.
- Create or update monitor dashboard.
- Testing of the modified field-components and the related fields-components it affects (Feature Branch testing) (component testing for UI or API or both).
- Creation of test data(with fake data) for the component or components and transferring it to the development environment.
- Integration of test reports with Slack, Jenkins, Jira, etc., and delivering the reports.DEV => STAGE(PRE-PROD)
- Compile Code
- Code-Metrics
- Build container images or package
- Preparation or update in deployment templated
- Create or update monitor dashboard
- Code-base integration testing (unit tests, smoke tests, contract tests etc.)
- Creation of test data(with fake data) related to the component during the testing phase and transferring it to the staging environment.
- Integration of test reports with Slack, Jenkins, Jira, etc., and delivering the reports.STAGE(PRE-PROD) => PROD
- Compile Code
- Code-Metrics
- Build container images or package
- Preparation or update in deployment templated
- Create or update monitor dashboard
- Preparing Release notesVersion taggingIntegration of test reports with Slack, Jenkins, Jira, etc., and delivering the reports.The steps in the environments
In DEV env
- Verification of test reports at the end of the pipeline.
- Code Metric controls.
- QA Manuel control (Accessibility Test)In STAGE(PRE-PROD) env
- Performing and reporting performance and stress tests using machines that have the same power as the one in the prod environment.
- UAT tests (Product Owner).
- Third party users tests.
- Deleting all data(with backup) and running end-to-end tests with Cron (during time zones when nobody actively uses it, based on country) and simultaneously generating high coverage fake data.In PROD env
- Avoiding testing whenever possible (to prevent excessive server load, unnecessary log generation, etc.).
- Monitoring user notifications and logging incoming notifications (We have currently set up a pipeline in Slack to record notifications received from the field).
- vHealth ChecksLogger
A winston logger with custom format is used. This logger is registered into the dependency injection container.
Import the logger from utils/logger.ts. It is using the Winston logging library.
Logging should be done according to the following severity levels (ascending order from most important to least important):
import logger from '@utils/logger';
logger.error('message'); // level 0
logger.warn('message'); // level 1
logger.info('message'); // level 2
logger.http('message'); // level 3
logger.verbose('message'); // level 4
logger.debug('message'); // level 5Example logging:
logger.info('stepDefinition', { additional: 'info' });Reports
Testing
Tags, deployment process etc
- For Local Test
docker-compose up docker-compose -f docker-compose.yml up docker-compose -f docker-compose.dev.yml up docker-compose -f docker-compose.stage.yml up
- For Local Parallel Test
- For Remote Docker Parallel Test
Linting
Linting is done using ESLint and Prettier.
To modify the ESLint configuration, update the .eslintrc.json file. To modify the Prettier configuration, update the .prettierrc.json file.
To prevent a certain file or directory from being linted, add it to .eslintignore and .prettierignore.
To maintain a consistent coding style across different IDEs, the project contains .editorconfig


