react-beautiful-dnd-test v6.0.2-beta2
react-beautiful-dnd
Beautiful, accessible drag and drop for lists with React.js

Examples 🎉
See how beautiful it is for yourself!
Viewing on a desktop
Viewing on a mobile or tablet
- Simple list
- Board - best viewed in landscape
We provide different links for touch devices as currently storybook does not have a good mobile menu experience more information
Basic usage examples
We have created some basic examples on codesandbox for you to play with directly:
Coming soon: a getting starting guide!
Upgrading
We have created upgrade instructions in our release notes to help you upgrade to the latest version!
Core characteristics
- Beautiful, natural movement of items
- Clean and powerful api which is simple to get started with
- Plays extremely well with standard browser interactions
- Unopinionated styling
- No creation of additional wrapper dom nodes - flexbox and focus management friendly!
- Accessible
Currently supported feature set
- Vertical lists ↕
- Horizontal lists ↔
- Movement between lists (▤ ↔ ▤)
- Mouse 🐭, keyboard 🎹 and touch 👉📱 (mobile, tablet and so on) support
- Auto scrolling - automatically scroll containers and the window as required during a drag (even with keyboard 🔥)
- Multi drag support
- Incredible screen reader support - we provide an amazing experience for english screen readers out of the box 📦. We also provide complete customisation control and internationalisation support for those who need it 💖
- Conditional dragging and dropping
- Multiple independent lists on the one page
- Flexible item sizes - the draggable items can have different heights (vertical lists) or widths (horizontal lists)
- Custom drag handles - you can drag a whole item by just a part of it
- A
Droppablelist can be a scroll container (without a scrollable parent) or be the child of a scroll container (that also does not have a scrollable parent) - Independent nested lists - a list can be a child of another list, but you cannot drag items from the parent list into a child list
- Server side rendering compatible
- Plays well with nested interactive elements by default
Lots more coming soon
You can check out all the features that will be landing soon on our issue page.
Not for everyone
There are a lot of libraries out there that allow for drag and drop interactions within React. Most notable of these is the amazing react-dnd. It does an incredible job at providing a great set of drag and drop primitives which work especially well with the wildly inconsistent html5 drag and drop feature. react-beautiful-dnd is a higher level abstraction specifically built for vertical and horizontal lists. Within that subset of functionality react-beautiful-dnd offers a powerful, natural and beautiful drag and drop experience. However, it does not provide the breadth of functionality offered by react-dnd. So this library might not be for you depending on what your use case is.
react-beautiful-dnd uses position: fixed to position the dragging element. In some layouts, this might break how the element is rendered. One example is a <table>-based layout which will lose column widths for dragged <tr>s. Follow #103 for updates on support for this use case.
Driving philosophy: physicality
The core design idea of react-beautiful-dnd is physicality: we want users to feel like they are moving physical objects around
Application 1: no instant movement
It is a fairly standard drag and drop pattern for things to disappear and reappear in response to the users drag. For a more natural drag we animate the movement of items as they need to move out of the way while dragging to more clearly show a drags effect. We also animate the drop of an item so that it animates into its new home position. At no point is an item instantly moved anywhere — regardless of whether it is dragging or not.
Application 2: knowing when to move
It is quite common for drag and drop interactions to be based on the position that user started the drag from.
In react-beautiful-dnd a dragging items impact is based on its centre of gravity — regardless of where a user grabs an item from. A dragging items impact follows similar rules to a set of scales ⚖️. Here are some rules that are followed to allow for a natural drag experience even with items of flexible height:
- A list is dragged over when the centre position of a dragging item goes over one of the boundaries of the list
- A resting drag item will move out of the way of a dragging item when the centre position of the dragging item goes over the edge of the resting item. Put another way: once the centre position of an item (A) goes over the edge of another item (B), B moves out of the way.
Application 3: no drop shadows
Drop shadows are useful in an environment where items and their destinations snap around. However, with react-beautiful-dnd it should be obvious where things will be dropping based on the movement of items. This might be changed in the future - but the experiment is to see how far we can get without any of these affordances.
Application 4: maximise interactivity
react-beautiful-dnd works really hard to avoid as many periods of non-interactivity as possible. The user should feel like they are in control of the interface and not waiting for an animation to finish before they can continue to interact with the interface. However, there is a balance that needs to be made between correctness and power in order to make everybody's lives more sane. Here are the only situations where some things are not interactive:
- From when a user cancels a drag to when the drop animation completes. On cancel there are lots of things moving back to where they should be. If you grab an item in a location that is not its true home then the following drag will be incorrect.
- Starting a drag on an item that is animating its own drop. For simplicity this is the case - it is actually quite hard to grab something while it is animating home. It could be coded around - but it seems like an edge case that would add a lot of complexity.
Keep in mind that these periods of inactivity may not always exist.
Application 5: no drag axis locking
For now, the library does not support drag axis locking (aka drag rails). This is where the user is restricted to only dragging along one axis. The current thinking is this breaks the physical metaphor we are going for and sends a message to the user that they are interacting with a piece of software rather than moving physical objects around. It is possible to ensure that a user can only drop in a single list by using props type and isDropDisabled. You can also do some visual treatment to the list onDragStart to show the user that this is the only place they can interact with.
Application 6: natural cross list movement
Rather than using an index based approach for keyboard movement between lists, react-beautiful-dnd performs cross list movement based on inertia, gravity and collisions. You can find out more about how this works by reading the blog "Natural keyboard movement between lists".
Carefully designed animations
With things moving a lot it would be easy for the user to become distracted by the animations or for them to get in the way. We have tweaked the various animations to ensure the right balance of guidance, performance and interactivity.
Dropping
When you drop a dragging item its movement is based on physics (thanks react-motion). This results in the drop feeling more weighted and physical.
Moving out of the way
Items that are moving out of the way of a dragging item do so with a CSS transition rather than physics. This is to maximise performance by allowing the GPU to handle the movement. The CSS animation curve has been designed to communicate getting out of the way.
How it is composed:
- A warm up period to mimic a natural response time
- A small phase to quickly move out of the way
- A long tail so that people can read any text that is being animated in the second half of the animation
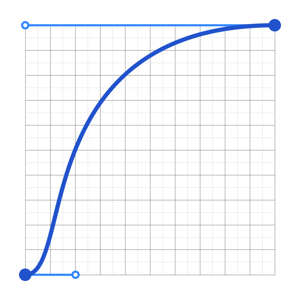
animation curve used when moving out of the way
Caring about the interaction details
Focus management
react-beautiful-dnd does not create any wrapper elements. This means that it will not impact the usual tab flow of a document. For example, if you are wrapping an anchor tag then the user will tab to the anchor directly and not an element surrounding the anchor. Whatever element you wrap will be given a tab-index to ensure that users can tab to the element to perform keyboard dragging.
Auto scrolling
When a user drags a Draggable near the edge of a container we automatically scroll the container as we are able to in order make room for the Draggable.
