react-transpose v1.0.5
react-transpose
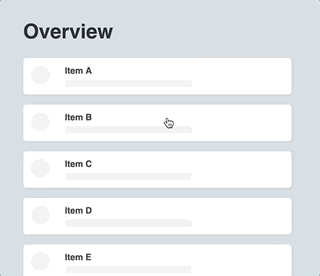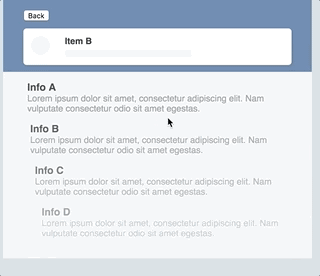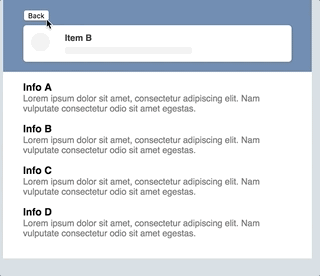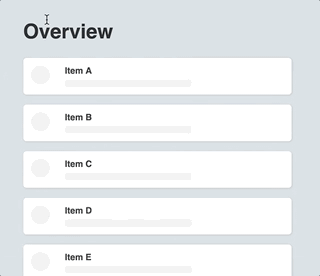
react-transpose is a set of tools which helps you animate route or component transitions. It also enables you to animate shared-element transitions.
This package makes use of the awesome library popmotion for it's animations. This means that under the hood it uses the same spring / tween / etc.. animations types, and since this is a react package, it has some strong simularities with react-pose. In a way, this package can be seen as an extension on top of react-pose.
Why not use PoseGroup?
While PoseGroup is excellent in most use-cases probably way more suffisticated, sometimes it's hard to handle route specific configuration. What if you wanted to animate the entering direction of a component based on the route it was comming from? That's where react-transpose comes in: for each transition-state (enter / exit) it gives you additional props for acting on specific route-transitions. On top of that this package provides tools to create so called shared-element transitions.
Install
npm install --save react-transposeor
yarn add react-transposeThis package has a peer-dependency on popmotion, so make sure to install this package together with popmotion@^8.6.0. If your project is using popmotion's react-pose there is no need to install popmotion since react-pose already has a dependency on it.
Usage
Simple demo
import * as React from "react";
import { SwitchGroup, Stage, transposedShared } from "react-transpose";
const Box = transposedShared.div({
// declare which style-props should be animated
animationProps: ["width", "height", "backgroundColor"],
// standard react-pose transition config
transition: {
// animation type (spring / tween / keyframes / etc...)
type: "tween",
duration: 300
},
// for identifying shared elements
sharedKey: "box"
});
function App() {
const [currentStage, setStage] = React.useState("route-a");
// toggle stage every second
React.useEffect(() => {
const id = setInterval(() => {
setStage(currentStage =>
currentStage === "route-a" ? "route-b" : "route-a"
);
}, 1000);
return () => clearInterval(id);
}, []);
return (
<div style={{ position: "relative" }}>
<SwitchGroup stage={currentStage}>
<Stage
stage="route-a"
render={() => (
<div style={{ position: "absolute" }}>
<Box
style={{ width: 100, height: 100, backgroundColor: "blue" }}
/>
</div>
)}
/>
<Stage
stage="route-b"
render={() => (
<div style={{ position: "absolute" }}>
<Box
style={{ width: 200, height: 200, backgroundColor: "red" }}
/>
</div>
)}
/>
</SwitchGroup>
</div>
);
}Other demo's
API
SwitchGroup
It's main purpose is to render the right <Stage /> out of one or multiple stages (paths/routes) given a current stage. It has a similar function to Switch in react-router.
| Prop | type | required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| children | ReactNode[] | yes | Must be one or more <Stage /> elements |
| stage | string | yes | the current stage |
| setStage | (stage: string) => void | no | Use in combination with useStage to set a stage from deeper within the tree |
example
import { SwitchGroup, Stage } from "react-transpose";
function App() {
const [currentStage, setStage] = React.useState("a");
return (
<SwitchGroup stage={currentStage} setStage={setStage}>
<Stage stage="a" render={() => <div>A</div>} />
<Stage stage="b" render={() => <div>B</div>} />
</SwitchGroup>
);
}Stage
Used to represent a stage or path, much like a <Route /> in react-router.
