saga-transaction-manager v1.0.1
summary
saga-transaction-manager is a Saga model distributed transaction framework that can easily handle distributed transactions
Introduction to the Saga Transaction Pattern
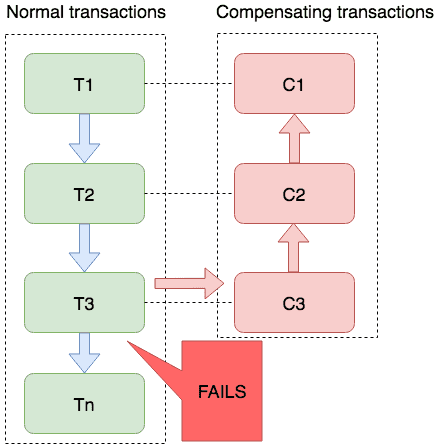
Saga = Long Live Transaction (LLT)
- Core Idea
A long transaction is divided into multiple local transactions, each with a corresponding compensation transaction. When a long transaction fails, the compensation transactions are executed in reverse order to roll back the entire long transaction.
- Applicable Scenarios
Long business processes, complex business processes Participants include other companies or legacy system services Need to ensure eventual consistency of the transaction
- Implementation Methods
There are two common Saga implementation methods: Choreography and Orchestration. This project uses the Saga Orchestration pattern.
- Choreography
Each local transaction publishes domain events in other services to trigger local transactions in those services. The responsibility is distributed among the Saga participants. Each service is independent and has its own business logic, and needs to ensure whether to continue the next process.
- Orchestration
The Saga orchestrator handles all transactions and instructs the participants to perform the appropriate operations based on the events. Simpler implementation
Quick Start
Run the example
From the examples/serviceProxy directory:
- Implement the
ISagaTransactionServiceinterface for local transactions and compensation transactions.
import { ISagaTransactionService } from 'saga-transaction-manager';
// Implement a short transaction
class CreateUserTransaction implements ISagaTransactionService {
execute() {
// Business logic for creating a user
return Promise.resolve();
}
compensate() {
// Business logic for rolling back the user creation operation
return Promise.resolve();
}
}
class UpdateProfileTransaction implements ISagaTransactionService {
...
}
class SendWelcomeEmailTransaction implements ISagaTransactionService {
...
}- Use
TmSequentialExecutionto orchestrate the transactions.
import { TmSequentialExecution } from 'saga-transaction-manager';
// Orchestrate the long transaction
const transactionManager = new TmSequentialExecution();
transactionManager.addTransaction(new CreateUserTransaction());
transactionManager.addTransaction(new UpdateProfileTransaction());
transactionManager.addTransaction(new SendWelcomeEmailTransaction());
// Execute the long transaction, compensation transactions will be automatically executed on failure
transactionManager.execute();- Orchestrator with Context
For long transactions that require storing shared variables, you can use the SagaServiceWithContext abstract class and TmSequentialExecutionWithContext to orchestrate the transactions.
import { SagaServiceWithContext } from 'saga-transaction-manager';
class CreateUserTransaction extends SagaServiceWithContext {
constructor() {
super();
}
execute() {
// set shared variables
this.context?.setVariable('A', 'valueA');
}
compensate() {
// get shared variables
this.context?.getVariable('A')
}
}import { TmSequentialExecutionWithContext } from 'saga-transaction-manager';
// Orchestrate the long transaction
const transactionManagerWithCtx = new TmSequentialExecutionWithContext();
transactionManagerWithCtx.addTransaction(new CreateUserTransaction());
transactionManagerWithCtx.addTransaction(new UpdateProfileTransaction());
transactionManagerWithCtx.addTransaction(new SendWelcomeEmailTransaction());
// Execute the long transaction, compensation transactions will be automatically executed on failure
transactionManagerWithCtx.execute();Limitations
- Cannot guarantee isolation
- No control over hanging: If the original service times out and the compensation service executes, the original service may still complete.
- Implementation Suggestions
Ensure that the service and compensation service are idempotent.
todo
- Actor model retry mechanism
- Annotation-based implementation of Saga
service1(){}
@SagaCompensiable(method='service1')
compensiteFunction(){}
@SagaTransactional
process(){
service1()
service2()
}- Support the use of message queues to store orchestration information
- Implement Saga using a state machine engine, Orchestrator is extensible