yuomi v1.0.5
installation:
npm i yuomiFeatures and Usages • server • anime • console • facebook • google • http • imgur • instagram • uptime • tiktok • new shell • new duckduckgo • new anilist
Question and Answer
server
const { server } = require("yuomi");you just need to call the server function as a variable to your main file after that your all set
result:
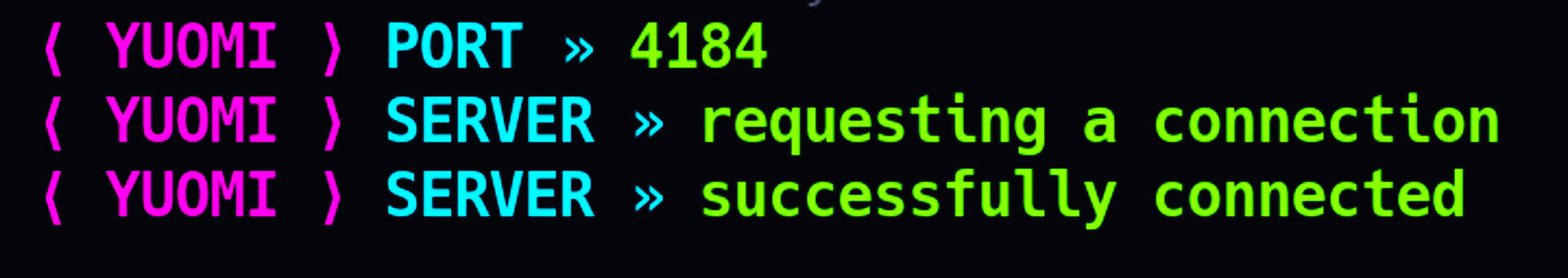 also take note the server port is randomize and the web output is just a simple http
also take note the server port is randomize and the web output is just a simple http
anime
anime.get({ type: "nsfw", tag: "waifu" }).then(yume => { console.log(yume); });
**result:**

i don't write some object output so that you can easily get the response link also please see the `SAVE` example because it's have a built-in downloader
<details><summary>NSFW tags</summary>
```js
"waifu"
"neko"
"trap"
"blowjob"await anime.save({ type: "nsfw", tag: "waifu", file: __dirname + "/cache/anime.png" });
**result:**

this method uses async function because you need to wait the process of image before you send the attachment also this is have a built-in downloader so all you need to do is just manipulate the file section you can set where do you want to save that file and you can also change the file format to jpg, webp, webm, etc
<br>
if you don't know how to make a async please read the `ASYNC` for example
<details><summary>NSFW tags</summary>
```js
"waifu"
"neko"
"trap"
"blowjob"//GET async function leiamGet() { const yume = await anime.get({type: "nsfw", tag: "waifu"}); console.log(yume); } leiamGet();
//SAVE async function leiamSave() { await anime.save({ type: "nsfw", tag: "waifu", file: __dirname + "/cache/anime.png" }); } leiamSave();
