@symphoniacloud/cdk-website v0.1.0
CDK Construct for deploying a website
Deploying a "static" website on AWS is surprisingly tricky - it requires managing S3, CloudFront, the security between them, Route 53, and more. This CDK construct provides a higher level CDK abstraction over all of these services to make life a little easier.
This construct can't support every use case - if it doesn't work for you feel free to grab the source and make your own version, or let me know if you have a suggestion for how it can be extended!
What it deploys
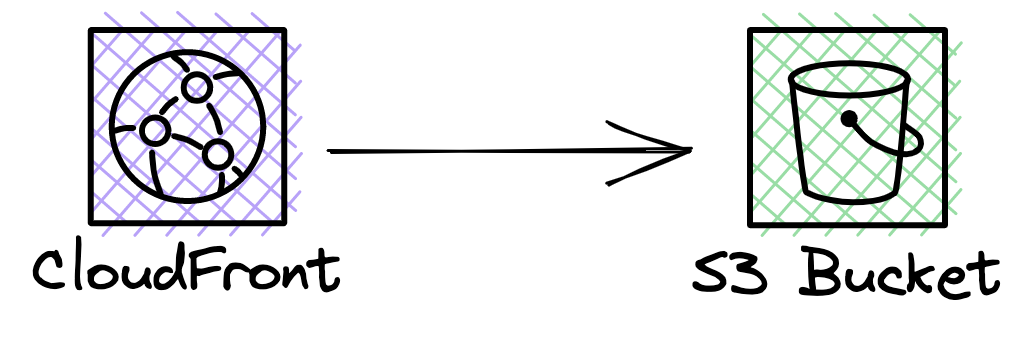
This construct deploys the following primary resources:
- An S3 bucket, with a few configuration options to make it more secure than default
- A CloudFront distribution, using the S3 bucket as the "origin".
- The AWS provided CloudFront construct sets up an "Origin Access Identity" to allow access to the bucket from CloudFront
- Mostly the construct uses the defaults in the
AWS
Distributionconstruct , apart from:- It always redirects
httprequests tohttps - It sets http version to "2 and 3", enabling http3 support
- It always redirects
- Any
DistributionPropsproperty can be overridden by setting the optionaldistributionPropertyOverridesonWebsiteProps
- If custom domain properties are set in the configuration, then the construct sets a domain name and certificate on the
distribution
- It will also create a Route53 DNS record if a Route53 Zone is specified
- If a local content path is specified, then content will be uploaded to the S3 bucket during deployment
For more details, see the source.
Using cdk-website
This README assumes that you are already very familiar with deploying to AWS using CDK.
If you need help getting started with CDK in general, then I recommend my CDK bare-bones app.
Examples
- the one included in this repo
- Coffee Store Web Basic - A similar example as a template project
- Coffee Store Web Full - An extension of Coffee Store Web Basic that is a real working demo of a production-ready website project, including TLS certificates, DNS hosting, Github Actions Workflows, multiple CDK environments (prod vs test vs dev)
Getting started
To get started:
- Add this cdk-website library to your project dependencies
- In your application stack instantiate the construct, e.g. in TypeScript:
new Website(this, 'website')- Deploy as usual
Deploying content
If you set the optional content property then the construct will configure
a BucketDeployment resource
that will
upload files from a local path to your website's S3 bucket.
e.g. the following configuration will upload everything from the local public directory to your website:
new Website(this, 'website', {
content: { path: 'public' }
})To specify that an
invalidation should be created
during deployment to force a refresh of cached content, set
the performCacheInvalidation on content to true.
Note that
invalidations are not free
once you reach a certain number per month. For dev / test environments you may wish to disable caching (see further down on how to do this.)
Setting a custom domain name
In production and testing you will likely want to use a custom domain name, rather than the CloudFront-provided URL.
To do this you will first need to have created a certificate in AWS Certificate Manager in the us-east-1 region - see here for more details
Setting a single custom domain name
To set a single custom domain name, add or update the custom domain property:
new Website(this, 'website', {
customDomain: {
domainName: 'mywebsite.example.com',
certificate: {
fromArn: myCertificateArn
}
}
})... where myCertificateArn is the ARN of your certificate.
Alternatively you can just set certificate to be the actual CDK ICertificate object - this might be useful if you
manage the certificate in the same stack as your website.
Setting domainName and certificate will update CloudFront to use your custom domain name, but these two properties
alone aren't sufficient to register the CloudFront distribution in DNS. To do that you have two options:
Firstly, you can manage DNS yourself (again, see here.)
OR, if you manage DNS through Route53 in the same account as your website, then you can set the hostedZone property
on customDomain, e.g.:
new Website(this, 'website', {
customDomain: {
domainName: 'mywebsite.example.com',
certificate: {
fromArn: myCertificateArn
},
hostedZone: {
fromDomainName: `example.com`
}
}
})NB: fromDomainName should be the domain name of the hosted zone, not the website.
Similarly to the certificate property - if you already have the CDK object representing the Hosted Zone in your CDK
app then you can just set hostedZone to be that object.
Setting multiple custom domain names
A CloudFront distribution can have multiple domain names, but they must share a certificate.
For example, you might want to use www.mywebsite.example.com and mywebsite.example.com on the same distribution.
These would share a certificate that could support both names.
On the other hand each separate domain name might be resolved in a different hosted zone, and so the configuration
for the cdk-website construct reflects that.
Here's an example:
new Website(this, 'website', {
customDomain: {
certificate: {
fromArn: myCertificateArn
},
domains: [{
domainName: 'mywebsite.example.com',
hostedZone: {
fromDomainName: `mywebsite.example.com`
}
}, {
domainName: 'www.mywebsite.example.com',
hostedZone: {
fromDomainName: `mywebsite.example.com`
}
}]
}
})In this example both www.mywebsite.example.com and mywebsite.example.com share a hosted zone.
Note that just like with a single custom domain, the hostedZone property on each domain is optional - if you don't set it it's assumed that you'll manage DNS yourself.
Specifying a CloudFront Function for pre-processing requests
Since CloudFront doesn't support things like htaccess files, it's useful to be able pre-process all requests using CloudFront Functions , e.g. to redirect default paths in subdirectories.
To specify the source code of a CloudFront Function, add the following to the construct properties:
new Website(this, 'website', {
preProcessFunctionCode: { fromPath: 'src/cloudfront/preProcessFunction.js' },
})This will automatically add a VIEWER_REQUEST CloudFront function to your distribution, using the code at the specified
path.
If you want to bundle your own zip file then you can also set preProcessFunctionCode to any valid
FunctionCode object.
The Coffee Store Web Full has an example of using a CloudFront function.
Setting additional behavior options
The CloudFront distribution will use the default
BehaviorOptions from the underlying CDK library
by default (apart
from setting http requests to redirect to https) . You may want to change some of these, which you can do by setting
the optional additionalDefaultBehaviorOptions field on the construct properties.
This field is named this because it overrides the so-called "default behavior" settings in the distribution.
If you set additionalDefaultBehaviorOptions then it must be a valid
AddBehaviorOptions object
.
For example, by default CDK will create a distribution that uses the CachingOptimized cache policy. In test situations especially this might not be the best choice - instead you may want to use the CachingDisabled policy.
To do this with cdk-website, you would do the following:
new Website(this, 'website', {
additionalDefaultBehaviorOptions: {
cachePolicy: CachePolicy.CACHING_DISABLED
}
})TODO
- publish for other languages (currently just JavaScript / TypeScript to NPM)