A container is either a
Droppablethat is scrollable or has a scroll parent - or thewindow.
| Mouse and touch | Keyboard |
|---|---|
 | 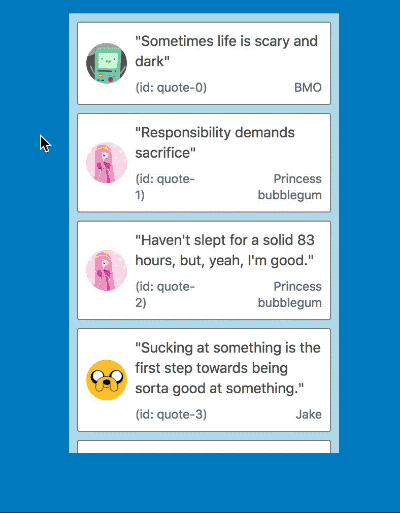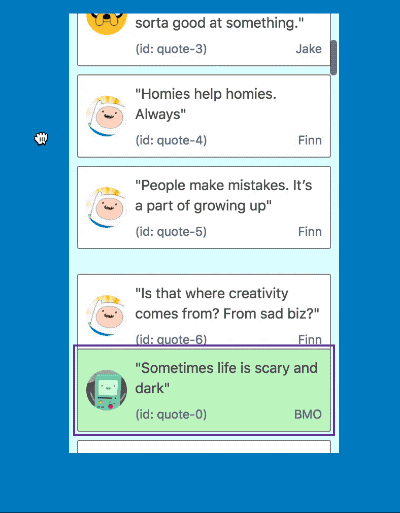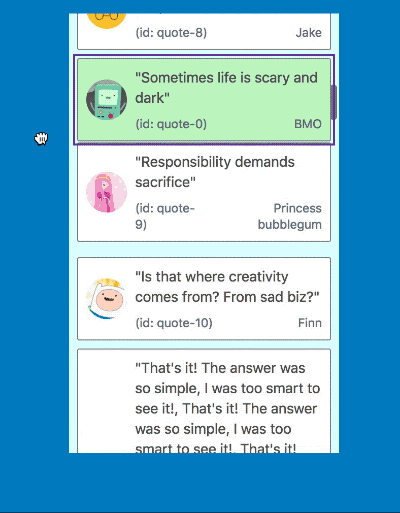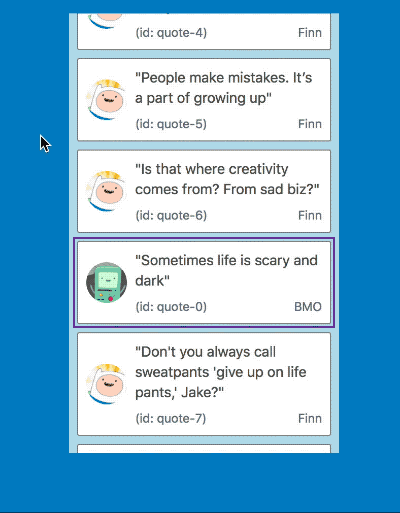 |
It also works in multi list configurations with all input types
| Mouse and touch | Keyboard |
|---|---|
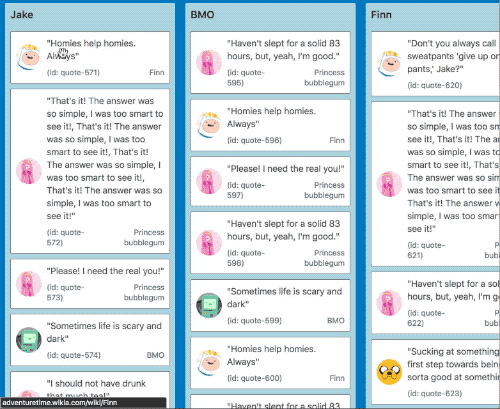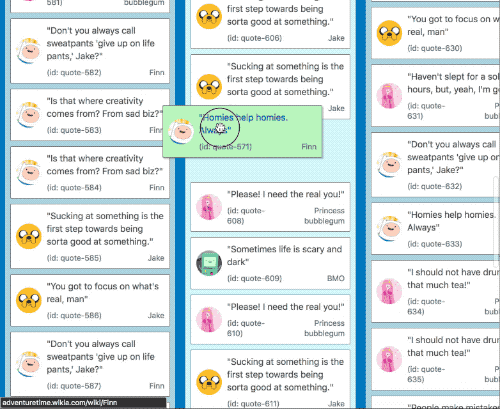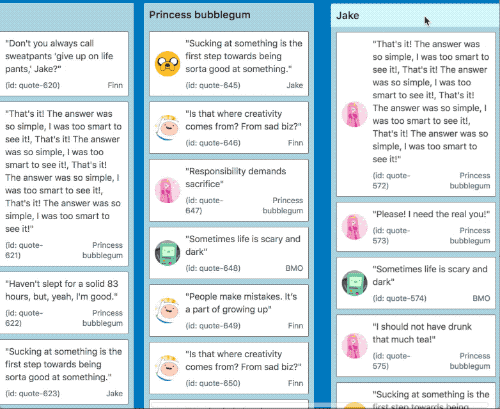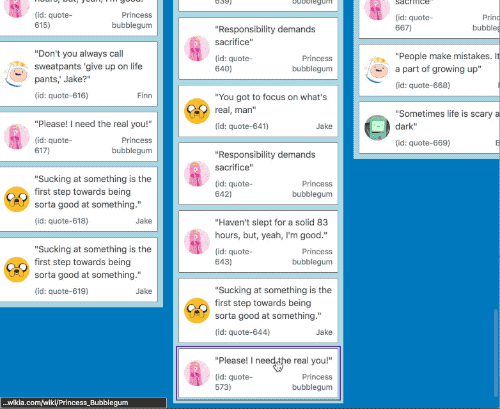 | 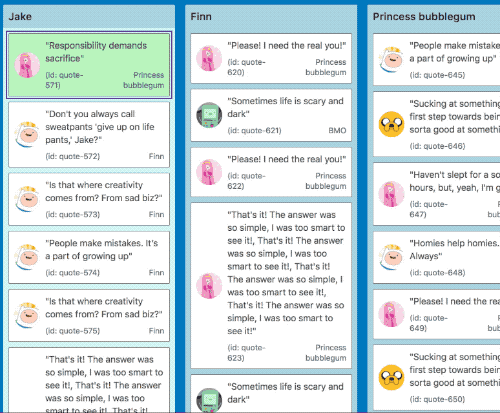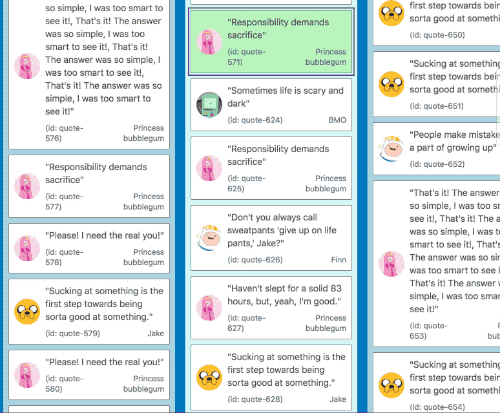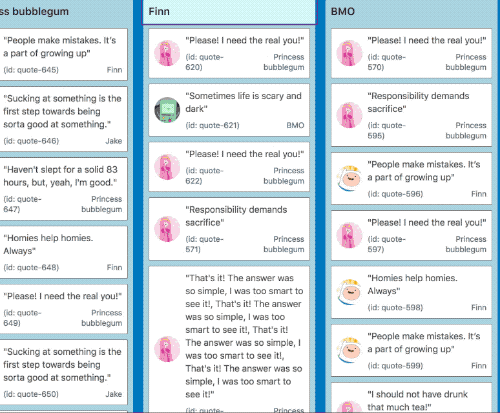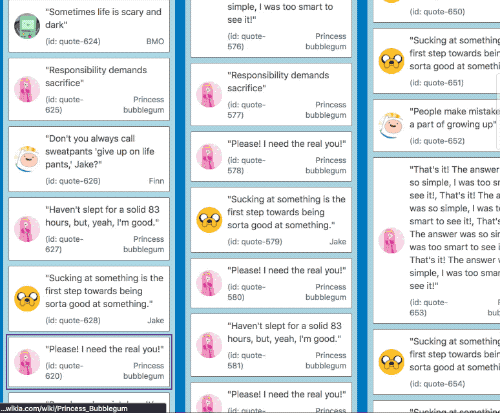 |
For mouse and touch inputs 🐭📱
When the center of a Draggable gets within a small distance from the edge of a container we start auto scrolling. As the user gets closer to the edge of the container we increase the speed of the auto scroll. This acceleration uses an easing function to exponentially increase the rate of acceleration the closer we move towards the edge. We reach a maximum rate of acceleration a small distance from the true edge of a container so that the user does not need to be extremely precise to obtain the maximum scroll speed. This logic applies for any edge that is scrollable.
