react-lingala v0.1.1
A Fully Typed Translation Library for React**
Introduction
react-lingala is a fully typed React library designed to simplify translations in your React applications. With strong TypeScript support, this library ensures type safety, scalability, and ease of use.
Local Usage
1. Define Your Language Set
Use TypeScript declaration augmentation to define your application's language set. Create a definition file, e.g., ./types.d.ts:
declare module "react-lingala" {
export interface AppTypes {
lang: "en" | "fr" | "it"; // Add your preferred languages here
}
}2. Create Translation Files
Organize your translations in a dedicated folder, e.g., __trans__/. Each file should export the translation object as const to ensure type safety.
Example: English Translations (
/en.ts)export default { "header.label.title": "Introduction To This Library", "header.text.hello-you": "Hello, my name is {{ name }}", } as const;Example: French Translations (
/fr.ts)export default { "header.label.title": "Introduction à cette librairie.", "header.text.hello-you": "Bonjour, je m'appelle {{ name }}", } as const;Example: Italian Translations (
/it.ts)export default { "header.label.title": "Introduzione alla libreria.", "header.text.hello-you": "Buongiorno, mi chiamo {{ name }}", } as const;
Note: Translation files are not mandatory for all languages, but ensure type consistency for any defined translations.
3. Create a Translation Hook
Define a custom hook to manage your local translations, e.g., useMyTranslations.ts:
import { createHook } from "react-lingala";
import en from "./__trans__/en";
// `en` will be the default translation dictionary
export const useMyTranslations = createHook(en, (lang) => import(`./__trans__/${lang}`));Using Translations in Components
Here’s how to use the translations in your components:
import { useState } from "react";
import { type AppLang } from "react-lingala";
import { useMyTranslations } from "./useMyTranslations";
export const Header = () => {
const [lang, setLang] = useState<AppLang>("en");
const t = useMyTranslations(lang);
return (
<header>
<label>{t("header.label.title")}</label>
<p>{t("header.text.hello-you", { name: "Fernando Ekutsu Mondele" })}</p>
<YourCustomLanguageSelector lang={lang} onChange={(newLang) => setLang(newLang)} />
</header>
);
};Translations Provider
Wrap your application in a TranslationsProvider to provide context for translations.
import { TranslationsProvider } from "react-lingala";
import { Header } from "./Header";
export const Root = () => {
return (
<TranslationsProvider>
<Header />
</TranslationsProvider>
);
};Global Usage
To use translations globally across multiple components, configure a global useTranslations hook. This approach reduces boilerplate and centralizes your translation logic.
Configuration for Global Translations
Set up the global context during project initialization. For example, in a Next.js project, configure it in next.config.js:
const lingala = require("react-lingala/configure");
const context = lingala.configure({
defaultLang: "en",
rootDir: __dirname,
destinationFolder: "src/translations", // Folder to store combined translations
languages: ["de", "en", "es", "fr", "it"], // Add your languages
alias: (file) => `@/${file.replace(/^src\//, "")}`, // Optional alias for imports
});
// Generate a `translations-lock.js` file to persist translations
context.loadTranslations();
module.exports = {
// Your Next.js config
};Note: Restart the project whenever a new translation file is added to ensure the global context is updated.
Global Provider
Use the global translations provider to inject the default translations into your application:
import { TranslationsProvider } from "react-lingala";
import { Header } from "./Header";
import { DEFAULT_TRANSLATIONS } from "./src/translations/global";
export const Root = () => {
return (
<TranslationsProvider defaultTranslations={DEFAULT_TRANSLATIONS}>
<Header />
</TranslationsProvider>
);
};Global Hook (useTranslations)
You can now replace the local translation hook (useMyTranslations) with the global useTranslations hook from your translations folder.
