0.1.4 • Published 6 years ago
react-sophia v0.1.4
React-Sophia
React-Sophia is a visualization plugin of javascript object trace which promotes development speed when you are debugging & logging variables. and it will provide other amazing features that is on the way!
Snapshot
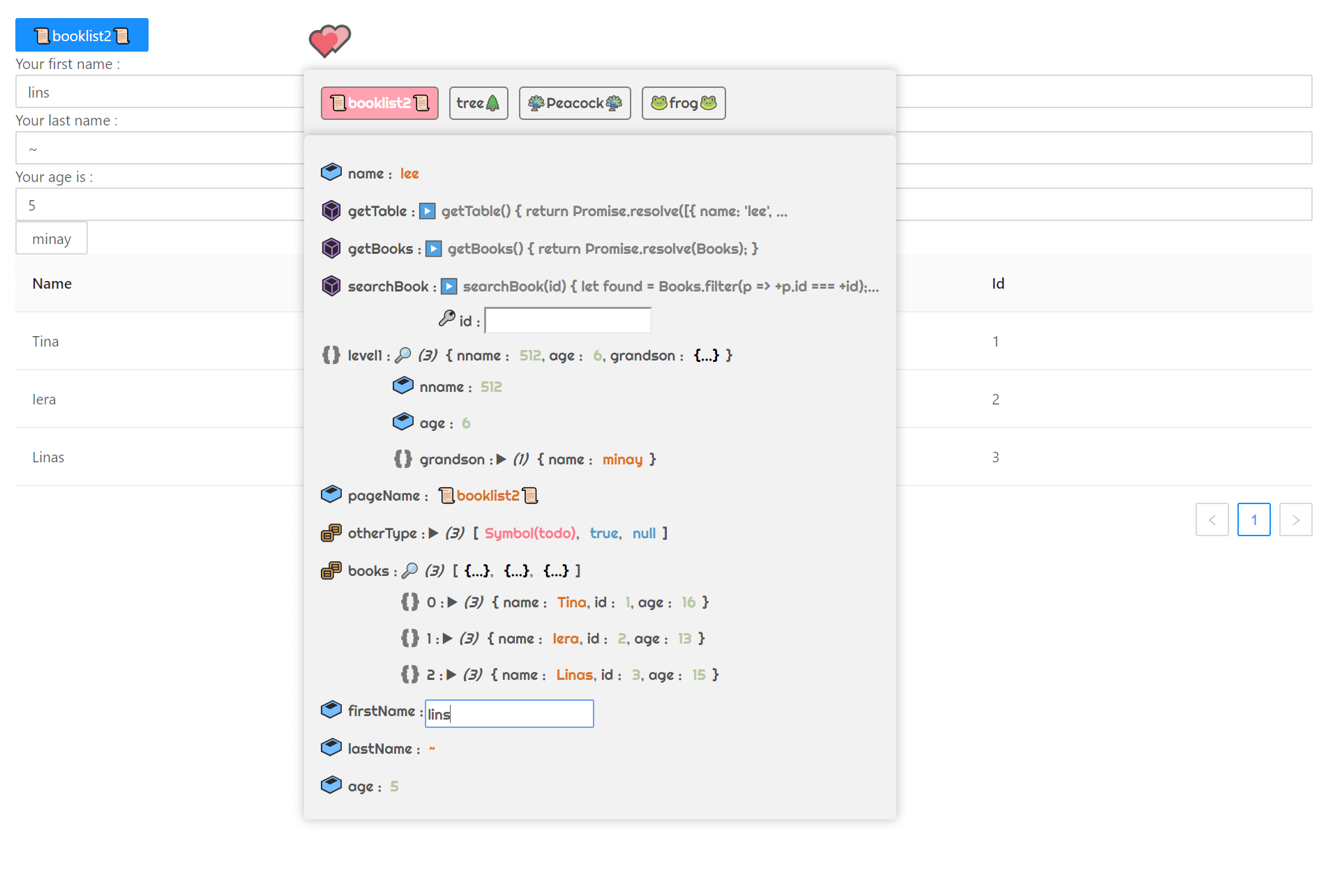
Features
- 🧹 Easy to update & maintain & restore Your ReactHookState by TypeScript data type inference
- 📺 Visualization Object Data Type
- 🐛 Debug your Code dynamically
- 🔌 Easy install & uninstall
- 🔮 Reflect metaData what ever you want
- 🖱️ Free drag to move by your 🐭.
Caution!!