the results will be the same also if you're using the module exports you can use
```js
module.exports.YOURCALL = async function({ /*CALL FUNC*/ }) { /*YOUR CODE HERE*/ }
or
exports.YOURCALL = async function({ /*CALL FUNC*/ }} { /*YOUR CODE HERE*/ }as long as you can call the async the await method will be worked
console
log("text here", "NAME HERE");
**result:**

you can easily manipulate your console.log with this, also this can help you to make your output readable
</details>
<details><summary>ERROR</summary>
```js
const { log } = require("yuomi");
try {
} catch (e) {
log.error("text here", "NAME HERE");
}result:
 you can easily notice the error output on your console by using the
you can easily notice the error output on your console by using the error tag on it
const { facebook } = require("yuomi");
facebook.get("https://fb.watch/jKl88Swrr4/").then(yume => {
console.log(yume);
});result:
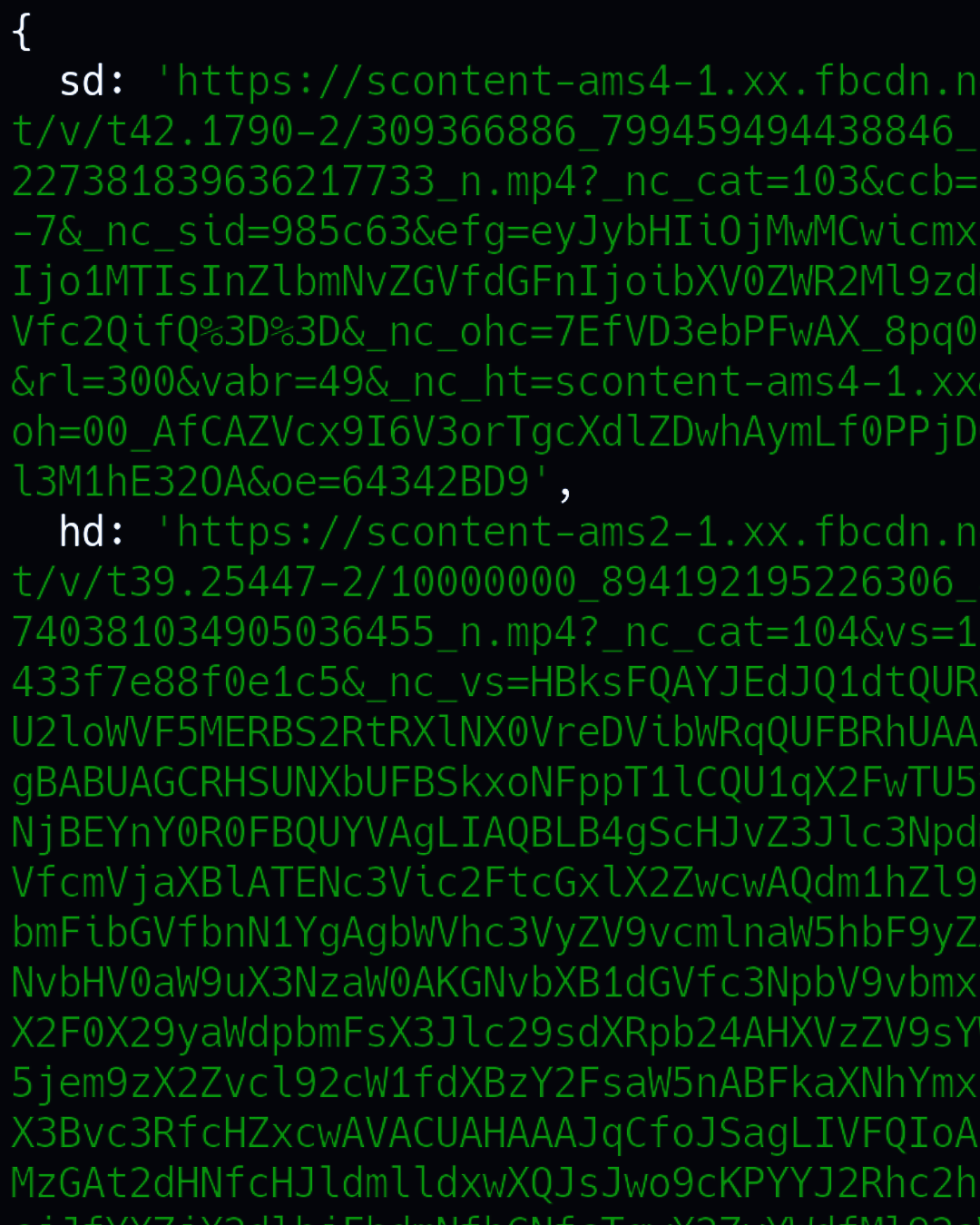 how to
how to get link?
console.log(yume.sd);
console.log(yume.hd);please go to the SAVE example because it's have a built-in downloader
const { facebook } = require("yuomi");
await facebook.save({
url: "https://fb.watch/jKl88Swrr4",
type: "sd", // or "hd"
file: __dirname + "/cache/facebook.mp4"
});this method uses async function because you need to wait the process of video before you send the attachment also this is have a built-in downloader so all you need to do is just manipulate the file section you can set where do you want to save that file and you can also change the file format to mp4a or mp3
if you don't know how to make a async please read the ASYNC for example
what is the difference?