Use either the render or the component prop.
| Prop | type | required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| stage | string | yes | |
| render | () => ReactElement | no | |
| component | Component | no |
useStage
Helper hook to set a stage from deeper within the tree. Note: the 'setStage' prop must be given to the <SwitchGroup /> component.
import { useStage } from "react-transpose";
function Route() {
const { setStage } = useStage();
return <button onClick={() => setStage("next")}>Goto next route</button>;
}Group
Similar to <SwitchGroup />, but lets you handle the routing mechanism. Useful in combination with react-router for example.
| Prop | type | required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| currentPath | string | yes | path of current location |
| children | ReactElement | yes | Can only be one child at a time |
example with react-router
function App({ location }) {
return (
<Group currentPath={location.pathname}>
<Switch location={location}>
<Route exact path={"/"} component={Home} />
<Route exact path={"/about"} component={About} />
</Switch>
</Group>
);
}transposed
Function which creates components with animation capabilities. As with libraries as styled-components and react-pose, you can either pass in a existing component (don't forgot to forward the ref to a dom-node), or a tag name. So these all work:
// existing component
import Box from "./Box";
const AnimatedBox = transposed(Box)({});
// argument string
const AnimatedBox = transposed("div")({});
// helper method
const AnimatedBox = transposed.div({});Config
| Prop | type | required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| animateFirst | boolean | no | defaults to false. Determines whether to animate entering the first route |
| enter | object | (props: TransitionProps) => object | yes | see below |
| exit | object | (props: TransitionProps) => object | yes | see below |
The enter and exit prop takes either a function returning an object, or a plain object. It is almost the same as how react-pose does it. For example:
const Box = transposed.div({
enter: {
// style props...
opacity: 1,
x: 0,
backgroundColor: 'red',
transition: { // info about transition
type: "spring"
stiffness: 200, // specfic spring prop
damping: 25, // specfic spring prop
delay: 500 // different from react-pose
}
},
exit: {
opacity: 0,
x: 100,
backgroundColor: 'blue',
transition: {
type: "tween"
duration: 400 // specific tween prop
}
}
})When passing a function, you'll get a object with these properties
| Prop | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| path | { from: string: to: string } | |
| props | object | Provides access to the wrapped component's props |
| direction | "in" | "out" | Especially useful for exit. When entering, react-transpose looks at the exit state to determine where to animate from. In that case the direction is "in". When exiting, react-transpose looks at the exit state again, only this time with direction "out" |
For example:
const Box = transposed.div({
enter: ({ props }) => ({
opacity: 1,
x: 0,
transition: {
type: "spring",
delay: props.index * 100 // staggering effect
}
}),
exit: ({ path, direction }) => ({
opacity: 0,
// animate differently based on direction and path.from
x: path.from === "a" && direction === "in" ? -100 : 300
})
});transposedShared
Quite similar to transposed, but it's main purpose is to animate shared-element transitions.
Config
| Prop | type | required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| sharedKey | string | (props: object) => string | yes | for identifying shared elements |
| animationProps | string[] | yes | style-props to be animated |
| transition | object | (props: TransitionProps) => object | yes | see below |
| whenNotShared | { enter: object; exit: object; animatedFirst: boolean } | no | see below |
Example:
const Box = transposedShared.div({
sharedKey: props => props.id,
animationProps: ["x", "y", "width", "height"],
transition: {
type: "spring",
stiffness: 400,
damping: 30
},
// (optional) practically same as transposed config
whenNotShared: {
enter: { opacity: 1 },
exit: { opacity: 0 }
}
});
const BoxContext = React.createContext();
function List() {
const { gotoDetail } = React.useContext(BoxContext);
return (
<div>
<Box id="1" onClick={() => gotoDetail("1")} />
<Box id="2" onClick={() => gotoDetail("2")} />
<Box id="3" onClick={() => gotoDetail("3")} />
<Box id="4" onClick={() => gotoDetail("4")} />
</div>
);
}
function Detail() {
const { gotoList, selectedBox } = React.useContext(BoxContext);
return (
<>
<button onClick={gotoList}>Back</button>
<Box id={selectedBox} />
</>
);
}
function App() {
const [state, setState] = React.useState({
stage: "list",
selectedBox: null
});
const payload = React.useMemo(
() => ({
...state,
gotoDetail: box => setState({ stage: "detail", selectedBox: box }),
gotoList: box => setState({ stage: "list", selectedBox: null })
}),
[state]
);
return (
<BoxContext.Provider value={payload}>
<SwitchGroup stage={state.stage}>
<Stage stage="list" component={List} />
<Stage stage="detail" component={Detail} />
</SwitchGroup>
</BoxContext.Provider>
);
}License
MIT © everweij

