btreemap v0.1.14
btreemap



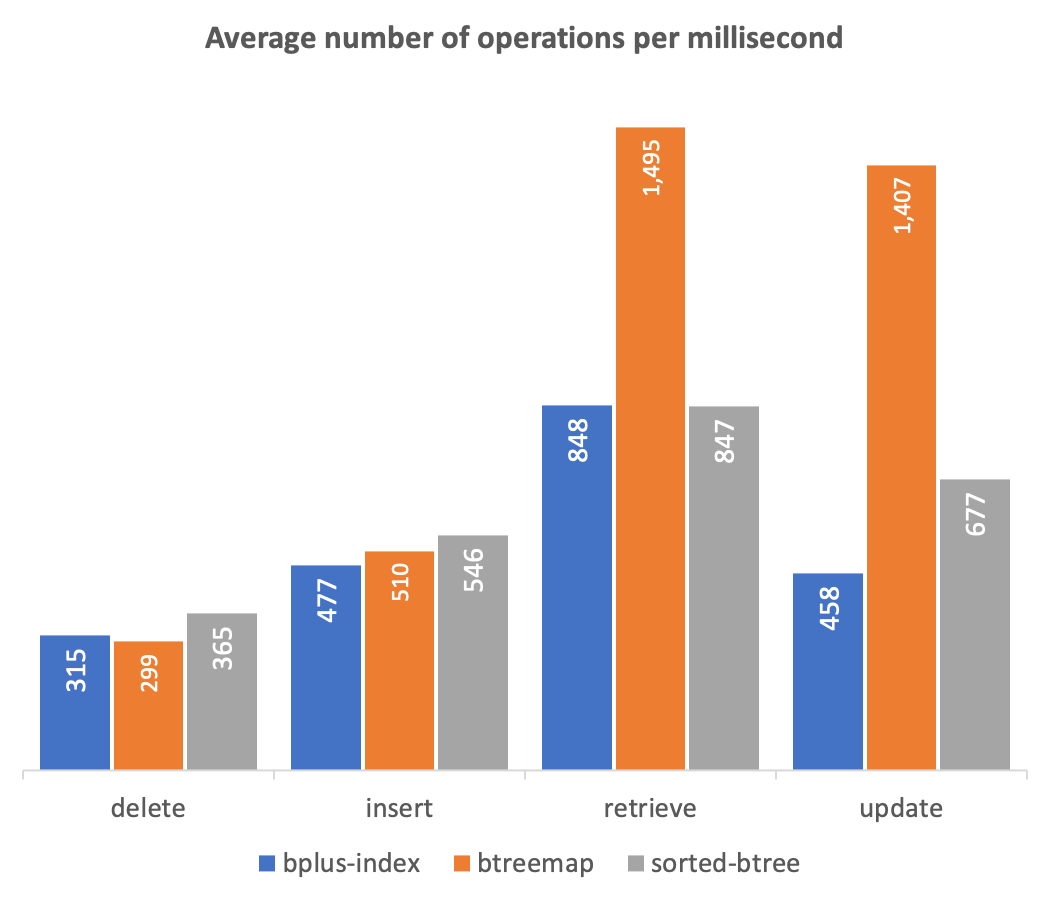
A BTreeMap is an indexed, sorted, type-aware, and persistable data store with a Map-like API and extensions for range-based methods. At its core is a Map object, used to store key/value pairs, and a B+ Tree for managing keys. This "best of both worlds" approach leverages the strengths of each: the efficient data access of a Map, and the sorting and range benefits of a B+ Tree. In benchmark tests, BTreeMap significantly outperforms the B+ Tree libraries sorted-btree and bplus-index when retrieving and updating existing values, and performs comparably on insertion and deletion tasks (see Benchmarks for details).
There is one important way in which a BTreeMap is different from a Map. The design inspiration comes from database indexes that can enforce unique keys constraints or allow keys to have multiple related values. A BTreeMap can be similarly configured either way. When keys are unique, a BTreeMap effectively functions the same as a Map, with the added benefit of key sorting and range-based access. When keys are non-unique, each key can have an array of associated values, and this has several implications:
- The
getmethod returns an array of values for a key, as opposed to returning a single value. - The
deletemethod removes the entire array of values associated with a key, as opposed to deleting just a single value. - The
valuesiterator yields a result for each individual element of a key's array of associated values. - The
entriesiterator yields a key/value pair for each individual element of a key's array of associated values, as opposed to a single key/value pair per key. - The
forEachmethod, being based on theentriesiterator, applies the supplied function to each individual element of a key's array of associated values.
By default, a BTreeMap is configured for unique keys.
Examples
Unique keys
const { BTreeMap } = require("btreemap");
const btm = new BTreeMap();
btm.set(1, "one");
btm.get(1); // returns "one"
btm.set(1, "two"); // overwrites "one" with "two"
btm.get(1); // returns "two"
btm.delete(1) // deletes key 1 and value "two"Non-unique keys
const { BTreeMap } = require("btreemap");
const btm = new BTreeMap({unique: false});
btm.set(1, "one");
btm.get(1); // returns ["one"]
btm.set(1, "two"); // adds "two" for key 1
btm.get(1); // returns ["one", "two"]
btm.delete(1); // deletes key 1 and values "one" and "two"There are two other important factors to be aware of: the use of BSON to serialize and deserialize data with persistent storage; and the default comparator used to determine the sort order of keys.
