react-native-observable-list v3.3.1
react-native-observable-list
This library was developed as a replacement for the browser's IntersectionObserver API.
It provides item tracking functionality for lists that offer an onViewableItemsChanged callback with the type ({viewableItems: ViewToken[]}) => void and a renderItem property with the type ({item: ItemT, index: number}) => React.ReactElement.
demo1 (useInViewPort, Example 1-3)
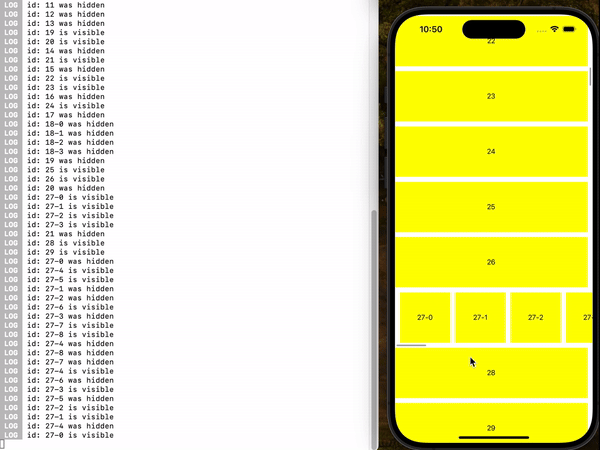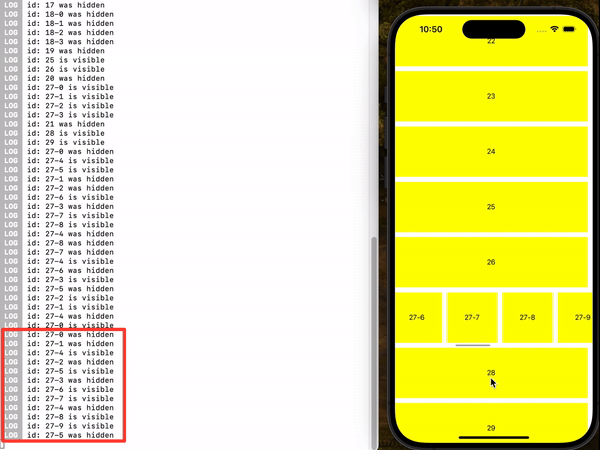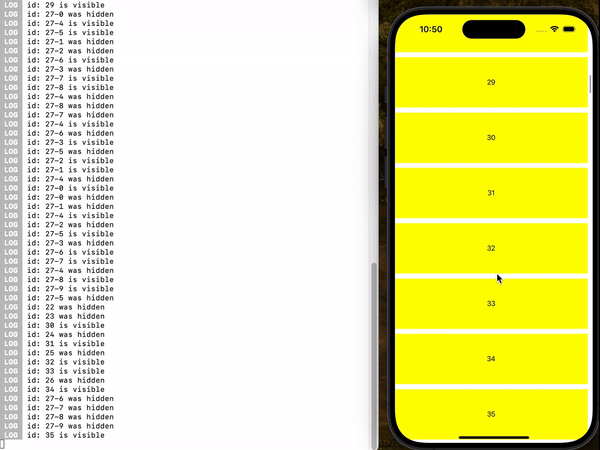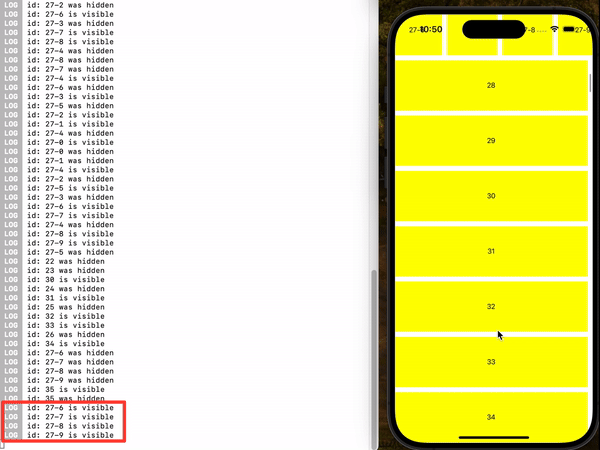
demo2 (useIsFirst, Example 4)

Installation
npm install react-native-observable-listUsage
You can use the useInViewPort hook anywhere within the item to register an event handler that will trigger when the item enters or leaves the viewport.
The newly created component with observe will have an $$enabled (optional, default is true) property.
import { FlatList } from 'react-native';
import { observe, useInViewPort } from 'react-native-observable-list';
import { useIsFocused } from '@react-navigation/native';
const ObservableFlatList = observe(FlatList);
const data = Array.from({ length: 100 });
const Item = ({ id }) => {
// The callback is re-registered whenever deps change.
// clean is executed when an item leaves the viewport. (not unmount)
useInViewPort(() => {
console.log(`id: ${id} is visible.`);
return () => {
console.log(`id: ${id} has been hidden.`);
};
}, []);
return <View style={{ height: 100 }} />;
};
const App = () => {
const isFocused = useIsFocused();
return (
<ObservableFlatList
$$enabled={isFocused} // if you need
data={data}
renderItem={() => <Item />}
/>
);
};Examples
install dependencies
yarn installrun on expo android
yarn example androidrun on expo ios
yarn example iosExample1 (Nesting)
It supports both reverse and forward nesting.