- ❓ Don't forget to provide the sceneName as second parameter to useObject to when supervise mode
Installing
npm install react-sophiaSupported Framework
React
Example
- 🏗️ Step 1 : Put react-sophia component inside your top level of Component, it should be installed only once in your entire project that is better.
import React from 'react'
import { Book } from './test/bookList' // page components
import { Sophia } from 'react-sophia'
function App() {
return (
<div>
{/*🥦 import react-sophia in your top level of React components is recommended 🥦 */}
<Sophia emojiIcon="💕" supervise /> {/* you can enable supervise in development mode or remove supervise property in production mode */}
<Book />
<.../>
</div>
)
}
export default App- 🏗️🏗️ step 2 : To provide Data to react-sophia for supervise. you should call useObject from react-sophia
import React from 'react'
import { useObject } from 'react-sophia'
const Home = () => {
const { object, updateObject, recover } = useObject(
{
house: {
address: 'milkyway...'
area: { width: 10000: height:20000}
},
bookshelf: ["English","Math"],
firstName: 'linda',
lastName: 'fosn',
age: 999,
},
{ sceneName: `🦠linda's home🦠` }
)
return (
<>
Your first name : <Input type="text" value={object.firstName} onChange={e => updateObject('firstName', e.target.value)} />
Your last name : <Input type="text" value={object.lastName} onChange={e => updateObject('lastName', e.target.value)} />
<button>my age is {object.age}</button>
</>
)
}react-sophia API
- import { useObject } from 'react-sophia'
/**
* This function is a multifunction which take 2 arguments that used to reserve ObjectState for you in your page,
* you can call this function multi times in the same page or other pages.
* @template T is object type like `{} , {age:5} , {age:5, cardNames:[100,200,300]}` all were valid.
* @param initO The data object typeof `T` which want to reserve data for you
* @param [option]
* @returns { object,updateObject,recover}
*/
export function useObject<T extends { [key: string]: any }>(
initO: T,
option: {
/**
*In supervise mode only... remember that `Do Not Use` the same `name` in the project otherwise stateName in the panel will be rendered only once...
* sceneName = 'name1' or 'name2' were corrent.
* sceneName = 'abc' or 'abc' were incorrent.
*/
sceneName?: string
} = {}
)
// usage 1 regular mode
const { object, updateObject, recover } = useObject({ name: 'lee', age: 5 })
// usage 2 regular & supervise mode
const { object, updateObject, recover } = useObject({ name: 'lee', age: 5 }, { sceneName: '🐷hello twins🐷' })- object is readonly which as same as UseState() of hooks's return arguments of the index 0 at the Array,
const { object } = useObject({ name: 'lee', age: 5 })- updateObject is overload and super function basically as same as UseState of hooks's return arguments of the index 1 at the Array. but its other features
function updateObject(obj: Partial<T>): void
function updateObject<P extends keyof T>(key: P, value: T[P]): void
function updateObject<P extends keyof T>(key?: P, value?: T[P]) {.......}
const { updateObject } = useObject({ name: 'lee', age: 5 })
// usage 1 update a single property for object directly
// 💡in TypeScript the first & second arguments keys value range were restricted and infered which can help you check data type is valid. but also in Javascript, unfortunately Javascript didn't throw a error when you are developing.
updateObject('name', 'li') //syntax available ✅
// usage2 update arbitrary properties for object directly
// in TypeScript update object properties count should not be out of range of initO(previous parameter name) when you passed into useObject({...}) because here has a type checking
updateObject({ name: 'li', age: 6 }) // syntax available ✅
updateObject({ name: 'li'}) //syntax available ✅- recover to restore the initial object state
/** Recover all the values of each property which you passed in at the `useObject` at the beginning.*/
function recover(): void
/**
* Recover all the values of each property which you passed in at the `useObject` at the beginning.
* @param omit Omit some of properties of those you wouldn't want to recover.
*/
function recover(omit?: (keyof T)[]): void
function recover(omit?: (keyof T)[]): void {......}
//usage 1
const {object, updateObject,recover } = useObject({ name: 'lee', age: 5 ,male : true})
updateObject({ name: 'li', age: 6000 }) // => object : { name : "li", age : 6000, male : true }
recover() // => object : { name: 'lee', age: 5 ,male : true}
//usage2
const {object, updateObject,recover } = useObject({ name: 'lee', age: 5 ,male : true})
updateObject({ name: 'lee222', age: 5555, male: false }) // => object : { name : "li", age : 6000, male : true }
recover(['male']) // => object : { name: 'lee', age: 5 ,male : false}