1.0.2 • Published 9 years ago
vue-hyper v1.0.2
Vue-hyper
Prototyping extremely dynamic interfaces. Programming html without directly using html
Install
# Using npm
$ npm install --save vue-hyper
# Using yarn
$ yarn add vue-hyperImport
import Vue from 'vue'
import VueHyper from 'vue-hyper'
import Schema from './schema'
new Vue({
el: '#app',
name: 'hello',
data () {
return {
schema: Schema
}
},
template: '<VueHyper :schema="schema"/>',
components: { VueHyper }
})Schema
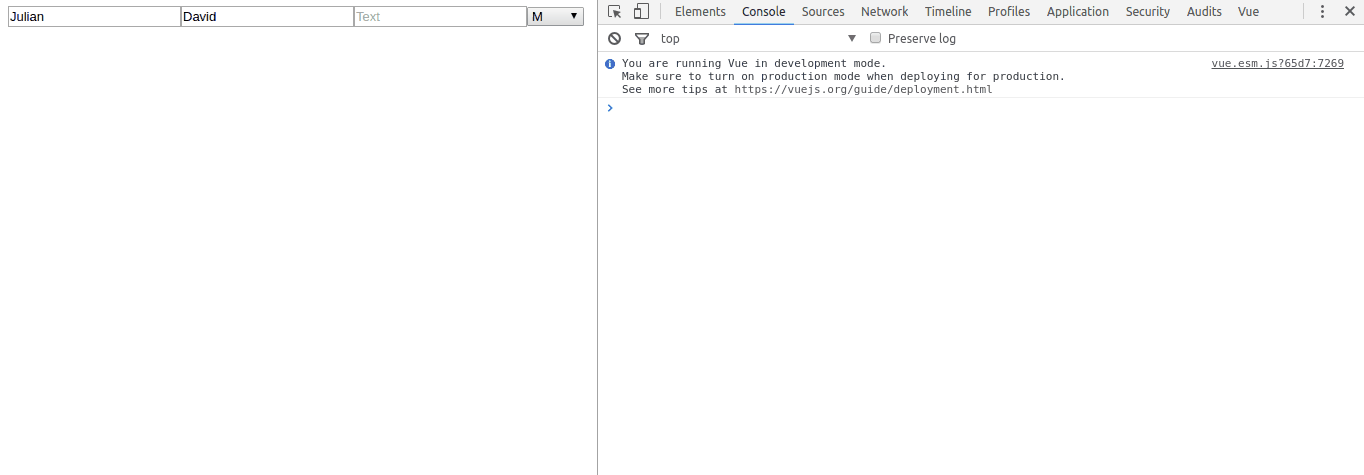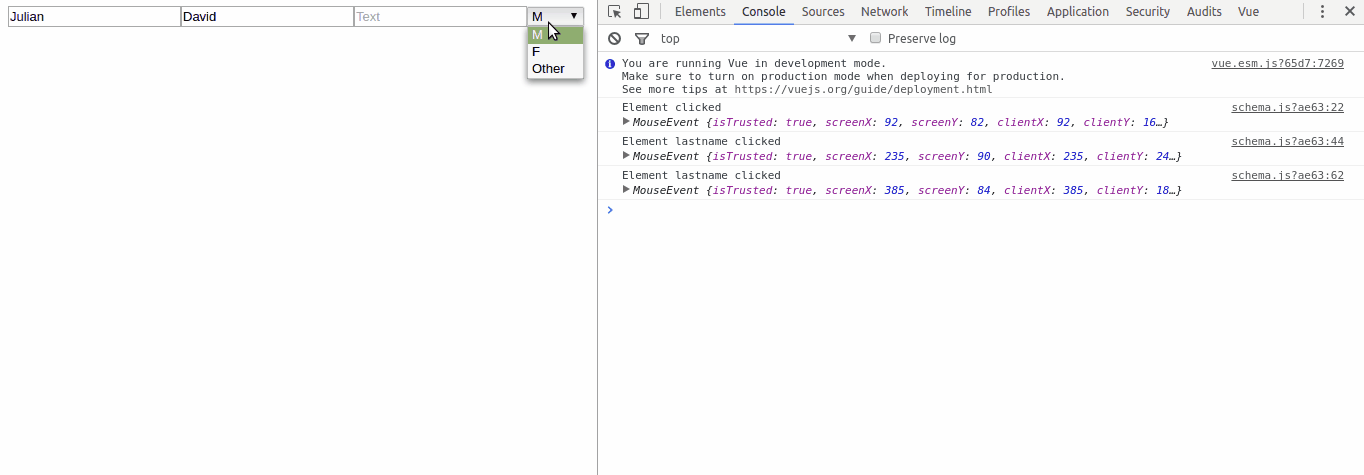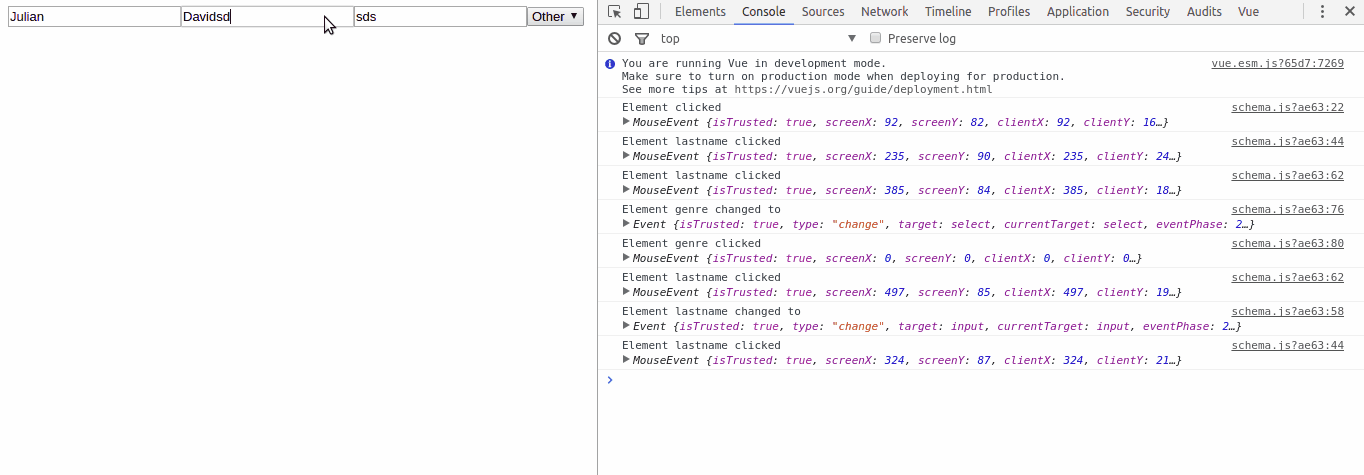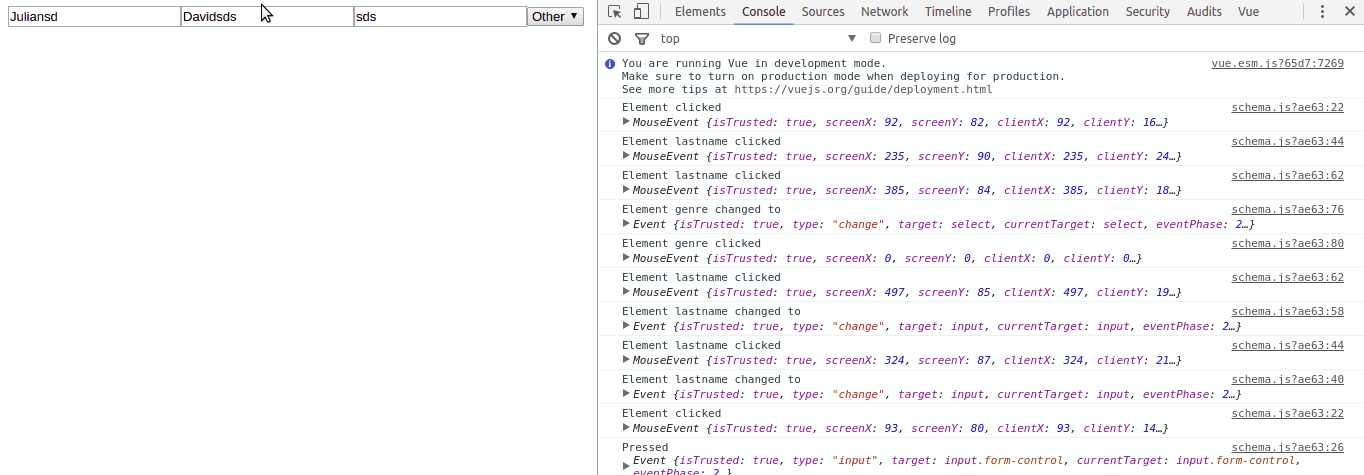
The scheme is a direct bridge that leads directly to the creation of native components of vues. Therefore, properties follow the style of VueJS names, such as click, change, input... The same applies to attributes: title, class, placeholder, value, innerHtml...
// filename: schema.js
// dir: examples/schema.js
module.exports = {
root: {
type: 'form',
method: 'post'
},
name: {
type: 'input',
properties: {
title: 'Name',
class: 'form-control',
tooltip: 'Input your first name',
value: 'Julian',
innerHtml: 'hello',
placeholder: ''
},
events: {
change: function (data) {
console.log('Element changed to', data.target.value)
},
click: function (data) {
console.log('Element clicked ', data)
},
input: function (data) {
console.log('Pressed input', data.target.value)
},