The distances required for auto scrolling are based on a percentage of the height or width of the container for vertical and horizontal scrolling respectively. By using percentages rather than raw pixel values we are able to have a great experience regardless of the size and shape of your containers.
Mouse wheel and trackpads
In addition to auto scrolling we also allow users to scroll the window or a Droppable manually using their mouse wheel or trackpad 👌
A note about big Draggables
If the Draggable is bigger than a container on the axis you are trying to scroll - we will not permit scrolling on that axis. For example, if you have a Draggable that is longer than the height of the window we will not auto scroll vertically. However, we will still permit scrolling to occur horizontally.
iOS auto scroll shake 📱🤕
When auto scrolling on an iOS browser (webkit) the Draggable noticeably shakes. This is due to a bug with webkit that has no known work around. We tried for a long time to work around the issue! If you are interesting in seeing this improved please engage with the webkit issue.
For keyboard dragging 🎹
We also correctly update the scroll position as required when keyboard dragging. In order to move a Draggable into the correct position we can do a combination of a Droppable scroll, window scroll and manual movements to ensure the Draggable ends up in the correct position in response to user movement instructions. This is boss 🔥.
This is amazing for users with visual impairments as they can correctly move items around in big lists without needing to use mouse positioning.
Accessibility
Traditionally drag and drop interactions have been exclusively a mouse or touch interaction. This library ships with support for drag and drop interactions using only a keyboard. This enables power users to drive their experience entirely from the keyboard. As well as opening up these experiences to users who would have been excluded previously.
We provide fantastic support for screen readers to assist users with visual (or other) impairments. We ship with english messaging out of the box 📦. However, you are welcome to override these messages by using the announce function that it provided to all of the DragDropContext > hook functions.
See our screen reader guide for a guide on crafting useful screen reader messaging.
Example screen reader behaviour

Mouse dragging
Sloppy clicks and click prevention 🐱🎁
When a user presses the mouse down on an element, we cannot determine if the user was clicking or dragging. Also, sometimes when a user clicks they can move the cursor slightly — a sloppy click. So we only start a drag once the user has moved beyond a certain distance with the mouse down (the drag threshold) — more than they would if they were just making a sloppy click. If the drag threshold is not exceeded then the user interaction behaves just like a regular click. If the drag threshold is exceeded then the interaction will be classified as a drag and the standard click behaviour will not occur.
This allows consumers to wrap interactive elements such as an anchor and have it be both a standard anchor as well as a draggable item in a natural way.
(🐱🎁 is a schrodinger's cat joke)
To see more indepth information about how we impact standard browser events see our how we use DOM events guide
Keyboard shortcuts: mouse dragging
When a drag is not occurring react-beautiful-dnd does not impact any of the standard keyboard interactions (it has no listeners bound).
When a drag is occurring with a mouse the user is able to execute the following keyboard shortcuts:
- escape esc - cancel the drag
During a mouse drag the following standard keyboard events are prevented to prevent a bad experience:
- tab tab ↹ - preventing tabbing
- enter ⏎ - preventing submission
Other than these explicitly prevented keyboard events all standard keyboard events should work as expected.
Keyboard dragging
react-beautiful-dnd supports dragging with only a keyboard. We have audited how our keyboard shortcuts interact with standard browser keyboard interactions. When the user is not dragging they can use their keyboard as they normally would. While dragging we override and disable certain browser shortcuts (such as tab) to ensure a fluid experience for the user.
To see more indepth information about how we impact standard browser events see our how we use DOM events guide
Keyboard shortcuts: keyboard dragging
When a drag is not occurring, the user will be able to navigate through the Draggable's on a page using the standard tab tab ↹ key to move forward through the tabbable elements and (shift + tab) (shift + )tab ↹) to move backwards. We achieve this by adding a tab-index to the Draggable. When a Draggable has focus the spacebar space will lift a Draggable. This will start the drag.
Once a drag is started the following keyboard shortcuts can be used:
- spacebar space - drop the
Draggable - escape esc - cancel the drag
The following commands are also available but they depend on the type of Droppable that the Draggable is currently in:
Within a vertical list
- Up arrow ↑ - move a
Draggableupwards in aDroppable - Down arrow ↓ - move a
Draggabledownwards in aDroppable - Right arrow → - move a
Draggableto aDroppableto the right of the currentDroppable(move to new list) - Left arrow ← - move a
Draggableto aDroppableto the left of the currentDroppable(move to new list)
Within a horizontal list
- Up arrow ↑ - move a
Draggableto aDroppableto above the currentDroppable(move to new list) - Down arrow ↓ - move a
Draggableto aDroppableto below the currentDroppable(move to new list) - Right arrow → - move a
Draggableto the right in the currentDroppable - Left arrow ← - move a
Draggableto the left in the currentDroppable
During a drag the following standard keyboard events have their default behaviour prevented (through event.preventDefault()) to avoid a bad experience:
- tab tab ↹ - preventing tabbing
- enter ⏎ - preventing submission
Touch dragging
react-beautiful-dnd supports dragging on touch devices such as mobiles and tablets.
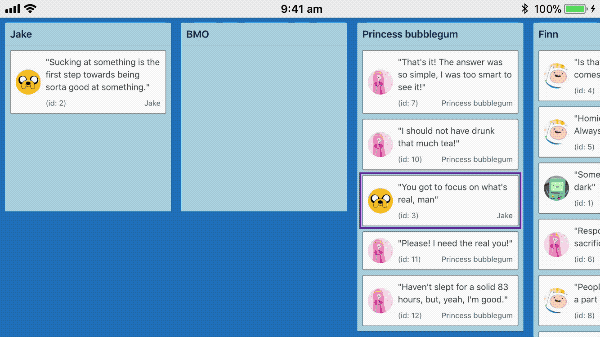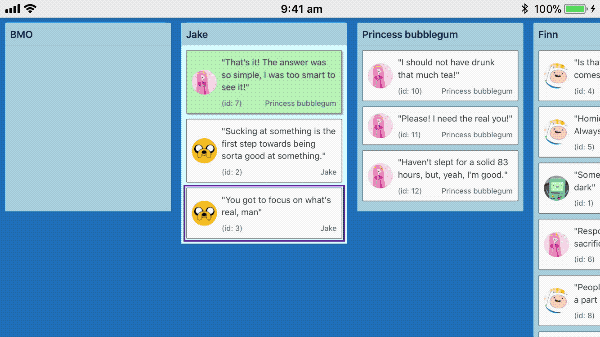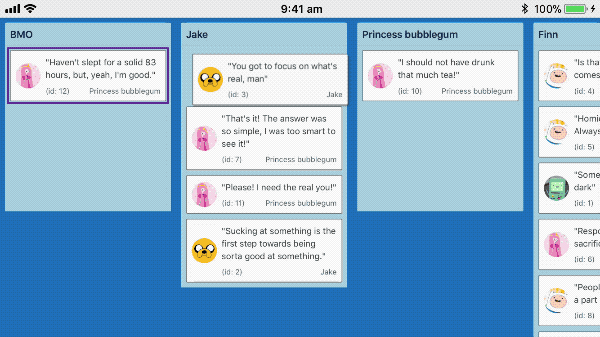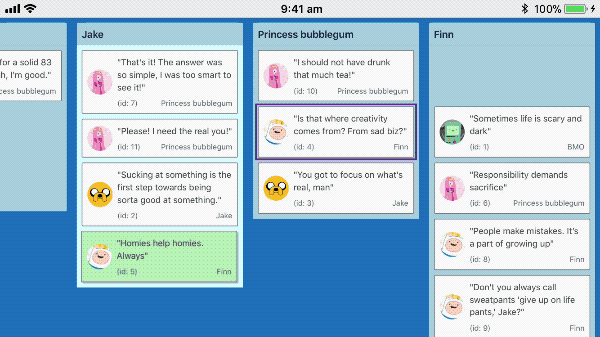
Recorded on iPhone 6s
Understanding intention: tap, force press, scroll and drag
When a user presses their finger (or other input) on a Draggable we are not sure if they where intending to tap, force press, scroll the container or drag. As much as possible react-beautiful-dnd aims to ensure that a users default interaction experience remains unaffected.