SD => standard quality (480p) low mb/kb
HD => high quality (1080p) large mb/2mb +
also if the facebook video doesn't supports 1080p the higher resolution gonna be downloaded (720p)
const { facebook } = require("yuomi");
//GET
async function leiamGet() {
const yume = await facebook.get("https://fb.watch/jKl88Swrr4/");
console.log(yume);
}
leiamGet();
//SAVE
async function leiamSave() {
await facebook.save({
url: "https://fb.watch/jKl88Swrr4",
type: "sd", // or "hd"
file: __dirname + "/cache/facebook.mp4"
});
}
leiamSave();the results will be the same also if you're using the module exports you can use
module.exports.YOURCALL = async function({ /*CALL FUNC*/ }) { /*YOUR CODE HERE*/ }
or
exports.YOURCALL = async function({ /*CALL FUNC*/ }} { /*YOUR CODE HERE*/ }as long as you can call the async the await method will be worked
const { google } = require("yuomi");
google("anime").then(yume => {
console.log(yume);
});result:
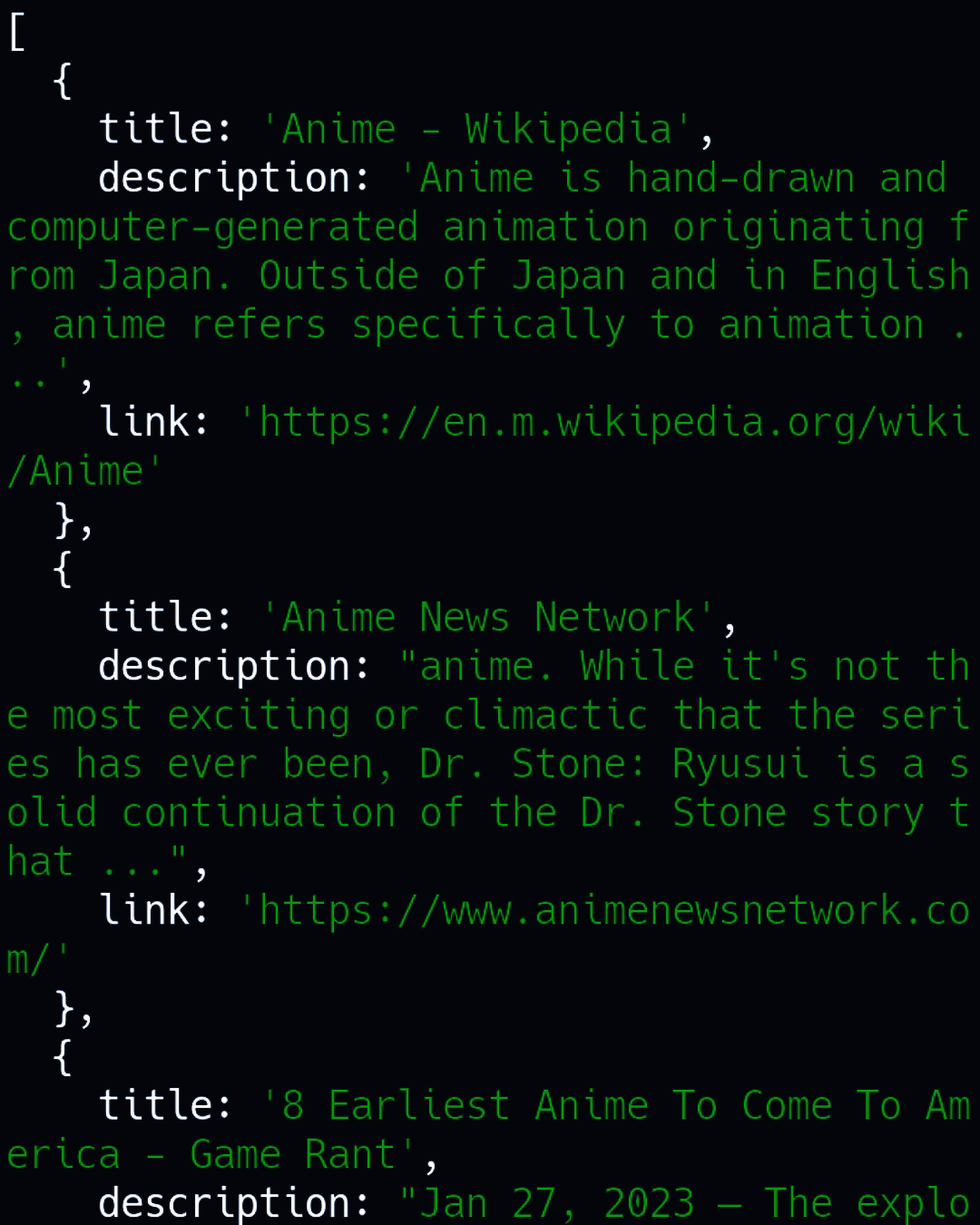 this is written in json output showing only 6 results also you can manipulate this in object for example
this is written in json output showing only 6 results also you can manipulate this in object for example
console.log(yume[0].description);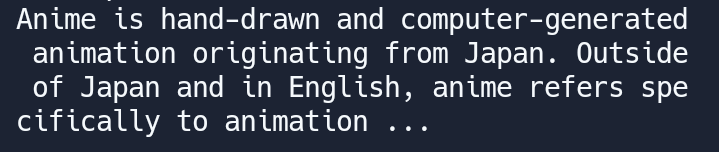 you can easily get the first object results by putting a number on your variable callback
you can easily get the first object results by putting a number on your variable callback
usage:
yume[0].title
yume[0].description
yume[0].urlhttp
yumi.get("https://api.leiamnash.repl.co/brainly?lang=ph&question=tae").then(yume => { console.log(yume); });
**result:**
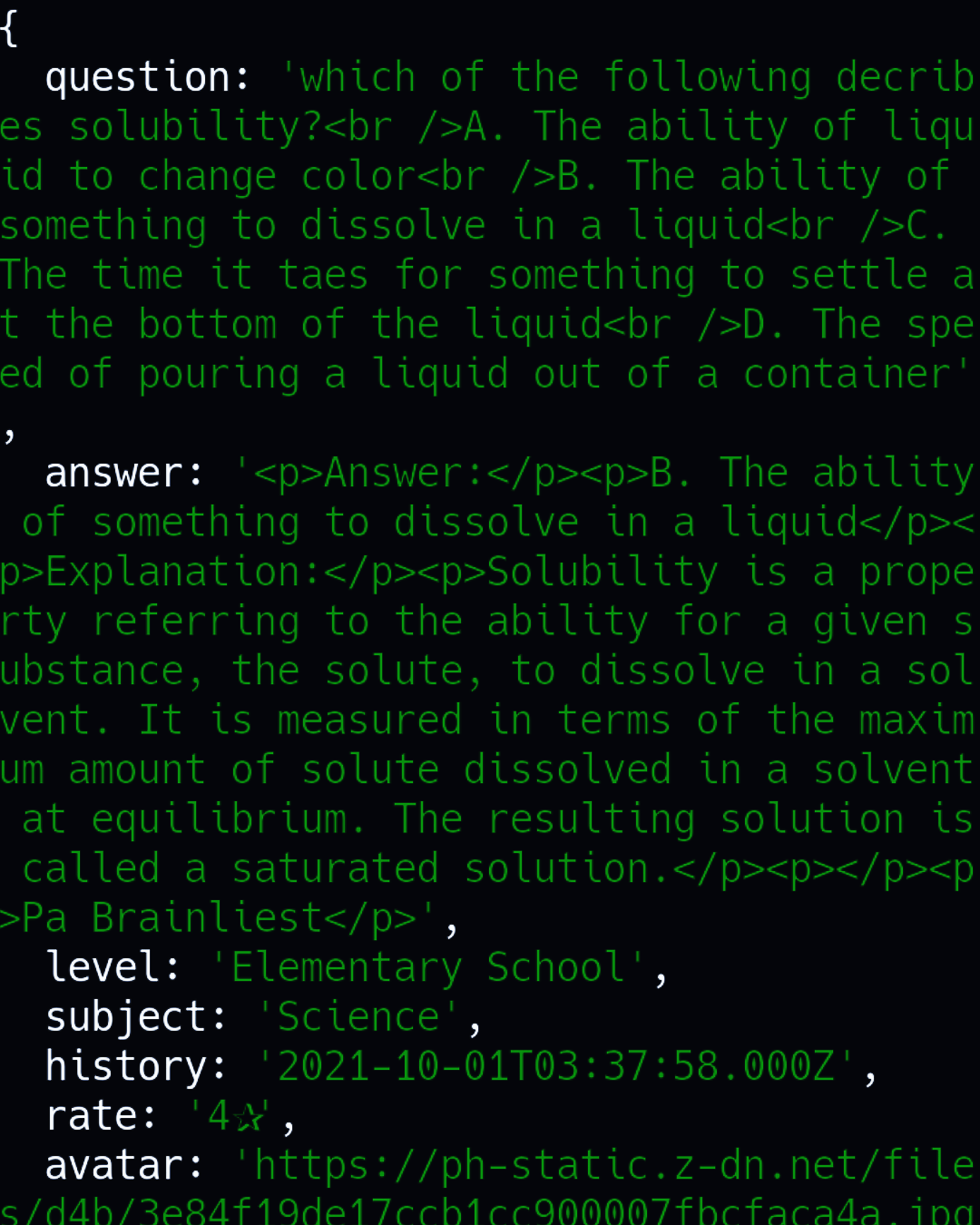
you can manipulate the internet by using this also you don't need to put `data` to get the output you just need to follow the json of api for example
```js
console.log(yume.question);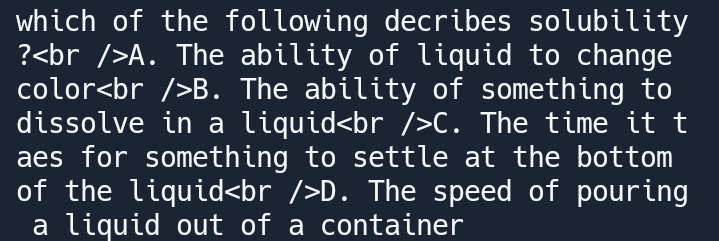 it's so pretty simple and easy to use right? also take note if you write
it's so pretty simple and easy to use right? also take note if you write yume.data.question the output will be error because you don't need to include the data you just need to follow the api output yume.question
const { yumi } = require("yuomi");
await yumi.save({
url: "https://github.com/LeiamNashRebirth/Package/raw/main/amv/yt1s.com%20-%20Gym%20Class%20Heroes%20%20My%20Heart%20Stereo%20%20Kimi%20No%20Nawa%20Edit_v720P.mp4",
