react-form-with-constraints v0.19.1
react-form-with-constraints
Simple form validation for React
- Installation:
npm install react-form-with-constraints - CDN: https://unpkg.com/react-form-with-constraints/dist/
Check the changelog for breaking changes and fixes between releases.
Introduction: what is HTML5 form validation?
⚠️ Client side validation is cosmetic, you should not rely on it to enforce security
<form>
<label for="email">Email:</label>
<input type="email" id="email" required>
<button>Submit</button>
</form>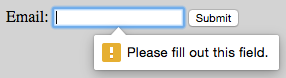
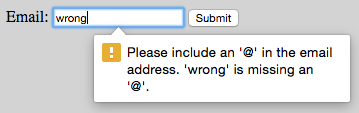
The required HTML5 attribute specifies that the user must fill in a value, type="email" checks that the entered text looks like an email address.
Resources:
- Making Forms Fabulous with HTML5
- Constraint Validation: Native Client Side Validation for Web Forms
- MDN - Form data validation
- MDN - Form input types
What react-form-with-constraints brings
- Minimal API and footprint
- Unobtrusive: easy to adapt regular React code
- Control HTML5 error messages:
<FieldFeedback when="valueMissing">My custom error message</FieldFeedback> - Custom constraints:
<FieldFeedback when={value => ...}> - Warnings and infos:
<FieldFeedback ... warning>,<FieldFeedback ... info> - Async validation
- No dependency beside React (no Redux, MobX...)
- Re-render only what's necessary
- Easily extendable
- Support for React Native with npm package
react-form-with-constraints-native - Bootstrap 4 styling with npm package
react-form-with-constraints-bootstrap4 - Material-UI integration with npm package
react-form-with-constraints-material-ui - ...
<input type="password" name="password"
value={this.state.password} onChange={this.handleChange}
required pattern=".{5,}" />
<FieldFeedbacks for="password">
<FieldFeedback when="valueMissing" />
<FieldFeedback when="patternMismatch">
Should be at least 5 characters long
</FieldFeedback>
<FieldFeedback when={value => !/\d/.test(value)} warning>
Should contain numbers
</FieldFeedback>
<FieldFeedback when={value => !/[a-z]/.test(value)} warning>
Should contain small letters
</FieldFeedback>
<FieldFeedback when={value => !/[A-Z]/.test(value)} warning>
Should contain capital letters
</FieldFeedback>
</FieldFeedbacks>Examples
CodePen basic example: https://codepen.io/tkrotoff/pen/BRGdqL

CodeSandbox Bootstrap 4 example: https://codesandbox.io/s/nkqrr17qqj
- CodeSandbox Material-UI example: https://codesandbox.io/s/zx62rw4k64
- CodeSandbox WizardForm example: https://codesandbox.io/s/my0ojyzq6p
- CodeSandbox SignUp example: https://codesandbox.io/s/62qwozvm0k
CodeSandbox ClubMembers example: https://codesandbox.io/s/q8364yn60j
iOS Android 
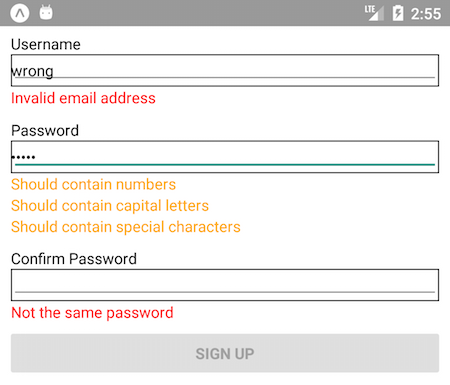
Other examples inside the examples directory.
How it works
The API works the same way as React Router v4:
<Router>
<Route exact path="/" component={Home} />
<Route path="/news" component={NewsFeed} />
</Router>It is also inspired by AngularJS ngMessages.
If you had to implement validation yourself, you would end up with a global object that tracks errors for each field.
react-form-with-constraints works similarly.
