prismaql v0.1.5
PrismaQL Core - Advanced Prisma Schema Editing Library
Introduction
PrismaQL Core provides a powerful SQL-like DSL for safely and programmatically editing Prisma schema files. It allows you to manage models, fields, relations, enums, database connections, and generators while preserving schema integrity via AST-based validation, change tracking, and backup mechanisms. This ensures a flexible and robust development workflow.
Designed as a standalone library or to be used alongside the PrismaQL CLI, PrismaQL Core offers:
- Declarative Command Syntax – Intuitive and human-readable commands like
GET MODELS,ADD FIELD, and more. - Query & Mutation Separation – Clear distinction between read-only operations (
GET,PRINT,VALIDATE) and modifying ones (ADD,DELETE,UPDATE). - Configurable Workflow – Easily extend and integrate custom handlers for queries and mutations.
- Safe & Reversible Edits – Built-in validation with automatic backups to ensure data integrity.
- Flexible Relation Management – Supports 1:1, 1:M, and M:N relationships, including pivot table-based relations. Allows both direct and indirect (foreign-key-only) associations, with the ability to choose the FK holder side for precise schema control.
How It Works
- Parsing DSL – Raw text commands (e.g.
GET MODEL User;) go through the PrismaQlDslParser, producing a structured object. - Chained Commands – You can chain multiple commands in a single line, separated by semicolons, and they will be executed sequentially.
- Validation & Execution – Queries simply inspect the schema; mutations modify it, ensuring AST-level integrity.
- Backup & Save – Each mutation can undergo a dry run, then save changes. Old versions are stored in
.prisma/backups. - Extensible Handlers – You can register query or mutation handlers to shape how commands are processed.
Supported Commands
PrismaQL CLI supports the same Query and Mutation commands as the core library:
1. Query Commands
GET MODELS– List all models with highlighting.GET MODEL <name>– Show details for a specific model (fields, relations, etc.).GET ENUM_RELATIONS <enum>– Show references to a specific enum across models.GET FIELDS <model>– List fields for a model.GET FIELDS <field,field2> IN <model>– Show specific fields.GET RELATIONS <model,model2> (depth?=1)– Display relations; optionally set a depth.GET ENUMS (raw?)/GET ENUMS <enum, ...>– Show one or more enums.GET MODELS_LIST– Display a sorted list of all models.PRINT– Print the entire schema in color.GET DB– Show the current database connection.GET GENERATORS– List all generators.VALIDATE– Validate the schema.
2. Mutation Commands
ADD MODEL <name> ({...})– Create a new model with a Prisma block.ADD FIELD <name> TO <model> ({String})– Add a field to a model.ADD RELATION <modelA> AND <modelB> (type=1:M, ...)– Create a relation between two models.ADD ENUM <name> ({A|B|C})– Create a new enum.DELETE MODEL <name>– Delete a model.DELETE FIELD <name> IN <model>– Remove a field.DELETE RELATION <modelA>, <modelB> (relationName=...)– Remove a relation.DELETE ENUM <name>– Delete an enum.UPDATE FIELD <name> IN <model> ({...})– Recreate a field (caution).UPDATE ENUM <name> ({A|B}) (replace=?)– Append or replace enum values.UPDATE DB (url='...', provider='...')– Update the database connection.UPDATE GENERATOR <name> ({...}) (provider='...', output='...')– Update a generator.ADD GENERATOR <name> ({...})– Add a new generator.DELETE GENERATOR <name>– Remove a generator.