keypress: function (data) {
console.log('Pressed key', data.key, data.keyCode)
}
}
},
lastname: {
type: 'input',
properties: {
title: 'lastname',
tooltip: 'Input your first lastname',
value: 'David'
},
events: {
input: function (data) {
console.log('Element changed to', data.target.value)
}
}
},
description: {
type: 'input',
properties: {
title: 'biografy',
tooltip: 'Here your text',
placeholder: 'Text'
},
events: {
input: function (data) {
console.log('Element changed to', data.target.value)
}
}
},
genre: {
type: 'select',
properties: {
title: 'genre',
tooltip: 'Input your genre',
value: ['M', 'F', 'Other']
},
events: {
change: function (value) {
console.log('Element genre changed to ', value.target.value)
},
click: function (value) {
console.log('Element genre clicked ', value)
}
}
}
}See example schema.js
The rendered elements look like this:
Events
| Prop | Description |
|---|---|
click | Custom class to add to the component |
change | Custom url that the component will load |
input | Custom text |
See full list of events
Development, Build Setup
# install dependencies
npm install
# serve with hot reload at localhost:8080
npm run dev
# build for production with minification
npm run build
# build for production and view the bundle analyzer report
npm run build --report
# run unit tests
npm run unit
# run e2e tests
npm run e2e
# run all tests
npm testLicense
MIT @juliandavidmr