rfvis v0.1.0
RFVis
A tool for visualizing the structure and performance of Random Forests.
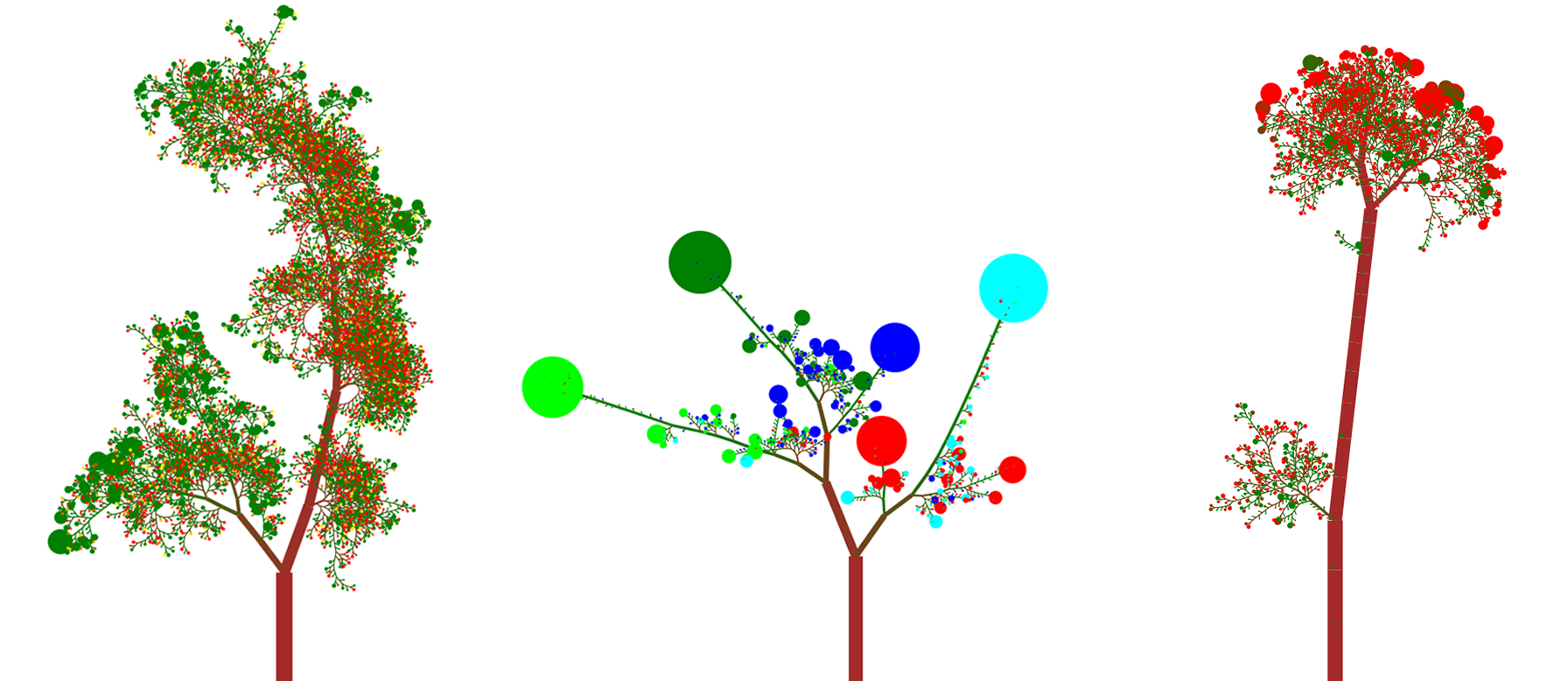
Getting Started
As a prerequisite you need Node.js v8 or higher. To install RFVis run:
$ npm install -g rfvisThe tool offers a command line interface to either generate SVG files directly from your input data (rfvis cli <data>) or to spin up a web-based GUI for a more interactive analysis (rfvis gui <data>).