To see more indepth information about how we impact standard browser events see our how we use DOM events guide
Starting a drag: long press
A user can start a drag by holding their finger 👇 on an element for a small period of time 🕑 (long press)
Tap support
If the user lifts their finger before the timer is finished then we release the event to the browser for it to determine whether to perform the standard tap / click action. This allows you to have a Draggable that is both clickable such as a anchor as well as draggable. If the item was dragged then we block the tap action from occurring.
Native scrolling support
If we detect a touchmove before the long press timer expires we cancel the pending drag and allow the user to scroll normally. This means that the user needs to be fairly intentional and precise with their grabbing. Once the first touchmove occurs we have to either opt in or out of native scrolling.
- If the long press timer has not expired: allow native scrolling and prevent dragging
- If the long press timer has expired: a drag has started and we prevent native scrolling
Force press support
Safari only
If the user force presses on the element before they have moved the element (even if a drag has already started) then the drag is cancelled and the standard force press action occurs. For an anchor this is a website preview.
Vibration
This is merely an idea - it is up to you to add this if you want this behavior.
If you like you could also trigger a vibration event when the user picks up a Draggable. This can provide tactile feedback that the user is doing something. It currently is only supported in Chrome on Android.
class App extends React.Component {
onDragStart = () => {
// good times
if (window.navigator.vibrate) {
window.navigator.vibrate(100);
}
};
/*...*/
}Multi drag
We have created a multi drag pattern that you can build on top of react-beautiful-dnd in order to support dragging multiple Draggable items at once.
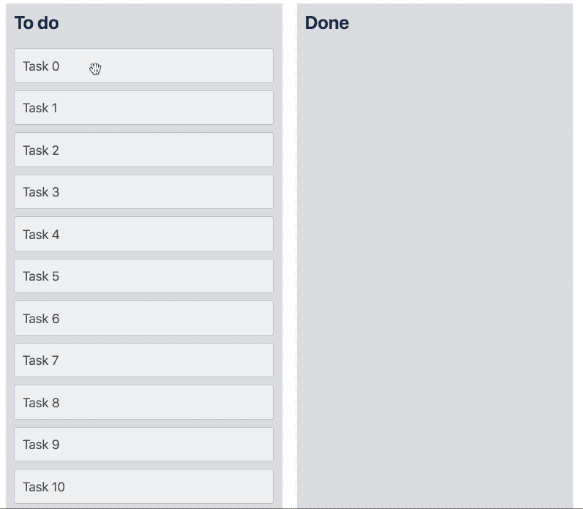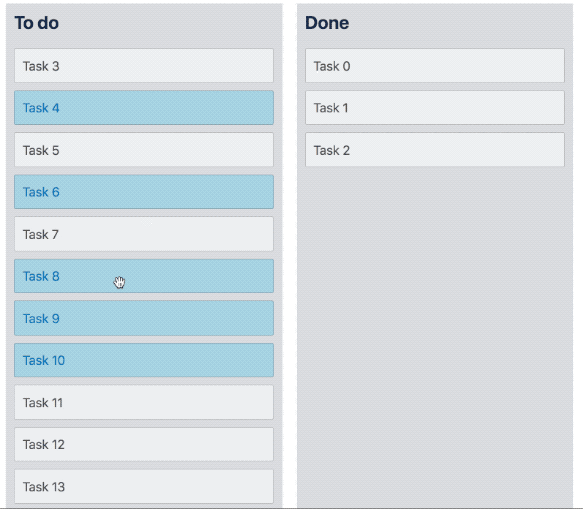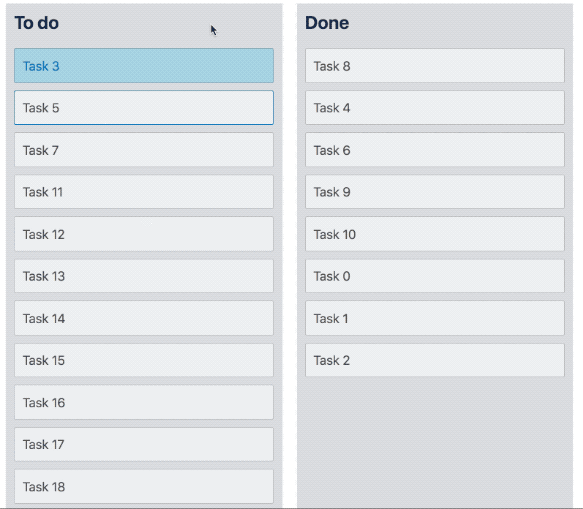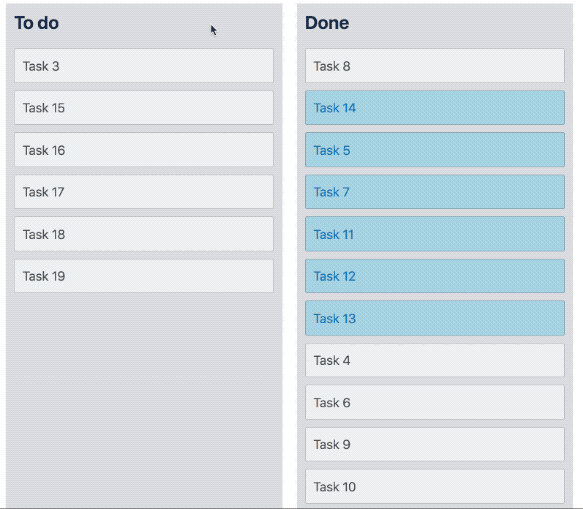
Preset styles
We apply a number of non-visible styles to facilitate the dragging experience. We do this using combination of styling targets and techniques. It is a goal of the library to provide unopinioned styling. However, we do apply some reasonable cursor styling on drag handles by default. This is designed to make the library work as simply as possible out of the box. If you want to use your own cursors you are more than welcome to. All you need to do is override our cursor style rules by using a rule with higher specificity.
Here are the styles that are applied at various points in the drag lifecycle:
In every phase
Always: drag handle
Styles applied to: drag handle element using the data-react-beautiful-dnd-drag-handle attribute.
A long press on anchors usually pops a content menu that has options for the link such as 'Open in new tab'. Because long press is used to start a drag we need to opt out of this behavior
-webkit-touch-callout: none;Webkit based browsers add a grey overlay to anchors when they are active. We remove this tap overlay as it is confusing for users. more information.
-webkit-tap-highlight-color: rgba(0,0,0,0);Avoid the pull to refresh action and delayed anchor focus on Android Chrome
touch-action: manipulation;Always: Droppable
Styles applied to: droppable element using the data-react-beautiful-dnd-droppable attribute.
Opting out of the browser feature which tries to maintain the scroll position when the DOM changes above the fold. We already correctly maintain the scroll position. The automatic overflow-anchor behavior leads to incorrect scroll positioning post drop.
overflow-anchor: none;Phase: resting
(Phase: resting): drag handle
Styles applied to: drag handle element using the data-react-beautiful-dnd-drag-handle attribute.
Adding a cursor style to let the user know this element is draggable. You are welcome to override this.
cursor: grab;Phase: dragging
(Phase: dragging): drag handle element
Styles applied using the data-react-beautiful-dnd-drag-handle attribute
An optimisation to avoid processing pointer-events while dragging. Also used to allow scrolling through a drag handle with a track pad or mouse wheel.
point-events: none;(Phase: dragging): Draggable element
Styles applied using the data-react-beautiful-dnd-draggable attribute
This is what we use to control Draggables that need to move out of the way of a dragging Draggable.
transition: ${string};Styles applied using inline styles
This is described by the type DraggableStyle.