It uses React context to share the FieldsStore object across FieldFeedbacks and FieldFeedback.
API
The API reads like this: "for field when constraint violation display feedback", example:
<FieldFeedbacks for="password">
<FieldFeedback when="valueMissing" />
<FieldFeedback when="patternMismatch">Should be at least 5 characters long</FieldFeedback>
</FieldFeedbacks>for field "password"
when constraint violation "valueMissing" display <the HTML5 error message (*)>
when constraint violation "patternMismatch" display "Should be at least 5 characters long"Async support works as follow:
<FieldFeedbacks for="username">
<Async
promise={checkUsernameAvailability} /* Function that returns a promise */
then={available => available ?
<FieldFeedback key="1" info style={{color: 'green'}}>Username available</FieldFeedback> :
<FieldFeedback key="2">Username already taken, choose another</FieldFeedback>
// Why key=*? Needed otherwise React gets buggy when the user rapidly changes the field
}
/>
</FieldFeedbacks>Trigger validation:
class MyForm extends React.Component {
async handleChange(e) {
const target = e.target;
// Validates only the given fields and returns Promise<Field[]>
const fields = await this.form.validateFields(target);
const fieldIsValid = fields.every(field => field.isValid());
if (fieldIsValid) console.log(`Field '${target.name}' is valid`);
else console.log(`Field '${target.name}' is invalid`);
if (this.form.isValid()) console.log('The form is valid');
else console.log('The form is invalid');
}
async handleSubmit(e) {
e.preventDefault();
// Validates the non-dirty fields and returns Promise<Field[]>
const fields = await this.form.validateForm();
// or simply this.form.isValid();
const formIsValid = fields.every(field => field.isValid());
if (formIsValid) console.log('The form is valid');
else console.log('The form is invalid');
}
render() {
return (
<FormWithConstraints
ref={formWithConstraints => this.form = formWithConstraints}
onSubmit={this.handleSubmit} noValidate
>
<input
name="username"
onChange={this.handleChange}
required minLength={3}
/>
<FieldFeedbacks for="username">
<FieldFeedback when="tooShort">Too short</FieldFeedback>
<Async
promise={checkUsernameAvailability}
then={available => available ?
<FieldFeedback key="1" info style={{color: 'green'}}>Username available</FieldFeedback> :
<FieldFeedback key="2">Username already taken, choose another</FieldFeedback>
}
/>
<FieldFeedback when="*" />
</FieldFeedbacks>
</FormWithConstraints>
);
}
}for: string=> reference to anameattribute (e.g<input name="username">), should be unique to the current formstop?: 'first' | 'first-error' | 'first-warning' | 'first-info' | 'no'=> when to stop renderingFieldFeedbacks, by default stops at the first error encountered (FieldFeedbacks order matters)
Note: you can place
FieldFeedbacksanywhere, have as many as you want for the samefield, nest them, mix them withFieldFeedback... Example:<input name="username" ... /> <FieldFeedbacks for="username" stop="first-warning"> <FieldFeedbacks> <FieldFeedback ... /> <Async ... /> <FieldFeedbacks stop="first-info"> ... </FieldFeedbacks> </FieldFeedbacks> <FieldFeedback ... /> <Async ... /> </FieldFeedbacks> <FieldFeedbacks for="username" stop="no"> ... </FieldFeedbacks>when?:ValidityStateas a string => HTML5 constraint violation name'*'=> matches any HTML5 constraint violation'valid'=> displays the feedback only if the field is valid(value: string) => boolean=> custom constraint
error?: boolean=> treats the feedback as an error (default)warning?: boolean=> treats the feedback as a warninginfo?: boolean=> treats the feedback as an infochildren=> what to display when the constraint matches; if missing, displays the HTML5 error message if any
Async<T>=> Async version ofFieldFeedback, similar API as react-promisepromise: (value: string) => Promise<T>=> a promise you want to wait forpending?: React.ReactNode=> runs when promise is pendingthen?: (value: T) => React.ReactNode=> runs when promise is resolvedcatch?: (reason: any) => React.ReactNode=> runs when promise is rejected
