restea v0.0.0-0
restea
restea is a collection of several middleware functions that can be composed in order to validate incoming (and outgoing) data in a declarative and documenting way. restea is built to be used with TypeScript and koa with @koa/router.
These middleware, not only do the validation but they also provide types inside the handler function. See example below:
router.get(
'/users',
compose(
description('Fetch a paginated list of users.'),
paginated(),
sortable({ fields: ['id', 'name'], default: '+id' }),
query('role', string('none', 'admin'), {
description: 'If provided will filter users based on this role',
}),
returns(Ok(ArrayOfSchema(UserSchema)))
),
(ctx, next) => {
const {
offset, // `number`
limit, // `number`
sort, // `Sorting<'id' | 'name'>`
role, // `'none' | 'admin'`
} = ctx.state.params;
...
}
);If the wrong value is passed for any of the parameters the endpoint will return an error explaining what went wrong:
curl http://localhost:3000/users?role=nonne{
"error": {
"status": 422,
"code": "InvalidParameter",
"message": "Invalid query parameter 'role'. Expected 'none' | 'admin' but received: 'nonne'"
}
}An additional benefit of using restea is that these middleware are holding the necessary metadata that allows the generation of an Open API schema. See below an example of the generated docs for the previous example.
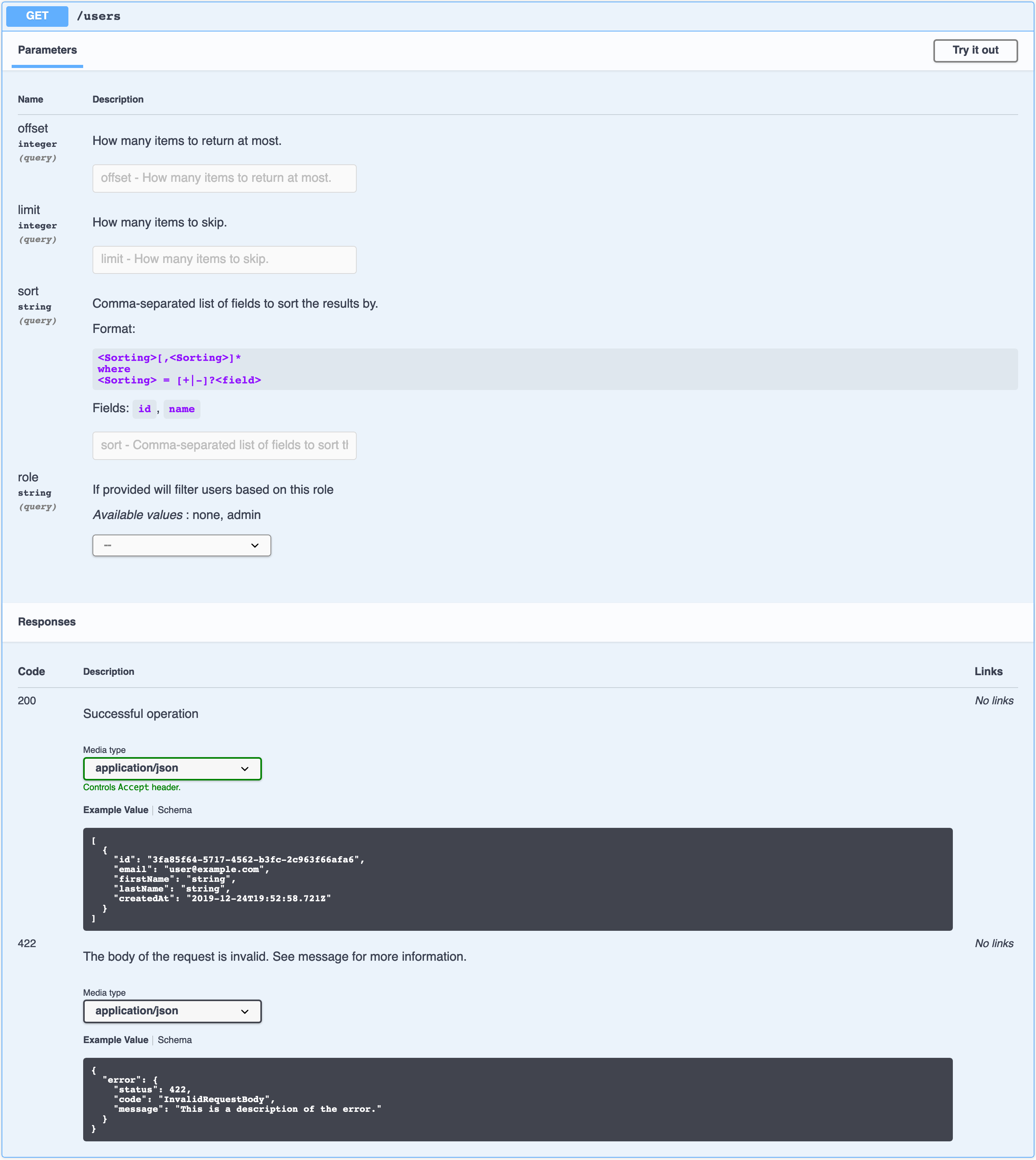
Run the example
Running the example is the best way to see restea in action
git clone https://github.com/santialbo/restea
cd restea
yarn
cd example
yarn
yarn devNow head to https://editor.swagger.io/ and load the spec from http://localhost:3000/schema.
How to use
Installation
npm install resteaor
yarn add resteaList of middleware
query: Use it to validate/parse query parameters. See example:import { query, regex } from 'restea'; ... router.get('/post', query('slug', regex(/^[a-z0-9-]+$/), async (ctx, next) => { return await controller.loadPost(ctx.state.params.slug); })parameter: Use it to validate/parse path parameters. See example:import { query, uuid } from 'restea'; ... router.get('/post/:postId', query('slug', uuid()), async (ctx, next) => { return await controller.loadPost(ctx.state.params.postId); })body: Use it to validate/parse the incoming body of the request:import { query, uuid } from 'restea'; ... interface CreatePost { title: string; content: string; } const CreatePostSchema: JsonSchema<CreatePost> = { type: 'object', required: ['title'], properties: { title: { type: 'string', maxLength: 255 }, content: { type: 'string' } } }; router.post('/post/', body({ schema: CreatePostSchema }), async (ctx, next) => { return await controller.createPost(ctx.state.body); // ctx.state.body is `CreatePost` })
6 years ago