(Phase: dragging): body element
We apply a cursor while dragging to give user feedback that a drag is occurring. You are welcome to override this. A good point to do this is the onDragStart event.
cursor: grabbing;To prevent the user selecting text as they drag apply this style
user-select: none;Phase: dropping
(Phase: dropping): drag handle element
Styles applied using the data-react-beautiful-dnd-drag-handle attribute
We apply the grab cursor to all drag handles except the drag handle for the dropping Draggable. At this point the user is able to drag other Draggable's if they like.
cursor: grab;(Phase: dropping): draggable
Same as dragging phase
Phase: user cancel
When a user explicitly cancels a drag
This is the same as Phase: dropping. However we do not apply a cursor: grab to the drag handle. During a user initiated cancel we do not allow the dragging of other items until the drop animation is complete.
Preset styles are vendor prefixed
All styles applied are vendor prefixed correctly to meet the requirements of our supported browser matrix. This is done by hand to avoid adding to react-beautiful-dnd's size by including a css-in-js library
Installation
Package manager
# yarn
yarn add react-beautiful-dnd
# npm
npm install react-beautiful-dnd --saveDistribution bundle
A universal module definition bundle is published on npm under the /dist folder for consumption . We publish the following files:
dist/react-beautiful-dnd.jsdist/react-beautiful-dnd.min.js(minified bundle)
These bundles list react as an external which needs to be provided. This is done to reduce the size of the bundle and prevent consumers from loading react multiple times. You can provide react through your module system or simply by having react on the window.
You can use the UMD to run react-beautiful-dnd directly in the browser.
<!-- peer dependency -->
<script src="https://unpkg.com/react@15.6.0/dist/react.js"></script>
<!-- lib (change x.x.x for the version you would like) -->
<script src="https://unpkg.com/react-beautiful-dnd@x.x.x/dist/react-beautiful-dnd.js"></script>
<!-- needed to mount your react app -->
<script src="https://unpkg.com/react-dom@15.6.0/dist/react-dom.js"></script>
<script>
const React = window.React;
const ReactDOM = window.ReactDOM;
const { DragDropContext, Draggable, Droppable } = window.ReactBeautifulDnd;
class App extends React.Component {
//...
}
// You can use JSX if your environment supports it
ReactDOM.render(React.createElement(App), document.getElementById('app'));
</script>There is also an example codepen you can use to play with this installation method.
ClojureScript
You can consume react-beautiful-dnd from within ClojureScript using CLJSJS!
API
Okay, into the fun stuff - so how do you use the library?
DragDropContext
In order to use drag and drop, you need to have the part of your React tree that you want to be able to use drag and drop in wrapped in a DragDropContext. It is advised to just wrap your entire application in a DragDropContext. Having nested DragDropContext's is not supported. You will be able to achieve your desired conditional dragging and dropping using the props of Droppable and Draggable. You can think of DragDropContext as having a similar purpose to the react-redux Provider component
Props
type Hooks = {|
// optional
onDragStart?: OnDragStartHook,
onDragUpdate?: OnDragUpdateHook,
// always required
onDragEnd: OnDragEndHook,
|}
type OnDragStartHook = (start: DragStart, provided: HookProvided) => void;
type OnDragUpdateHook = (update: DragUpdate, provided: HookProvided) => void;
type OnDragEndHook = (result: DropResult, provided: HookProvided) => void;
type Props = {|
...Hooks,
children: ?Node,
|}Basic usage
import { DragDropContext } from 'react-beautiful-dnd';
class App extends React.Component {
onDragStart = () => {
/*...*/
};
onDragUpdate = () => {
/*...*/
}
onDragEnd = () => {
// the only one that is required
};
render() {
return (
<DragDropContext
onDragStart={this.onDragStart}
onDragUpdate={this.onDragUpdate}
onDragEnd={this.onDragEnd}
>
<div>Hello world</div>
</DragDropContext>
);
}
}Hooks
These are top level application events that you can use to perform your own state updates as well as to make screen reader announcements. For more information about controlling the screen reader see our screen reader guide
provided: HookProvided
type HookProvided = {|
announce: Announce,
|}
type Announce = (message: string) => void;All hooks are provided with a second argument: HookProvided. This object has one property: announce. This function is used to synchronously announce a message to screen readers. If you do not use this function we will announce a default english message. We have created a guide for screen reader usage which we recommend using if you are interested in controlling the screen reader messages for yourself and to support internationalisation. If you are using announce it must be called synchronously.
onDragStart (optional)
type OnDragStartHook = (start: DragStart, provided: HookProvided) => void;onDragStart will get notified when a drag starts. This hook is optional and therefore does not need to be provided. It is highly recommended that you use this function to block updates to all Draggable and Droppable components during a drag. (See Best practices for hooks )
You are provided with the following details:
start: DragStart
type DragStart = {|
draggableId: DraggableId,
type: TypeId,
source: DraggableLocation,
|}start.draggableId: the id of theDraggablethat is now draggingstart.type: thetypeof theDraggablethat is now draggingstart.source: the location (droppableIdandindex) of where the dragging item has started within aDroppable.
onDragStart type information
type OnDragStartHook = (start: DragStart, provided: HookProvided) => void;
// supporting types
type DragStart = {|
draggableId: DraggableId,
type: TypeId,
source: DraggableLocation,
|}
type DraggableLocation = {|
droppableId: DroppableId,
// the position of the draggable within a droppable
index: number
|};
type Id = string;
type DraggableId = Id;
type DroppableId = Id;
type TypeId = Id;onDragUpdate (optional)
type OnDragUpdateHook = (update: DragUpdate, provided: HookProvided) => void;This hook is called whenever something changes during a drag. The possible changes are:
- The position of the
Draggablehas changed - The
Draggableis now over a differentDroppable - The
Draggableis now over noDroppable
It is important that you not do too much work as a result of this function as it will slow down the drag.
update: DragUpdate
type DragUpdate = {|
...DragStart,
// may not have any destination (drag to nowhere)
destination: ?DraggableLocation,
|}update.draggableId: the id of theDraggablethat is now draggingupdate.type: thetypeof theDraggablethat is now draggingupdate.source: the location (droppableIdandindex) of where the dragging item has started within aDroppable.update.destination: the location (droppableIdandindex) of where the dragging item is now. This can be null if the user is currently not dragging over anyDroppable.
onDragEnd (required)
This function is extremely important and has an critical role to play in the application lifecycle. This function must result in the synchronous reordering of a list of Draggables
It is provided with all the information about a drag:
result: DropResult
type DropResult = {|
...DragUpdate,
reason: DropReason,
|}
type DropReason = 'DROP' | 'CANCEL';result.draggableId: the id of theDraggablethat was dragging.result.type: thetypeof theDraggablethat was dragging.result.source: the location where theDraggablestarted.result.destination: the location where theDraggablefinished. Thedestinationwill benullif the user dropped while not over aDroppable.result.reason: the reason a drop occurred. This information can be helpful in crafting more useful messaging in theHookProvided>announcefunction.
Synchronous reordering
Because this library does not control your state, it is up to you to synchronously reorder your lists based on the result: DropResult.
Here is what you need to do
- if the
destinationisnull: all done! - if
source.droppableIdequalsdestination.droppableIdyou need to remove the item from your list and insert it at the correct position. - if
source.droppableIddoes not equaldestination.droppableId, then you need to remove theDraggablefrom thesource.droppableIdlist and add it into the correct position of thedestination.droppableIdlist.
Persisting a reorder
If you need to persist a reorder to a remote data store - update the list synchronously on the client and fire off a request in the background to persist the change. If the remote save fails it is up to you how to communicate that to the user and update, or not update, the list.