To see all available commands run:
$ node rfvis
rfvis [command]
Commands:
rfvis cli <data> Command line interface to generate SVGs
rfvis gui <data> Graphical User Interface
Options:
--help Show help [boolean]
--version Show version number [boolean]The Graphical User Interface
To interactively analyze your forest with the web-based GUI run:
$ rfvis gui /path/to/data
Starting server
GUI running at http://localhost:3000You can now open up your browser at http://localhost:3000 to see something like this:
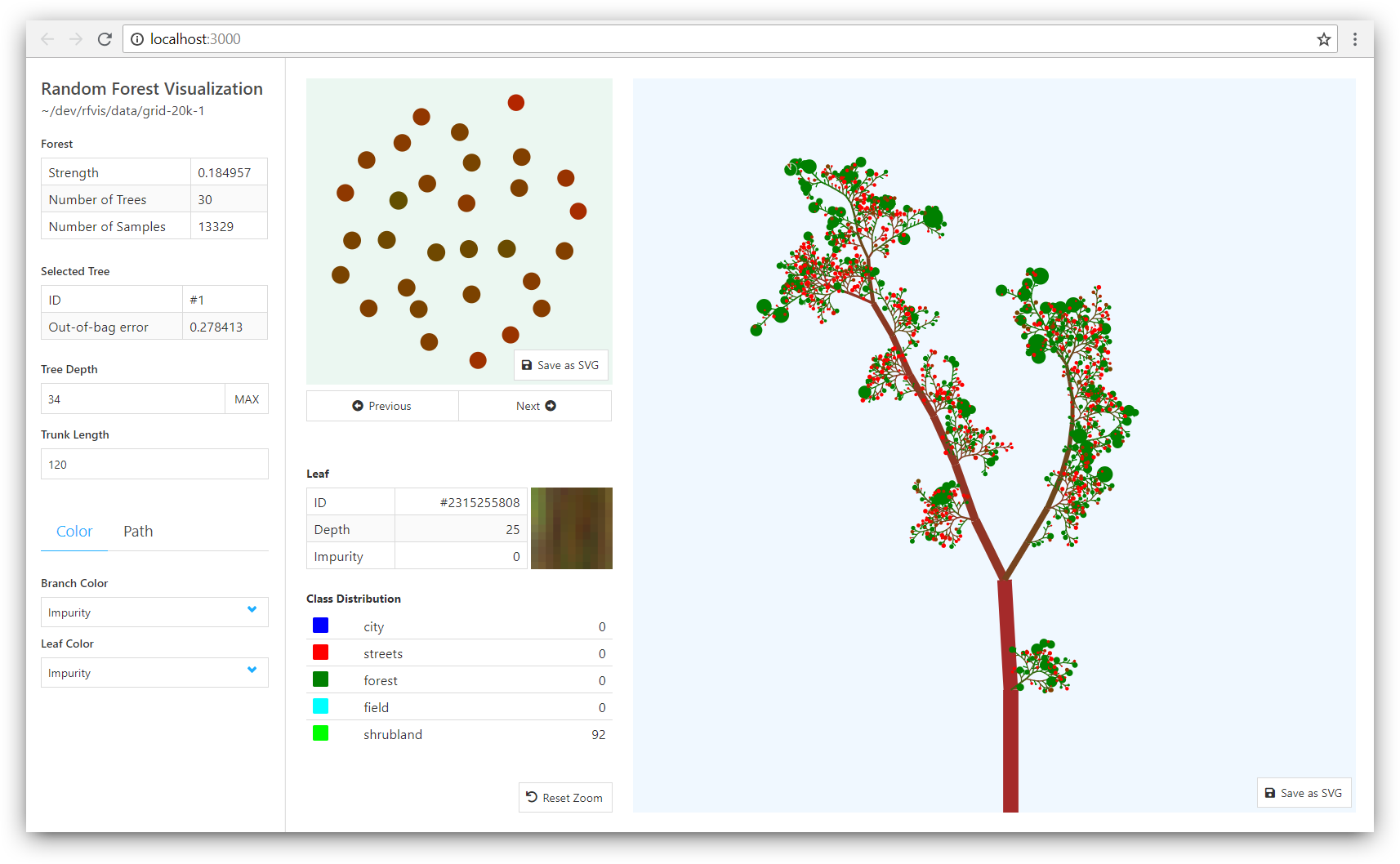
Note: The web-based GUI is currently only tested on Google Chrome.
The Command Line Interface
To use the command line interface and generate SVG files for each tree in the input data, run:
$ rfvis cli /path/to/data --out result
>> Exported "/dev/random-forest-visualization/result/tree-0.svg"
>> Exported "/dev/random-forest-visualization/result/tree-1.svg"
>> Exported "/dev/random-forest-visualization/result/tree-2.svg"
>> Exported "/dev/random-forest-visualization/result/tree-3.svg"
...Get a full list of available options with --help:
$ rfvis --help
rfvis cli <data>
Command line interface to generate SVGs
Positionals:
data Folder containing the forest data [required]
Options:
--help Show help [boolean]
--version Show version number [boolean]
--out, -o Output folder for the SVG files. If omitted the current
working directory is used.
--width, -w Width of the SVG [number] [default: 800]
--height, -h Height of the SVG [number] [default: 800]
--trunk-length, -t Length of the trunk which influences the entire tree size
[number] [default: 100]
--depth, -d Depth of the tree rendering. Cut of leaves are visualized
as pie chart consolidation nodes. [number]
--leaf-color Color of the leaves. Either the leaf impurity or the
class assigned to the leaf.
[choices: "impurity", "class"] [default: "impurity"]
--branch-color Color of the branches. Either the node impurity or the
node drop-of-impurity.
[choices: "impurity", "impurity-drop"] [default: "impurity"]Input Data
The input data is expected to come in text files in the following folder structure:
./forest.txt: A text file containing the correlation matrix, tree strengths and overall forest strength./tree_<index>.txt: One text file per tree in the forest with semicolon-separated values in the following format:Internal nodes: height; -; 0; size; impurity; drop of impurity; splitting grade; list of used feature IDs; fusion ID; path prediction, split point def; list of score IDsLeaf nodes: height; ID; 1; size; impurity; class frequency
Development
To build and use the project locally just run npm run build and npm link.
In order to make development more convenient (which means not having to run npm run build after every change) you can run watchers on the source files. The recommended setup for development is to open two terminal processes and run:
1. npm run watch:frontend to automatically build any changes in the frontend related JS or SCSS files
2. npm run watch:backend to automatically build any changes in the command line interface or the server related JS files
Note that many files are used by the frontend and backend, e.g. the logic for constructing and drawing the trees. A change to ./src/draw_tree.js will therefore trigger both watchers.
Built With
- D3.js - Data Visualization Library
- Yargs - Command Line Parsing Library
- Bulma - Lightweight CSS Framework
- Express - Web Application Framework
- rollup.js - Module Bundler / Build Tool
TODOs
- Simplify and document input data format
- Provide scripts to export RFVis-readable data for the most common Random Forest implementations, e.g. sklearn.ensemble.RandomForestClassifier
- Refactor the project to use a proper frontend lib instead of jQuery to be able to add more features in the future