file: __dirname + "/cache/yuomi.mp4"
}); result:
 this method uses async function because you need to wait the downloader to finish downloading your request before you send the attachment also you can set where do you want to save that file and you can also change the file format to jpg, png, jpeg, mp4, mp3, mp4a, webp, webm, etc
this method uses async function because you need to wait the downloader to finish downloading your request before you send the attachment also you can set where do you want to save that file and you can also change the file format to jpg, png, jpeg, mp4, mp3, mp4a, webp, webm, etc
if you don't know how to make a async please read the ASYNC for example
yumi.get("https://api.waifu.pics/nsfw/waifu").then(yume => { await yumi.load({ data: yume.url, file: "yuomi.png" }); });
**result:**

you can easily download the api output just use the GET method and LOAD method this is the combination, also the LOAD method uses async function because you need to wait the process of your request before you send the attachment and you can set where do you want to save that file and you can also change the file format to jpg, png, jpeg, mp4, mp3, mp4a, webp, webm, etc
<br>
if you don't know how to make a async please read the `ASYNC` for example
</details>
<details><summary>ASYNC</summary>
```js
const { yumi } = require("yuomi");
//GET
async function leiamGet() {
const yume = await yumi.get("https://api.leiamnash.repl.co/brainly?lang=ph&question=tae");
console.log(yume);
}
leiamGet();
//SAVE
async function leiamSave() {
await yumi.save({
url: "https://github.com/LeiamNashRebirth/Package/raw/main/amv/yt1s.com%20-%20Gym%20Class%20Heroes%20%20My%20Heart%20Stereo%20%20Kimi%20No%20Nawa%20Edit_v720P.mp4",
file: __dirname + "/cache/yuomi.mp4"
});
}
leiamSave();
//LOAD
async function leiamLoad() {
const yume = await yumi.get("https://api.waifu.pics/nsfw/waifu");
await yumi.load({
data: yume.url,
file: "yuomi.png"
});
}
leiamLoad();the results will be the same also if you're using the module exports you can use
module.exports.YOURCALL = async function({ /*CALL FUNC*/ }) { /*YOUR CODE HERE*/ }
or
exports.YOURCALL = async function({ /*CALL FUNC*/ }} { /*YOUR CODE HERE*/ }as long as you can call the async the await method will be worked