Best practices for hooks
Block updates during a drag
It is highly recommended that while a user is dragging that you block any state updates that might impact the amount of Draggables and Droppables, or their dimensions. Please listen to onDragStart and block updates to the Draggables and Droppables until you receive at onDragEnd.
When the user starts dragging we take a snapshot of all of the dimensions of the applicable Draggable and Droppable nodes. If these change during a drag we will not know about it.
Here are a few poor user experiences that can occur if you change things during a drag:
- If you increase the amount of nodes, then the library will not know about them and they will not be moved when the user would expect them to be.
- If you decrease the amount of nodes, then there might be gaps and unexpected movements in your lists.
- If you change the dimensions of any node, then it can cause the changed node as well as others to move at incorrect times.
- If you remove the node that the user is dragging, then the drag will instantly end
- If you change the dimension of the dragging node, then other things will not move out of the way at the correct time.
Force focus after a transition between lists
When an item is moved from one list to a different list, it loses browser focus if it had it. This is because React creates a new node in this situation. It will not lose focus if transitioned within the same list. The dragging item will always have had browser focus if it is dragging with a keyboard. It is highly recommended that you give the item (which is now in a different list) focus again. You can see an example of how to do this in our stories. Here is an example of how you could do it:
onDragEnd: move the item into the new list and record the id of the item that has moved- When rendering the reordered list, pass down a prop which will tell the newly moved item to obtain focus
- In the
componentDidMountlifecycle call back check if the item needs to gain focus based on its props (such as anautoFocusprop) - If focus is required - call
.focuson the node. You can obtain the node by usingReactDOM.findDOMNodeor monkey patching theprovided.innerRefcallback.
onDragStart and onDragEnd pairing
We try very hard to ensure that each onDragStart event is paired with a single onDragEnd event. However, there maybe a rogue situation where this is not the case. If that occurs - it is a bug. Currently there is no mechanism to tell the library to cancel a current drag externally.
Droppable
Droppable components can be dropped on by a Draggable. They also contain Draggables. A Draggable must be contained within a Droppable.
import { Droppable } from 'react-beautiful-dnd';
<Droppable droppableId="droppable-1" type="PERSON">
{(provided, snapshot) => (
<div
ref={provided.innerRef}
style={{ backgroundColor: snapshot.isDraggingOver ? 'blue' : 'grey' }}
{...provided.droppableProps}
>
<h2>I am a droppable!</h2>
{provided.placeholder}
</div>
)}
</Droppable>;Droppable props
droppableId: A requiredDroppableId(string)that uniquely identifies the droppable for the application. Please do not change this prop - especially during a drag.type: An optionalTypeId(string)that can be used to simply accept a class ofDraggable. For example, if you use the typePERSONthen it will only allowDraggables of typePERSONto be dropped on itself.Draggables of typeTASKwould not be able to be dropped on aDroppablewith typePERSON. If notypeis provided, it will be set to'DEFAULT'. Currently thetypeof theDraggables within aDroppablemust be the same. This restriction might be loosened in the future if there is a valid use case.isDropDisabled: An optional flag to control whether or not dropping is currently allowed on theDroppable. You can use this to implement your own conditional dropping logic. It will default tofalse.direction: The direction in which items flow in this droppable. Options arevertical(default) andhorizontal.ignoreContainerClipping: When aDroppableis inside a scrollable container its area is constrained so that you can only drop on the part of theDroppablethat you can see. Setting this prop opts out of this behavior, allowing you to drop anywhere on aDroppableeven if it's visually hidden by a scrollable parent. The default behavior is suitable for most cases so odds are you'll never need to use this prop, but it can be useful if you've got very longDraggables inside a short scroll container. Keep in mind that it might cause some unexpected behavior if you have multipleDroppables inside scroll containers on the same page.
Children function
The React children of a Droppable must be a function that returns a ReactElement.
<Droppable droppableId="droppable-1">
{(provided, snapshot) => ({
/*...*/
})}
</Droppable>;The function is provided with two arguments:
1. provided: (DroppableProvided)**
type DroppableProvided = {|
innerRef: (?HTMLElement) => void,
droppableProps: DroppableProps,
placeholder: ?ReactElement,
|}
type DroppableProps = {|
// used for shared global styles
'data-react-beautiful-dnd-droppable': string,
|}provided.innerRef: In order for the droppable to function correctly, you must bind theprovided.innerRefto the highest possible DOM node in theReactElement. We do this in order to avoid needing to useReactDOMto look up your DOM node. This prop is planned to be removed when we move to React 16provided.placeholder: This is used to create space in theDroppableas needed during a drag. This space is needed when a user is dragging over a list that is not the home list. Please be sure to put the placeholder inside of the component for which you have provided the ref. We need to increase the size of theDroppableitself. This is different fromDraggablewhere theplaceholderneeds to be a sibling to the draggable node.provided.droppableProps (DroppableProps): This is an Object that contains properties that need to be applied to a Droppable element. It needs to be applied to the same element that you applyprovided.innerRefto. It currently contains adataattribute that we use to control some non-visible css.
<Droppable droppableId="droppable-1">
{(provided, snapshot) => (
<div ref={provided.innerRef} {...provided.droppableProps}>
Good to go
{provided.placeholder}
</div>
)}
</Droppable>;2. snapshot: (DroppableStateSnapshot)**
type DroppableStateSnapshot = {|
// Is the Droppable being dragged over?
isDraggingOver: boolean,
// What is the id of the draggable that is dragging over the Droppable?
draggingOverWith: ?DraggableId,
|};The children function is also provided with a small amount of state relating to the current drag state. This can be optionally used to enhance your component. A common use case is changing the appearance of a Droppable while it is being dragged over.
<Droppable droppableId="droppable-1">
{(provided, snapshot) => (
<div
ref={provided.innerRef}
style={{ backgroundColor: snapshot.isDraggingOver ? 'blue' : 'grey' }}
{...provided.droppableProps}
>
I am a droppable!
{provided.placeholder}
</div>
)}
</Droppable>;Conditionally dropping
Droppables can only be dropped on byDraggables who share the sametype. This is a simple way of allowing conditional dropping. If you do not provide atypefor theDroppable, then it will only acceptDraggables which also have the default type.Draggables andDroppables both will have theirtypesset to'DEFAULT'when none is provided. There is currently no way to set multipletypes, or atypewildcard that will acceptDraggables of multiple any types. This could be added if there is a valid use case.- Using the
isDropDisabledprop you can conditionally allow dropping. This allows you to do arbitrarily complex conditional transitions. This will only be considered if thetypeof theDroppablematches thetypeof the currently draggingDraggable. - You can disable dropping on a
Droppablealtogether by always settingisDropDisabledto false. You can do this to create a list that is never able to be dropped on, but containsDraggables. - Technically you do not need to use
typeand do all of your conditional drop logic with theisDropDisabledfunction. Thetypeparameter is a convenient shortcut for a common use case.
Scroll containers
This library supports dragging within scroll containers (DOM elements that have overflow: auto; or overflow: scroll;). The only supported use cases are:
- The
Droppablecan itself be a scroll container with no scrollable parents - The
Droppablehas one scrollable parent
where a scrollable parent refers to a scroll container that is not the window itself.
Empty Droppables
It is recommended that you put a min-height on a vertical Droppable or a min-width on a horizontal Droppable. Otherwise when the Droppable is empty there may not be enough of a target for Draggable being dragged with touch or mouse inputs to be over the Droppable.
Recommended Droppable performance optimisation
When a user drags over, or stops dragging over, a Droppable we re-render the Droppable with an updated DroppableStateSnapshot > isDraggingOver value. This is useful for styling the Droppable. However, by default this will cause a render of all of the children of the Droppable - which might be 100's of Draggables! This can result in a noticeable frame rate drop. To avoid this problem we recommend that you create a component that is the child of a Droppable who's responsibility it is to avoid rendering children if it is not required.
