supercollider-redux-sequencers v0.9.14
supercollider-redux-sequencers
A Node.js and SuperCollider framework for generative musical sequencers based on supercollider-redux. Provides the ability to start and stop SuperCollider patterns from Node.js and state updates to the Node.js process at each event played.
The SuperCollider pattern generators are intended to be written using the Pbind library, a prominent way to build generative event generators in SuperCollider.
The Node.js interface to SuperCollider is a Redux state store, all starting and stopping of sequencers occurs via actions dispatched to the store, and all note events received from the sequencers are actions dispatched from the SuperCollider state store.
State Overview
State of all sequencers is stored by id in sequencers. Each sequencer has the following attributes:
sequencerId: A unique identifier for this sequencer, also used as the key to lookup insequencersclassString: A string representing the class to instantiate, expected to be a subclass of SCReduxSequencer. In SuperCollider this is interpreted as a class and instantiated.beat: A count of the events that have passed.nextBeat: The SuperCollider clock beat on which the next event will occur.nextTime: The time in seconds when the next event will occur (measured from the previous event).numBeats: The duration of the sequence in clock beats. If the sequence loops, this is the duration of one loop.playingState: One ofPLAYING_STATESindicating if the sequence is stopped, queued, playing, etc.isReady: True if the sequencer's resources have initialized and it is ready to play.playQuant,stopQuant, andpropQuant: These are the Quant values to determine when the sequencer should quantize play, stop, or property changes.lastPropChangeQueuedAt: A timestamp indicating when aPROP_CHANGE_QUEUEDwas dispatched.lastPropChangeAt: A timestamp indicating when properties last changed in response to aPROP_CHANGE_QUEUEDaction.event: The details of the most recently played event from the stream.midiOutDeviceName,midiOutPortName: If the stream is to send events to a midi socket instead of a SuperCollider synth, this is the device name and port.
Sequence Example
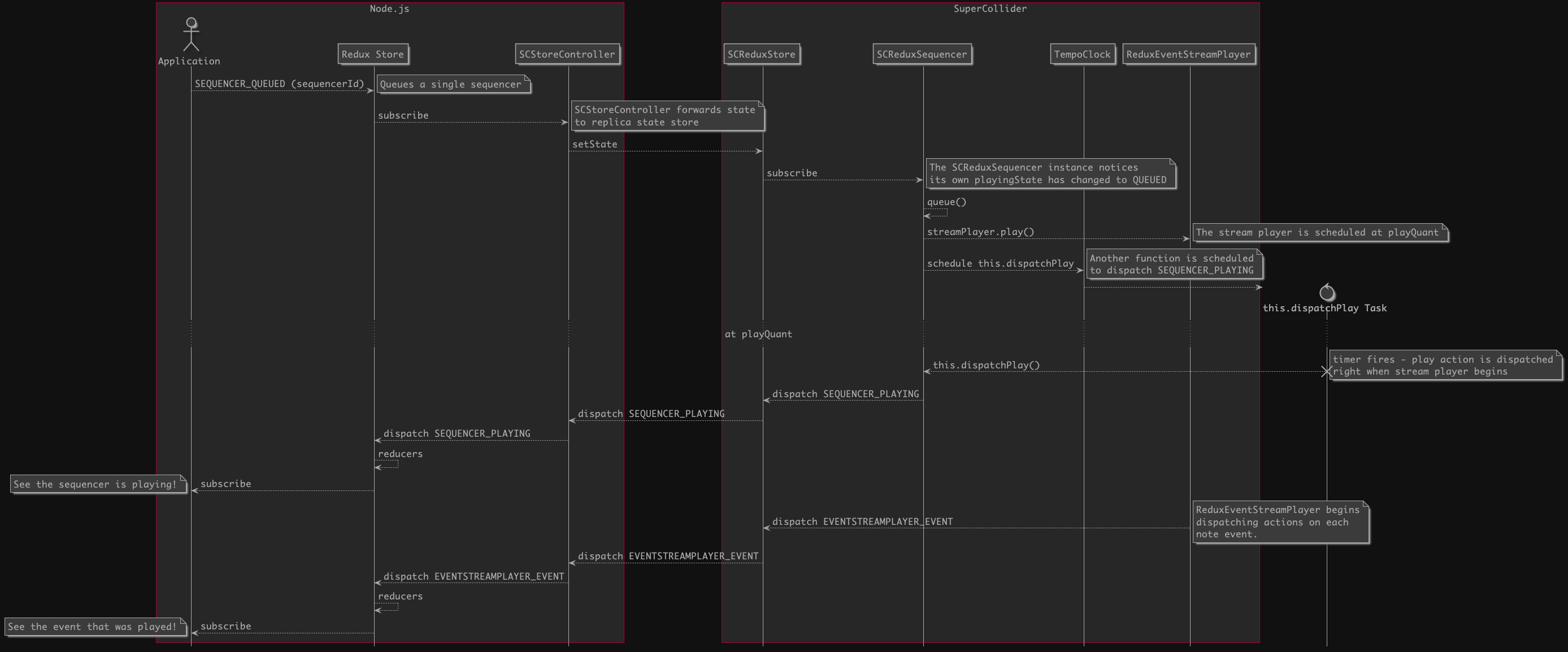
SuperCollider API
All SuperCollider code is included in a quark inside the quarks/supercollider-redux-sequencers directory.
SCReduxSequencer
Plays a stream to a specific clock and with a ReduxEventStreamPlayer. Responds to state changes in the store, scheduling starting and stopping of the event stream player appropriately. To use, create a subclass and implement initStream. Everything else is optional.
MetronomeSequencer : SCReduxSequencer {
var pat,
patStream,
patchSynth;
initPatch {
// define a simple synth
patch = Patch({
arg freq, amp = 0.0;
var out;
out = SinOsc.ar(freq, 0, amp) * EnvGen.kr(Env.linen(0.001, 0.05, 0.3), doneAction: 2);
[out, out];
});
patchSynth = patch.asSynthDef().add();
^patch
}
initStream {
pat = Pbind(
// the name of the SynthDef to use for each note
\instrument, patchSynth.name,
\midinote, Pseq([96, 84, 84, 84], inf),
// rhythmic values
\dur, 1
);
^pat.asStream();
}
}SCReduxSequencerFactory
Watches the sequencers dictionary at the root level of the state tree and instantiates sequencers. Expects a store from which to look for state changes:
var store, sequencerFactory;
store = SCReduxStore.getInstance();
sequencerFactory = SCReduxSequencerFactory.getInstance();
sequencerFactory.setStore(store);Internal classes:
ReduxEventStreamPlayer: This is a subclass ofEventStreamPlayerwhich will dispatch actions each time an event from the stream is played. Very useful for modifying other state based on the playback of a Pattern, for example.SCReduxSequencers: A class providing a static object for action types.
Examples
To run the examples:
npm installFor each example, there is a Node.js script and a SuperCollider script that must be run simultaneously.
Basic Example
This example plays a metronome implemented in MetronomeSequencer.sc. It is now in testMetroExample.js as well.
$ npm run start_exampleParameterized
This example demonstrates one way a SuperCollider pattern can be parameterized through the state store. See ParamExampleSequencer in the quark.
$ npm run start_parameter_exampleSampler
This example demonstrates a sampler that requires samples are loaded. NOTE: This example depends on cs-supercollider-lib. Perhaps best useful for reference.
$ npm run start_sampler_exampleUnit Tests
$ npm run test