Example2 (react-native-reanimated-carousel)
It can also be used with containers that do not have the onViewableItemsChanged and renderItem props.
import { observe } from 'react-native-observable-list';
import Carousel, {
type TCarouselProps,
} from 'react-native-reanimated-carousel';
function ViewableCarousel<T>(
props: TCarouselProps<T> & {
onViewableItemsChanged?: ({
changed,
viewableItems,
}: {
changed: ViewToken[];
viewableItems: ViewToken[];
}) => void;
}
) {
return (
<Carousel
{...props}
onProgressChange={(offsetProgress: number, absoluteProgress: number) => {
const index = Math.floor(absoluteProgress);
const item = props.data[index];
props.onViewableItemsChanged?.({
changed: [],
viewableItems: [{ item, index, isViewable: true, key: undefined }],
});
props.onProgressChange?.(offsetProgress, absoluteProgress);
}}
/>
);
}
const ObservableCarousel = observe(ViewableCarousel);Example3 (FlashList)
It can also be used with FlashList, which offers a similar interface to FlatList.
In this case, you have to use a key in the internal list to prevent recycling.
import { observe } from 'react-native-observable-list';
import { FlashList } from '@shopify/flash-list';
const ObservableFlatList = observe(FlashList);
const Example3 = () => {
return (
<ObservableFlatList
// ...
renderItem={({ index: outerIndex }) => {
return (
<ObservableFlatList
key={`inner-list-${outerIndex}`} // do not recycle !!
// ...
/>
);
}}
/>
);
};Example4 (Detect First Item)
The callback function registered with the useIsFirst hook is triggered when the first item changes.
import { useState } from 'react';
import { FlatList, View } from 'react-native';
import { observe, useIsFirst } from 'react-native-observable-list';
const ObservableFlatList = observe(FlatList);
const Item = ({
color,
onFirst,
height = 500,
}: {
color: string;
onFirst: () => void;
height?: number;
}) => {
useIsFirst(() => {
onFirst();
}, [color]);
return <View style={{ backgroundColor: color, height }} />;
};
const data = ['blue', 'yellow', 'green', 'orange'];
const Example4 = () => {
const [first, setFirst] = useState<string | undefined>(undefined);
return (
<ObservableFlatList
data={data}
renderItem={({ item: color }) => {
return (
<Item
color={color}
onFirst={() => {
setFirst(color);
}}
/>
);
}}
/>
);
};key
The item object is used as the key to store its visibility status by default.
However, if a keyExtractor is provided, the return value of that function is used as the key instead.
Known Issue
Visibility Judgment
FlatList considers an item component as non-existent if it doesn't occupy space (e.g., <View />), even if the component is within the viewport.
On the other hand, FlashList considers an item as existent as long as it is within the viewport, even if it doesn't occupy space.
const Item = ({ id }: any) => {
useInViewPort(() => {
console.log(`${id} mount !!`);
return () => {
console.log(`${id} unmount !!`); // executed on FlatList
};
});
const [hide, setHide] = useState(false);
useEffect(() => {
setTimeout(() => {
setHide(true);
}, 1000);
}, []);
if (hide) return <View />;
return <View style={{ width: 10, height: 10 }} />;
};Therefore, the cleanup function of useInViewPort was not designed to run when unmounted, but depending on the situation, it may still run during unmounting.
Type Cast
I was unable to cast the input type directly to add the $$enabled property.
Despite trying various casting methods, both FlatList and FlashList could not infer the item type.
As a result, I had to override the property that uses the item type in props.
Therefore, while there should be no issue when wrapping FlatList, if you wrap a custom component (e.g., Example2), newly added properties like getItemLayout, CellRendererComponent, and getItemType might be recognized by the newly created component.
You may need to check if the original component has the same properties and override them as needed, like in Example2.
Observable Lists Must Connect to the Root
I will define the component wrapped with observe as Observable List.
All lists up to the root of the item where the useInViewPort hook is used must be Observable Lists.
If the nested list is not an Observable List, its items will not be properly tracked.
In the example below, when the inner FlatList becomes visible on the screen, it is considered that all of its items are being in the viewport.
const Example1 = () => {
return (
<ObservableFlatList
style={styles.container}
data={outerData}
ListHeaderComponent={<View style={styles.header} />}
renderItem={({ index: outerIndex }) => {
if (outerIndex % 10) return <TrackableItem label={`${outerIndex}`} />;
return (
<FlatList // not allowed
data={innerData}
horizontal
renderItem={({ index: innerIndex }) => {
return (
<TrackableItem
width={100}
label={`${outerIndex}-${innerIndex}`}
/>
);
}}
/>
);
}}
/>
);
};Sticky
FlatList excludes items that start being managed as Sticky Headers from viewableItems.
Because of this, even if an item with the sticky property is visible on the screen, it may be perceived as gone.
FlashList duplicates sticky items and overlaps them.
Because of this, items may appear twice and be perceived as disappearing.
useIsFirst in FlashList
In FlashList, sticky items are duplicated and overlaid with an absolute position.
This may cause state changes to not function properly. As a result, Example 4 will not work when using FlashList.
Additionally, since sticky headers in FlashList are treated as items outside of the list, any item being tracked as the first header will be considered "first" once it scrolls up by the height of the sticky header.
License
MIT
Made with create-react-native-library
1 year ago
1 year ago
1 year ago
1 year ago
1 year ago
1 year ago
1 year ago
1 year ago
1 year ago
1 year ago
1 year ago
1 year ago
1 year ago
1 year ago
1 year ago
1 year ago
1 year ago
1 year ago
1 year ago
1 year ago
1 year ago
1 year ago
1 year ago
1 year ago