Here is an example of how you could do this:
import React, { Component } from 'react';
class Student extends Component<{ student: Person }> {
render() {
// Renders out a draggable student
}
}
class InnerList extends Component<{ students: Person[] }> {
// do not re-render if the students list has not changed
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps: Props) {
if(this.props.students === nextProps.students) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
// You could also not do your own shouldComponentUpdate check and just
// extend from React.PureComponent
render() {
return this.props.students.map((student: Person) => (
<Student student={student} />
))
}
}
class Students extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Droppable droppableId="list">
{(provided: DroppableProvided, snapshot: DroppableStateSnapshot) => (
<div
ref={provided.innerRef}
style={{ backgroundColor: provided.isDragging ? 'green' : 'lightblue' }}
{...provided.droppableProps}
>
<InnerList students={this.props.students} />
{provided.placeholder}
</div>
)}
</Droppable>
)
}
}By using the approach you are able to make style changes to a Droppable when it is being dragged over, but you avoid re-rendering all of the children unnecessarily. Keep in mind that if you are using React.PureComponent that your component will not respond to changes in the context.
Unfortunately we are unable to apply this optimisation for you. It is a byproduct of using the function-as-child pattern.
Draggable
Draggable components can be dragged around and dropped onto Droppables. A Draggable must always be contained within a Droppable. It is possible to reorder a Draggable within its home Droppable or move to another Droppable. It is possible because a Droppable is free to control what it allows to be dropped on it.
Every Draggable has a drag handle. A drag handle is the element that the user interacts with in order to drag a Draggable. A drag handle can be a the Draggable element itself, or a child of the Draggable.
import { Draggable } from 'react-beautiful-dnd';
<Draggable draggableId="draggable-1" type="PERSON" index={0}>
{(provided, snapshot) => (
<div>
<div
ref={provided.innerRef}
{...provided.draggableProps}
{...provided.dragHandleProps}
>
<h4>My draggable</h4>
</div>
{provided.placeholder}
</div>
)}
</Draggable>;Note: when the library moves to React 16 this will be cleaned up a little bit as we will be able to return the placeholder as a sibling to your child function without you needing to create a wrapping element
Draggable Props
draggableId: A requiredDraggableId(string)that uniquely identifies theDraggablefor the application. Please do not change this prop - especially during a drag.index: A requirednumberthat matches the order of theDraggablein theDroppable. It is simply the index of theDraggablein the list. Theindexneeds to be unique within aDroppablebut does not need to be unique betweenDroppables. Typically theindexvalue will simply be theindexprovided by aArray.prototype.mapfunction:
{this.props.items.map((item, index) => (
<Draggable draggableId={item.id} index={index}>
{(provided, snapshot) => (
<div>
<div ref={provided.innerRef} {...provided.draggableProps}>
{item.content}
</div>
</div>
)}
</Draggable>
))}type: An optional type (TypeId(string)) of theDraggable. This is used to control whatDroppables theDraggableis permitted to drop on.Draggables can only drop onDroppables that share the sametype. If notypeis provided, then it will be set to'DEFAULT'. Currently thetypeof aDraggablemust be the same as its containerDroppable. This restriction might be loosened in the future if there is a valid use case.isDragDisabled: An optional flag to control whether or not theDraggableis permitted to drag. You can use this to implement your own conditional drag logic. It will default tofalse.disableInteractiveElementBlocking: An optional flag to opt out of blocking a drag from interactive elements. For more information refer to the section Interactive child elements within aDraggable
Children function
The React children of a Draggable must be a function that returns a ReactElement.
<Draggable draggableId="draggable-1" index={0}>
{(provided, snapshot) => (
<div>
<div
ref={provided.innerRef}
{...provided.draggableProps}
{...provided.dragHandleProps}
>
Drag me!
</div>
{provided.placeholder}
</div>
)}
</Draggable>;The function is provided with two arguments:
1. provided: (DraggableProvided)**
type DraggableProvided = {|
innerRef: (HTMLElement) => void,
draggableProps: DraggableProps,
// will be null if the draggable is disabled
dragHandleProps: ?DragHandleProps,
// null if not required
placeholder: ?ReactElement,
|}Everything within the provided object must be applied for the Draggable to function correctly.
provided.innerRef (innerRef: (HTMLElement) => void): In order for theDroppableto function correctly, you must bind theinnerReffunction to theReactElementthat you want to be considered theDraggablenode. We do this in order to avoid needing to useReactDOMto look up your DOM node.
innerRef Example
<Draggable draggableId="draggable-1" index={0}>
{(provided, snapshot) => <div ref={provided.innerRef}>Drag me!</div>}
</Draggable>;provided.draggableProps (DraggableProps): This is an Object that contains adataattribute and an inlinestyle. This Object needs to be applied to the same node that you applyprovided.innerRefto. This controls the movement of the draggable when it is dragging and not dragging. You are welcome to add your own styles toDraggableProps.style– but please do not remove or replace any of the properties.
draggableProps Type information
// Props that can be spread onto the element directly
export type DraggableProps = {|
// inline style
style: ?DraggableStyle,
// used for shared global styles
'data-react-beautiful-dnd-draggable': string,
|}
type DraggableStyle = DraggingStyle | NotDraggingStyle
type DraggingStyle = {|
position: 'fixed',
width: number,
height: number,
boxSizing: 'border-box',
pointerEvents: 'none',
top: number,
left: number,
margin: 0,
transition: 'none',
transform: ?string,
zIndex: ZIndex,
|}
type NotDraggingStyle = {|
transition: ?string,
transition: null | 'none',
|}draggableProps Example
<Draggable draggableId="draggable-1" index={0}>
{(provided, snapshot) => (
<div>
<div ref={provided.innerRef} {...provided.draggableProps}>
Drag me!
</div>
</div>
)}
</Draggable>;Positioning ownership
It is a contract of this library that it owns the positioning logic of the dragging element. This includes properties such as top, right, bottom, left and transform. The library may change how it positions things and which properties it uses without performing a major version bump. It is also recommended that you do not apply your own transition property to the dragging element.
Warning: position: fixed
react-beautiful-dnd uses position: fixed to position the dragging element. This is quite robust and allows for you to have position: relative | absolute | fixed parents. However, unfortunately position:fixed is impacted by transform (such as transform: rotate(10deg);). This means that if you have a transform: * on one of the parents of a Draggable then the positioning logic will be incorrect while dragging. Lame! For most consumers this will not be an issue.
This will be changing soon as we move to a portal solution where we will be appending the Draggable to the end of the body to avoid any parent transforms. If you really need this feature right now we have created an example where we implement a portal on top of the current api. Please note however, this technique is not officially supported and might break in minor / patch releases.
Extending DraggableProps.style
If you are using inline styles you are welcome to extend the DraggableProps.style object. You are also welcome to apply the DraggableProps.style object using inline styles and use your own styling solution for the component itself - such as styled-components.
If you are overriding inline styles be sure to do it after you spread the provided.draggableProps or the spread will override your inline style.
<Draggable draggable="draggable-1" index={0}>
{(provided, snapshot) => {
// extending the DraggableStyle with our own inline styles
const style = {
backgroundColor: snapshot.isDragging ? 'blue' : 'white',
fontSize: 18,
...provided.draggableProps.style,
};
return (
<div>
<div
ref={provided.innerRef}
{...provided.draggableProps}
style={style}
>
Drag me!
</div>
</div>
);
}}
</Draggable>;Avoid margin collapsing between Draggables
margin collapsing is one of those really hard parts of CSS. For our purposes, if you have one Draggable with a margin-bottom: 10px and the next Draggable has a margin-top: 12px these margins will collapse and the resulting margin will be the greater of the two: 12px. When we do our calculations we are currently not accounting for margin collapsing. If you do want to have a margin on the siblings, wrap them both in a div and apply the margin to the inner div so they are not direct siblings.
Draggables should be visible siblings
It is an assumption that Draggables are visible siblings of one another. There can be other elements in between, but these elements should not take up any additional space. You probably will not do this anyway, but just calling it out to be super clear.