import { useState } from "react";
import { type AppLang } from "react-lingala";
import { useTranslations } from "./src/translations"; // Use the global hook
export const Header = () => {
const [lang, setLang] = useState<AppLang>("en");
const t = useTranslations(lang);
const NameElement = <strong>Fernando Ekutsu Mondele</strong>
return (
<header>
<label>{t("header.label.title")}</label>
<p>{t("header.text.hello-you", { name: NameElement })}</p>
<YourCustomLanguageSelector lang={lang} onChange={(newLang) => setLang(newLang)} />
</header>
);
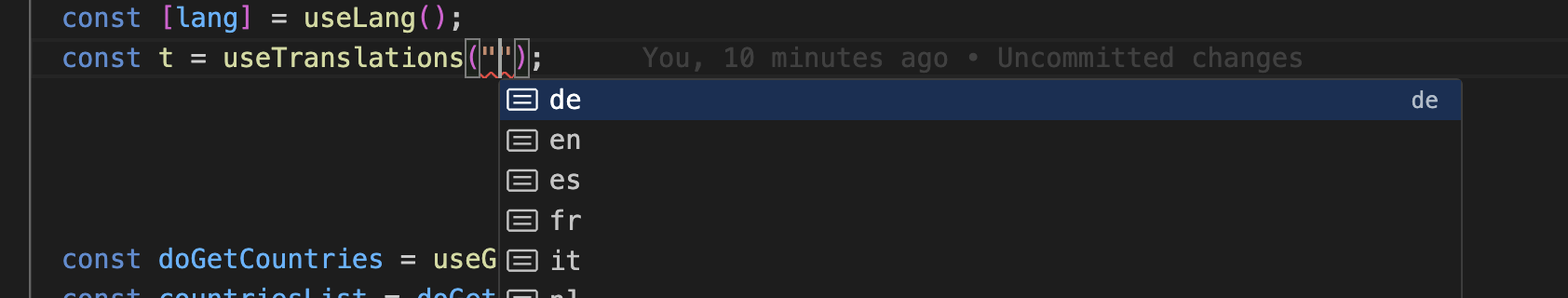
};- lang auto complete
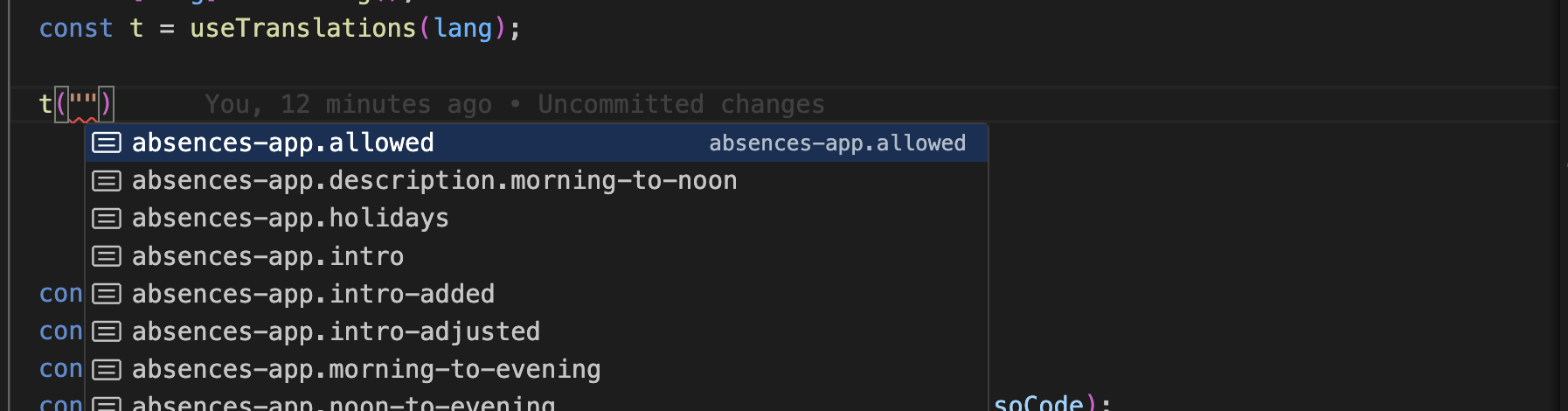
- keys auto complete
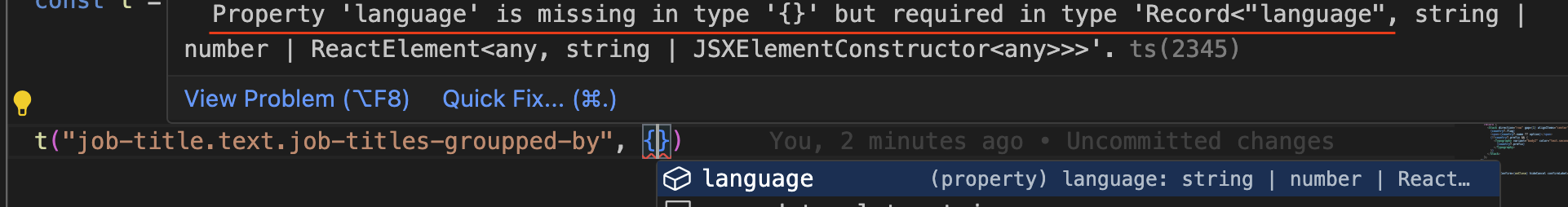
- missing value lint error
Key Features
- Type Safety: Define and validate your translations at compile time.
- Lazy Loading: Dynamically load only the required translations.
- Flexibility: Use locally scoped or global translations based on project needs.
Feel free to reach out for contributions or improvements. Happy coding! 🚀