📸 Preview
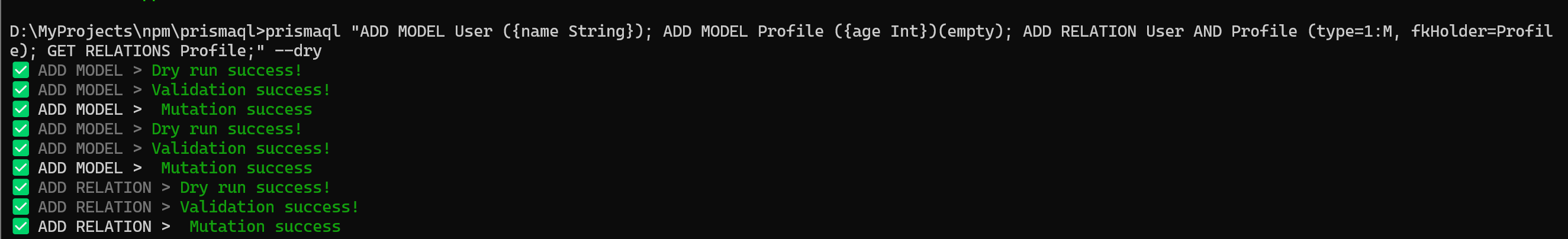
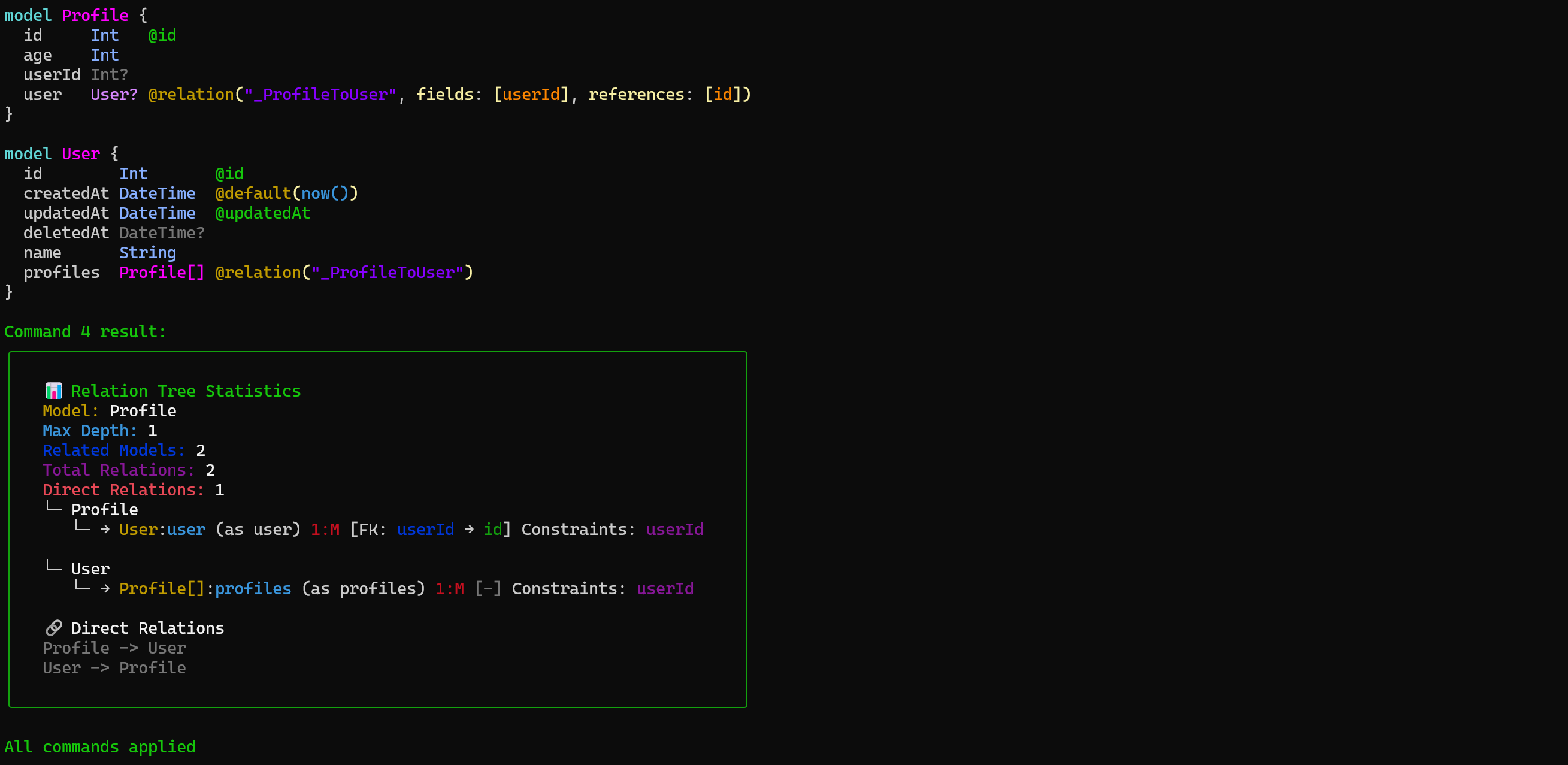
Flow of Execution
- Parse Command –
PrismaQlDslParserconverts your raw command string into a structuredPrismaQLParsedDSLobject. - Send to Provider –
PrismaQlProviderreceives the parsed command. For example:provider.apply(parsedCommand); - Handlers – The provider dispatches the command to the correct handler (
QueryHandlerorMutationHandler) based ontype. - Validation & Dry Run – Each mutation can be tested in a
dryRunmode before final merge. - Backup – If the command is valid, the old schema is backed up under
.prisma/backups. - Rebase – The schema loader can rebase the in-memory state to reflect the final updated schema.
