0.0.22 • Published 5 years ago
quickgraph v0.0.22
QuickGraph
A commandline tool to quickly make graphs from arbitrary text files.
Released under the Boost Software License (Version 1.0).
Note: I wouldn't use this just yet. It is probably littered with bugs and certainly incomplete ideas.
Syntax
Syntax: qg [options] logfile [... logfile]
Options:
-h,--help This help output
-v,--verbose Verbose mode
-o,--output FILENAME Output filename (default: quickgraph.html)
-a,--alias ALIAS Use named alias from your home directory's .quickgraphrc
-g,--graph Begin a new graph. This is not necessary if you're only making one
-t,--title TITLE Sets the title of the current graph
-x REGEX Matches a new X axis value, parsed by -e, formatted with -f or -F
-y REGEX Matches a new Y axis value, parsed by -e, formatted with -f or -F
-c,--color COLOR Sets the color for the current rule (only makes sense on Y axis rules)
-l,--legend LEGEND Sets the legend for the current axis
-e,--eval CODE Sets the evaluator for the axis regex's output. See examples
-f,--format CODE Sets the code used to format an x axis value
--consolidate FUNC Sets the consolidation function for the current axis (sum, count, avg, min, max, last)
--width Sets the graph's width. Defaults to use the whole width of the browser.
--height Sets the graph's height. Defaults to 480.
-A RESTOFLINE Create a new alias (like in quickgraphrc) statement; only works in a response fileExample 1
Data (example1.txt):
2015-12-16 5
2015-12-17 6
2015-12-18 7
2015-12-19 6
2015-12-20 5
2015-12-21 6
2015-12-22 8
2015-12-23 4
2015-12-24 3Commandline:
qg example1.txt -x "^[-\d]+" -a date -y "\d+$"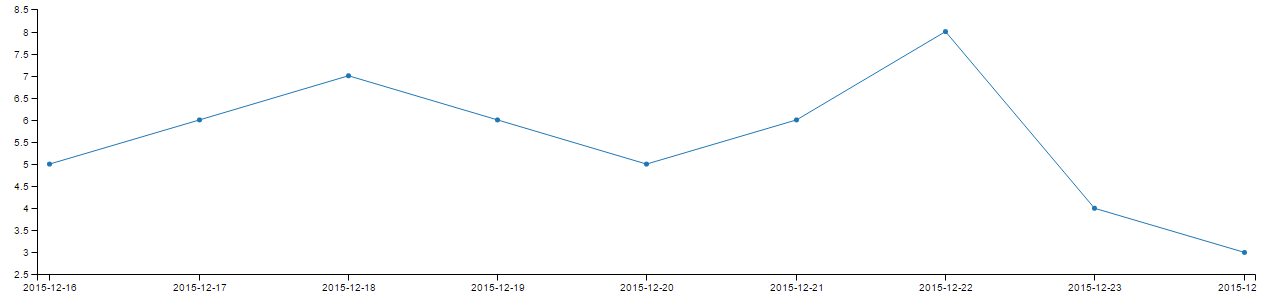
Example 2
Data: (example2.txt)
00:01:00 memory usage 21.3mb
00:01:03 memory usage 22.0mb
00:01:05 memory usage 21.3mb
00:01:09 memory usage 23.1mb
00:01:35 memory usage 24mb
00:01:45 memory usage 25mb
00:01:47 memory usage 27.3mb
00:01:49 memory usage 27.9mb
00:01:50 memory usage 28.3mbCommandline:
qg example2.txt -x "(?<H>\d\d):(?<M>\d\d):(?<S>\d\d)" -e "@f.H*3600+@f.M*60+@f.S" -y "memory usage ([\d\.]+)mb" -l "Memory Usage"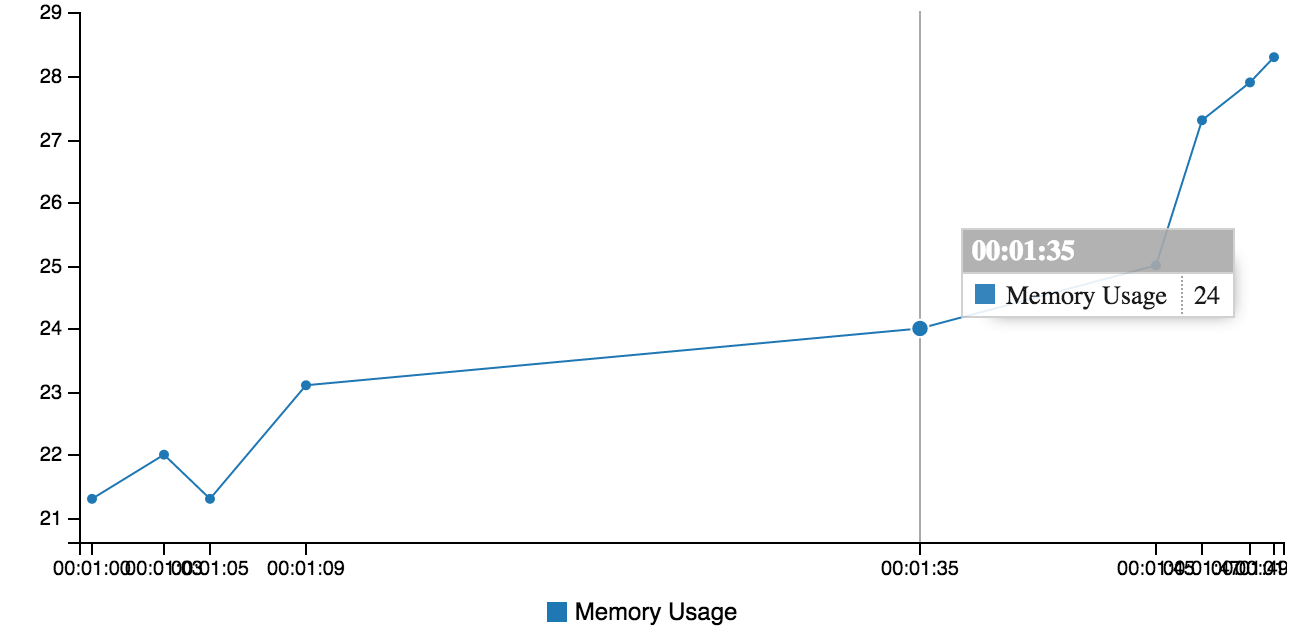
0.0.22
5 years ago
0.0.20
5 years ago
0.0.21
5 years ago
0.0.19
5 years ago
0.0.18
7 years ago
0.0.17
8 years ago
0.0.16
9 years ago
0.0.15
9 years ago
0.0.14
10 years ago
0.0.13
10 years ago
0.0.12
10 years ago
0.0.11
10 years ago
0.0.10
10 years ago
0.0.9
10 years ago
0.0.8
10 years ago
0.0.7
10 years ago
0.0.6
10 years ago
0.0.5
10 years ago
0.0.4
10 years ago
0.0.3
10 years ago
0.0.2
10 years ago
0.0.1
10 years ago