strict-content-mathml-editor v1.0.3
Strict Content MathML Editor
This editor helps to create Strict Content MathML 3.0 expressions.
Demo
Visit https://ifte-eda.github.io/strict-content-mathml-editor/ for a simple demo page that displays the generated Strict Content MathML code.
Screenshot
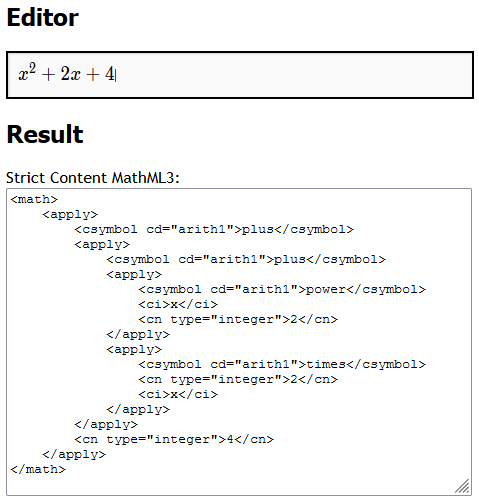
Features
- Support of custom symbols, e.g. type
Umaxand get the single symbol Umax instead of the product Umax in the formula editor - Support of SI prefixes and units
- Support of piecewise-defined expressions
- Automatic detection of integers, real numbers and rational numbers
Installation
npm install strict-content-mathml-editorUsage
The editor component is provided by Guppy which is licensed under the MIT License.
This package provides the function guppy_xml_to_mathml to convert Guppy's internal XML format to Strict Content MathML.
For a simple demo web page with the formula editor and a text field displaying the resulting MathML code, the following files index.html and mathml-editor.js are required.
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="node_modules/guppy-js/guppy-default-osk.min.css">
<script type="text/javascript" src="node_modules/guppy-js/guppy.min.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="node_modules/guppy-js/guppy_osk.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/vkiryukhin/vkBeautify@master/vkbeautify.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="node_modules/strict-content-mathml-editor/guppy-xml-to-mathml.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="mathml-editor.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<h2>Editor</h2>
<div id="guppy1"></div>
<h2>Result</h2>
<div class="label">Strict Content MathML3: </div>
<textarea type="text" id="output_mathml" class="output" rows="30" cols="100"></textarea>
</body>
</html>mathml_editor.js
window.onload = function(){
// ID of the editor's div
var editor_id = "guppy1";
// output textarea
var output_mathml = document.getElementById("output_mathml");
// update output textarea when editor content changes
var update_output = function(e) {
try {
var engine = e.target.engine;
var doc = engine.doc;
var content = (new XMLSerializer()).serializeToString(guppy_xml_to_mathml(engine, doc));
content = vkbeautify.xml(content, 4);
output_mathml.value = content;
}
catch(e) {
output_mathml.value = "Failed to parse input: " + e.message;
}
}
// tab completion after backslash prints all candidates in the output textarea
var completion = function(e) {
output_mathml.value = e.candidates.join(", ");
}
Guppy.init({
"osk":new GuppyOSK(),
"path":"node_modules/guppy-js",
"symbols":["node_modules/guppy-js/sym/symbols.json","node_modules/strict-content-mathml-editor/strict-content-mathml-symbols.json"],
"events": {
"ready": update_output,
"change": update_output,
"completion": completion
},
"settings":{
"empty_content": "{\\text{Click to start typing math!}}"
},
});
var g1 = new Guppy(editor_id);
}Custom Symbols
You can define custom mathematical/physical symbols for later use in the formula.
Example: By defining a custom symbol, you can type Umax in the formula editor and get the single symbol Umax instead of the product Umax. In this case, the resulting MathML is <ci>Umax</ci>.
Guppy.add_global_symbol("Umax", {
"output": {
"latex": "U_\\text{max}",
"asciimath": "Umax"
},
"attrs": {
"group": "custom",
"type": "Umax"
}
});Supported Content Dictionaries
In Strict Content MathML3, all mathematical concepts are grouped in content dictionaries. Currently, this formula editor supports the following content dictionaries and concepts:
arith1
- abs
- divide
- minus
- plus
- power
- product
- root
- sum
- times
- unary_minus
calculus1
- defint
- diff
- int
directives1
- evaluate
integer1
- factorial
linalg2
- matrix
- matrixrow
- vector
logic1
- and
- false
- nand
- nor
- not
- or
- true
- xnor
- xor
norm1
- Euclidean_norm
nums1
- infinity
piece1
- piece
- piecewise
- otherwise
prog1
- assignment
- block
- call_arguments
- def_arguments
- for
- global_var
- if
- function_block
- function_call
- function_definition
- local_var
- procedure_block
- procedure_call
- procedure_definition
- return
- while
relation1
- eq
- lt
- gt
- neq
- leq
- geq
rounding1
- ceiling
- floor
transc1
- arccos
- arcsin
- arctan
- cos
- cosh
- cot
- csc
- ln
- log
- sec
- sin
- sinh
- tan
- tanh
units_siprefix1
- yocto
- zepto
- atto
- femto
- pico
- nano
- micro
- milli
- centi
- deci
- deka
- hecto
- kilo
- mega
- giga
- tera
- peta
- exa
- zetta
- yotta
units_time1
- calendar_month
- calendar_year
SI_BaseUnits1
- ampere
- candela
- kelvin
- kilogram
- metre
- mole
- second
SI_NamedDerivedUnits1
- becquerel
- coulomb
- degree celsius
- farad
- gram
- gray
- henry
- hertz
- joule
- katal
- lumen
- lux
- newton
- ohm
- pascal
- radian
- siemens
- sievert
- steradian
- tesla
- volt
- watt
- weber
SIUsed_OffSystemUnits1
- bel
- day
- hour
- litre
- minute
- neper
- tonne
- degree of arc
- minute of arc
- second of arc