validateFields(...inputsOrNames: Array<Input | string>): Promise<Field[]>=> Should be called when afieldchanges, will re-render the properFieldFeedbacks (and update the internalFieldsStore). Without arguments, all fields ($('[name]')) are validated.validateForm(): Promise<Field[]>=> Should be called before to submit theform. Validates only all non-dirty fields (won't re-validate fields that have been already validated withvalidateFields(...)), If you want to force re-validate all fields, usevalidateFields()without arguments.isValid(): boolean=> should be called aftervalidateForm()orvalidateFields(), tells if the fields are validhasFeedbacks(): boolean=> tells if the fields have any kind of feedbackresetFields(...inputsOrNames: Array<Input | string>): Promise<Field[]>=> Resets the given fields and re-render the properFieldFeedbacks. Without arguments, all fields ($('[name]')) are reset.Field=>{ name: string; validations: { // FieldFeedbackValidation[] key: number; type: 'error' | 'warning' | 'info' | 'whenValid'; show: boolean | undefined; }[]; isValid: () => boolean }
If you want to style
<input>, use<Input>instead: it will add classeshas-errors,has-warnings,has-infosand/oris-validon<input>when the field is validated.Example:
<Input name="username" />can generate<input name="username" class="has-errors has-warnings">FYI
react-form-with-constraints-bootstrap4andreact-form-with-constraints-material-uialready style the fields to match their respective frameworks.
Browser support
You can use HTML5 attributes like type="email", required, pattern..., in this case a recent browser is needed,...
<label htmlFor="username">Username</label>
<input type="email" name="username" id="username"
value={this.state.username} onChange={this.handleChange}
required />
<FieldFeedbacks for="username">
<FieldFeedback when="*" />
</FieldFeedbacks>...or ignore them and rely on when functions:
<label htmlFor="username">Username</label>
<input name="username" id="username"
value={this.state.username} onChange={this.handleChange} />
<FieldFeedbacks for="username">
<FieldFeedback when={value => value.length === 0}>Please fill out this field.</FieldFeedback>
<FieldFeedback when={value => !/\S+@\S+/.test(value)}>Invalid email address.</FieldFeedback>
</FieldFeedbacks>In the last case you will have to manage translations yourself (see SignUp example).
react-form-with-constraints needs a polyfill such as core-js or babel-polyfill to support IE 11 and lower. See also React JavaScript Environment Requirements.
Notes
- A
readonlyordisabledinput won't trigger any HTML5 form constraint likerequired. - With
<input type="number">it's better to useonInputinstead ofonChange, see https://github.com/facebook/react/issues/11142
4 years ago
4 years ago
4 years ago
4 years ago
5 years ago
5 years ago
5 years ago
5 years ago
5 years ago
5 years ago
5 years ago
5 years ago
5 years ago
5 years ago
6 years ago
6 years ago
6 years ago
6 years ago
6 years ago
6 years ago
6 years ago
6 years ago
6 years ago
6 years ago
6 years ago
7 years ago
7 years ago
7 years ago
7 years ago
7 years ago
7 years ago
7 years ago
7 years ago
7 years ago
7 years ago
7 years ago
7 years ago
7 years ago
7 years ago
7 years ago
7 years ago
7 years ago
7 years ago
8 years ago
8 years ago
8 years ago
8 years ago
8 years ago
8 years ago
8 years ago
8 years ago
8 years ago
8 years ago
8 years ago
8 years ago
8 years ago
8 years ago
8 years ago
8 years ago
8 years ago
8 years ago
8 years ago
8 years ago
8 years ago
8 years ago
8 years ago
8 years ago
8 years ago
8 years ago
8 years ago
8 years ago
8 years ago
8 years ago
8 years ago
8 years ago
9 years ago
9 years ago
9 years ago
9 years ago
9 years ago
9 years ago
9 years ago
9 years ago
9 years ago
9 years ago
9 years ago
9 years ago