Extending PrismaQL
Custom Parsers
You can build your own DSL commands:
import {
PrismaQlDslParser,
BasePrismaQlDSLAction,
BasePrismaQLDSLCommand,
PrismaQlDSLArgsProcessor,
} from "prismaql";
// Extend base actions with a custom action
type CustomAction = BasePrismaQlDSLAction | "SAY";
// Extend base commands with a custom command
type CustomCommand = BasePrismaQLDSLCommand | "HI";
// Provide argument processors
const customArgsProcessors: Record<
CustomAction,
{
default: PrismaQlDSLArgsProcessor<any, any>;
} & Partial<Record<CustomCommand, PrismaQlDSLArgsProcessor<any, any>>>
> = {
// Use existing base processors here
...basePrismaQlAgsProcessor,
// Add custom action
SAY: {
default: (parsedArgs) => parsedArgs,
HI: (parsedArgs, rawArgs) => {
return {
models: rawArgs ? rawArgs.split(",").map((m) => m.trim()) : [],
};
},
},
};
// Create a custom parser
const customParser = new PrismaQlDslParser<CustomAction, CustomCommand>(
customArgsProcessors
);
// Register custom command
customParser.registerCommand("SAY", "HI", "query");
console.log(customParser.parseCommand("SAY HI model1, model2;"));Custom Handlers
Register your own logic for queries or mutations:
import {
PrismaQlMutationHandlerRegistry,
PrismaQlQueryHandlerRegistry,
} from "prismaql";
export const mutationsHandler = new PrismaQlMutationHandlerRegistry();
mutationsHandler.register("ADD", "MODEL", addModel);
export const queryHandler = new PrismaQlQueryHandlerRegistry();
queryHandler.register("GET", "MODEL", getModel);The Provider
Once you have parsers and handlers, set up a provider:
import {
PrismaQlProvider,
PrismaQlSchemaLoader,
PrismaQlRelationCollector,
} from "prismaql";
const manager = new PrismaQlSchemaLoader(new PrismaQlRelationCollector());
await manager.loadFromFile("./prisma/schema.prisma");
const provider = new PrismaQlProvider({
queryHandler: queryHandler,
mutationHandler: mutationsHandler,
loader: manager,
});
// Apply commands
provider.multiApply(`
ADD MODEL User ({ id Int @id, name String });
ADD FIELD email TO User ({String @unique});
`);This approach works both programmatically and through the CLI, making dynamic schema changes easy.
Example Usage
Using PrismaQL in Code
import { prismaQlParser, PrismaQlProvider } from "prismaql";
const command =
"ADD MODEL User ({ id Int @id @default(autoincrement()), name String });";
const parsedCommand = prismaQlParser.parseCommand(command);
const provider = new PrismaQlProvider({
queryHandler: myQueryHandler,
mutationHandler: myMutationHandler,
loader: mySchemaLoader,
});
provider.apply(parsedCommand);Using PrismaQL CLI
Check out the PrismaQL CLI:
# Add a new model (mutation)
prismaql "ADD MODEL TempData ({ name String });"
# Query schema
prismaql "GET MODELS"
# Add a field programmatically
prismaql "ADD FIELD email TO User ({String});"
# Delete an entire model
prismaql "DELETE MODEL TempData;"Current Status
If you're interested in contributing, reporting issues, or suggesting features, check out the GitHub repository.
License
PrismaQL Core is licensed under the MIT License. © 2025 Artyom Gorlovetskiy.