// Direct siblings ✅
<Draggable draggableId="draggable-1" index={0}>
{() => {}}
</Draggable>
<Draggable draggableId="draggable-2" index={1}>
{() => {}}
</Draggable>
// Not direct siblings, but are visible siblings ✅
<div>
<Draggable draggableId="draggable-1" index={0}>
{() => {}}
</Draggable>
</div>
<div>
<Draggable draggableId="draggable-2" index={1}>
{() => {}}
</Draggable>
</div>
// Spacer elements ❌
<Draggable draggableId="draggable-1" index={0}>
{() => {}}
</Draggable>
<p>I will break things!</p>
<Draggable draggableId="draggable-2" index={1}>
{() => {}}
</Draggable>
// Spacing on non sibling wrappers ❌
<div style={{padding: 10}}>
<Draggable draggableId="draggable-1" index={0}>
{() => {}}
</Draggable>
</div>
<div style={{padding: 10}}>
<Draggable draggableId="draggable-2" index={1}>
{() => {}}
</Draggable>
</div>provided.dragHandleProps (?DragHandleProps)everyDraggablehas a drag handle. This is what is used to drag the wholeDraggable. Often this will be the same node as theDraggable, but sometimes it can be a child of theDraggable.DragHandlePropsneed to be applied to the node that you want to be the drag handle. This is a number of props that need to be applied to theDraggablenode. The simplest approach is to spread the props onto the draggable node ({...provided.dragHandleProps}). However, you are also welcome to monkey patch these props if you also need to respond to them. DragHandleProps will benullwhenisDragDisabledis set totrue.
dragHandleProps Type information
type DragHandleProps = {|
onMouseDown: (event: MouseEvent) => void,
onKeyDown: (event: KeyboardEvent) => void,
onTouchStart: (event: TouchEvent) => void,
onTouchMove: (event: TouchEvent) => void,
'data-react-beautiful-dnd-drag-handle': string,
'aria-roledescription': string,
tabIndex: number,
draggable: boolean,
onDragStart: (event: DragEvent) => void,
|}dragHandleProps Example: standard
<Draggable draggableId="draggable-1" index={0}>
{(provided, snapshot) => (
<div>
<div
ref={provided.innerRef}
{...provided.draggableProps}
{...provided.dragHandleProps}
>
Drag me!
</div>
{provided.placeholder}
</div>
)}
</Draggable>;dragHandleProps Example: custom drag handle
Controlling a whole draggable by just a part of it
<Draggable draggableId="draggable-1" index={0}>
{(provided, snapshot) => (
<div>
<div ref={provided.innerRef} {...provided.draggableProps}>
<h2>Hello there</h2>
<div {...provided.dragHandleProps}>Drag handle</div>
</div>
{provided.placeholder}
</div>
)}
</Draggable>;dragHandleProps monkey patching
You can override some of the dragHandleProps props with your own behavior if you need to.
const myOnMouseDown = event => console.log('mouse down on', event.target);
<Draggable draggableId="draggable-1" index={0}>
{(provided, snapshot) => {
const onMouseDown = (() => {
// dragHandleProps might be null
if (!provided.dragHandleProps) {
return onMouseDown;
}
// creating a new onMouseDown function that calls myOnMouseDown as well as the drag handle one.
return (event) => {
provided.dragHandleProps.onMouseDown(event);
myOnMouseDown(event);
};
})();
return (
<div>
<div
ref={provided.innerRef}
{...provided.draggableProps}
{...provided.dragHandleProps}
onMouseDown={onMouseDown}
>
Drag me!
</div>
{provided.placeholder}
</div>
);
}}
</Draggable>;provided.placeholder (?ReactElement)TheDraggableelement hasposition: fixedapplied to it while it is dragging. The role of theplaceholderis to sit in the place that theDraggablewas during a drag. It is needed to stop theDroppablelist from collapsing when you drag. It is advised to render it as a sibling to theDraggablenode. This is unlikeDroppablewhere theplaceholderneeds to be within theDroppablenode. When the library moves toReact16 theplaceholderwill be removed from api.
placeholder example
<Draggable draggableId="draggable-1" index={0}>
{(provided, snapshot) => (
<div>
<div ref={provided.innerRef} {...provided.draggableProps}>
Drag me!
</div>
{/* Always render me - I will be null if not required */}
{provided.placeholder}
</div>
)}
</Draggable>;2. Snapshot: (DraggableStateSnapshot)**
type DraggableStateSnapshot = {|
isDragging: boolean,
// What Droppable (if any) the Draggable is currently over
draggingOver: ?DroppableId,
|};The children function is also provided with a small amount of state relating to the current drag state. This can be optionally used to enhance your component. A common use case is changing the appearance of a Draggable while it is being dragged. Note: if you want to change the cursor to something like grab you will need to add the style to the draggable. (See Extending DraggableProps.style above)
<Draggable draggableId="draggable-1" index={0}>
{(provided, snapshot) => {
const style = {
backgroundColor: snapshot.isDragging ? 'blue' : 'grey',
...provided.draggableProps.style,
};
return (
<div>
<div
ref={provided.innerRef}
{...provided.draggableProps}
{...provided.dragHandleProps}
style={style}
>
Drag me!
</div>
{provided.placeholder}
</div>
);
}}
</Draggable>;Adding an onClick handler to a Draggable or a drag handle
You are welcome to add your own onClick handler to a Draggable or a drag handle (which might be the same element). onClick events handlers will always be called if a click occurred. If we are preventing the click then we the event.defaultPrevented property will be set to true. We prevent click events from occurring when the user was dragging an item. See #sloppy-clicks-and-click-prevention-(sloppy clicks and click prevention) for more information.
Interactive child elements within a Draggable
It is possible for your Draggable to contain interactive elements. By default we block dragging on these elements. By doing this we allow those elements to function in the usual way. Here is the list of interactive elements that we block dragging from by default:
inputbuttontextareaselectoptionoptgroupvideoaudiocontenteditable(any elements that arecontenteditableor are within acontenteditablecontainer)
You can opt out of this behavior by adding the disableInteractiveElementBlocking prop to a Draggable. However, it is questionable as to whether you should be doing so because it will render the interactive element unusable. If you need to conditionally block dragging from interactive elements you can add the disableInteractiveElementBlocking prop to opt out of the default blocking and monkey patch the dragHandleProps (DragHandleProps) event handlers to disable dragging as required.
resetServerContext
The resetServerContext function should be used when server side rendering (SSR). It ensures context state does not persist across multiple renders on the server which would result in client/server markup mismatches after multiple requests are rendered on the server.
Use it before calling the server side render method:
import { resetServerContext } from 'react-beautiful-dnd';
import { renderToString } from 'react-dom/server';
...
resetServerContext();
renderToString(...);Flow usage
react-beautiful-dnd is typed using flowtype. This greatly improves internal consistency within the codebase. We also expose a number of public types which will allow you to type your javascript if you would like to. If you are not using flowtype this will not inhibit you from using the library. It is just extra safety for those who want it.
Public flow types
// id's
type Id = string;
type TypeId = Id;
type DroppableId = Id;
type DraggableId = Id;
// hooks
type DragStart = {|
draggableId: DraggableId,
type: TypeId,
source: DraggableLocation,
|}
type DragUpdate = {|
...DragStart,
// may not have any destination (drag to nowhere)
destination: ?DraggableLocation,
|}
type DropResult = {|
...DragUpdate,
reason: DropReason,
|}
type DropReason = 'DROP' | 'CANCEL'
type DraggableLocation = {|
droppableId: DroppableId,
// the position of the droppable within a droppable
index: number
|};
// Droppable
type DroppableProvided = {|
innerRef: (?HTMLElement) => void,
placeholder: ?ReactElement,
|}
type DroppableStateSnapshot = {|
isDraggingO7 years ago