imgur
const { imgur } = require("yuomi");
imgur("https://i.waifu.pics/klA4WVk.jpg").then(yume => {
console.log(yume);
});result:
 you can easily post and get the raw imgur link without the apikey, yes you read it right you don't need the apikey and also you can post unlimitedly
you can easily post and get the raw imgur link without the apikey, yes you read it right you don't need the apikey and also you can post unlimitedly
i don't write some object output so that you can easily get the response link
instagram.get("https://www.instagram.com/tv/CdmYaq3LAYo/").then(yome => { console.log(yome); }
**result:**

how to `get` link? <br>
```js
console.log(yome.video);please read SAVE example because it's have an built-in downloader
const { instagram } = require("yuomi");
await instagram.save({
url: "https://www.instagram.com/tv/CdmYaq3LAYo/",
file "instagram.mp4"
}); result:
 this method uses async function because you need to wait the process of video before you send the attachment also this is have a built-in downloader so all you need to do is just manipulate the file section you can set where do you want to save that file and you can also change the file format to mp4a or mp3
this method uses async function because you need to wait the process of video before you send the attachment also this is have a built-in downloader so all you need to do is just manipulate the file section you can set where do you want to save that file and you can also change the file format to mp4a or mp3
if you don't know how to make a async please read the ASYNC for example
//GET async function leiamGet() { const yome = await instagram.get("https://www.instagram.com/tv/CdmYaq3LAYo/"); console.log(yome); } leiamGet();
//SAVE async function leiamSave() { await instagram.save({ url: "https://www.instagram.com/tv/CdmYaq3LAYo/", file "instagram.mp4" }); } leiamSave();
the results will be the same also if you're using the module exports you can use
```js
module.exports.YOURCALL = async function({ /*CALL FUNC*/ }) { /*YOUR CODE HERE*/ }
or
exports.YOURCALL = async function({ /*CALL FUNC*/ }} { /*YOUR CODE HERE*/ }as long as you can call the async the await method will be worked
uptime
const { uptime } = require("yuomi");
uptime({
url: "",
console: "online"
});what is the difference?
online => your console will notify you if your link is online or not

error => your console will only notify you if there's any error

silent => your console will not notify you but don't worry the uptime is still working only your console is on silent
tiktok
tiktok.get("https://vt.tiktok.com/ZS8p5EmVW/").then(yome => { console.log(yome); });
**result:**
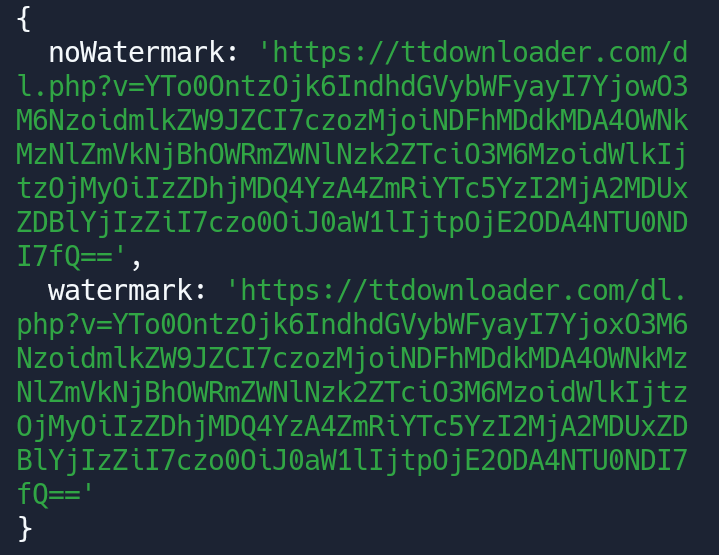
how to `get` link?
```js
console.log(yome.noWatermark)
console.log(yome.watermark)please read the SAVE example because it's have a built-in downloader
await tiktok.save({ url: "https://vt.tiktok.com/ZS8p5EmVW/", watermark: false, file: __dirname + "/cache/tiktok.mp4" });
**result:**
this method uses async function because you need to wait the process of video before you send the attachment also this is have a built-in downloader so all you need to do is just manipulate the file section you can set where do you want to save that file and you can also change the file format to mp4a or mp3
<br>
if you don't know how to make a async please read the `ASYNC` for example
<details><summary>watermark</summary>
the watermark supports only two function `true` and `false`
what is the difference? <br>
`true` => with watermark
_____________________________
`false` => no watermark
</details>
</details>
<details><summary>ASYNC</summary>
```js
const { tiktok } = require("yuomi");
//GET
async function leiamGet() {
const yome = await tiktok.get("https://vt.tiktok.com/ZS8p5EmVW/");
console.log(yome);
}
leiamGet();
//SAVE
async function leiamSave() {
await tiktok.save({
url: "https://vt.tiktok.com/ZS8p5EmVW/",
watermark: false,
file: __dirname + "/cache/tiktok.mp4"
});
}
leiamSave();the results will be the same also if you're using the module exports you can use
module.exports.YOURCALL = async function({ /*CALL FUNC*/ }) { /*YOUR CODE HERE*/ }
or
exports.YOURCALL = async function({ /*CALL FUNC*/ }} { /*YOUR CODE HERE*/ }as long as you can call the async the await method will be worked
developer LeiamNash