While a Map key or value can be any primitive or object, BSON cannot effectively serialize all of them, so if you attempt to save a BTreeMap that contains certain types of keys or values it may result in an error. In particular, the following primitives and object types are "safe": null, boolean, number, Date, string, RegExp, Array, and Object (that is, [object Object]). The BSON library will convert any undefined keys or values to null, will fail on bigint, and may not serialize other types of objects as you'd expect. When using BTreeMap completely in-memory, none of theses restrictions apply.
By default, BTreeMap uses a type-aware comparator function to compare and determine the sort order of keys. If two keys being compared are of the same type (null keys have their type converted from object to null), they are compared using the "less than" (<) operator and the Abstract Relational Comparison algorithm. If the keys are of different types, they are compared lexicographically using their type name. This results in a somewhat arbitrary ordering of differing types, but any ordering of types is bound to be somewhat arbitrary. If desired, a custom comparator function can be supplied when creating a BTreeMap instance.
Table of contents
- Constructor
- Properties
- Data manipulation methods
- Iterators
- Functional methods
- Input/Output methods
- Benchmarks
Constructor
Syntax
new BTreeMap([options]);Parameters
options
An object containing configuration options for the BTreeMap.
| Option | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
unique | boolean | Whether keys are unique | true |
order | number | The order of the B+ Tree | 3 |
comparator | function | The function used to compare keys | Described above. |
If a custom comparator is provided, it must take two values as input and return a value less than zero if the first value should be sorted before the second, greater than zero if the second value should be sorted before the first, or zero to keep the existing order.
Examples
const btm = new BTreeMap({
unique: false,
order: 5,
comparator: (a, b) => {
return (a < b) ? -1 : ((a > b) ? 1 : 0);
}
});Properties
BTreeMap.lowest
Returns the lowest key in the BTreeMap.
BTreeMap.highest
Returns the highest key in the BTreeMap.
BTreeMap.order
Returns the order of the BTreeMap object's B+ Tree.
BTreeMap.size
Returns the number of keys in a BTreeMap object. If configured for unique keys, this will be equal to the number of values; otherwise, the number of values may be greater.
BTreeMap.stats
Returns an object with statistics for a BTreeMap object's B+ Tree:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
depth | The depth of the tree |
nodes | The number of nodes in the tree |
leaves | The number of leaves in the tree |
keys | The number of keys in the tree |
values | The number of values in the tree |
The number of keys in the tree will be equal to the size of the BTreeMap, but the number of values could be greater if configured for non-unique keys.
Data manipulation methods
BTreeMap.has()
Returns a boolean indicating whether the specified key exists.
Syntax
has(key)Parameters
key
The key to test for presence in the BTreeMap object.
Return value
true if the specified key exists in the BTreeMap object; otherwise, false.
BTreeMap.set()
Adds a value for a specified key to a BTreeMap object. If configured for unique keys, overwrites the value if the key exits; otherwise, adds the value to the array of values for the key.
Syntax
set(key, value)Parameters
key
The key to add to the BTreeMap object.
value
The associated value to add to the BTreeMap object.
Return value
The BTreeMap object.
BTreeMap.get()
Returns a value associated with a specified key from a BTreeMap object or an iterator object for the values associated with a range of keys.
Syntax
get(key [, endKey, inclusive])Parameters
key
The key for the associated value to return from the BTreeMap object.
endKey
If an endKey is provided, get() returns a new iterator object for values in the BTreeMap object, from key to endKey, in sorted order.
inclusive
A boolean indicating whether to include the associated value for the endKey. Default is true.
Return value
The value associated with the specified key, or values associated with a range of keys, or undefined if the key, or keys in the range, can't be found in the BTreeMap object.
Examples
// Returns the value associated with key 1
btm.get(1);
// Returns an iterator for the values associated with keys 1 through 10
btm.get(1, 10);
// Returns an iterator for the values associated with keys 1 up to but not including 10
btm.get(1, 10, false);BTreeMap.delete()
Removes the specified key and its associated value, or range of keys and associated values, from a BTreeMap object.
Syntax
delete(key [, endKey, inclusive])Parameters
key
The key to remove from the BTreeMap object.
endKey
If an endKey is provided, delete() removes keys in the range from key to endKey from the BTreeMap object.
inclusive
A boolean indicating whether to include the endKey. Default is true.
See get for examples of how endKey and inclusive can be used.
Return value
true if a key, or range of keys, in the BTreeMap object existed and have been removed, or false if the key does not exist, or there are no keys in the range.
BTreeMap.clear()
Removes all elements from a BTreeMap object.
Syntax
clear()Return value
undefined
Iterators
BTreeMap[@@iterator]()
Returns the same iterator object as the entries method. If configured for non-unique keys, a key, value pair will be yielded for each value in a key's array of associated values.
Examples
for (const entry of btm) {
console.log(entry); // [key, value]
}BTreeMap.keys()
Returns a new iterator object that contains the keys in the BTreeMap object in sorted order.
Syntax
keys([start, end, inclusive])If start or end are provided, returns keys within the range from start to end.
Parameters
start
The lowest key that should be included in the iterator. Default is the lowest key in the BTreeMap object.
end
The highest key that should be included in the iterator. Default is the highest key in the BTreeMap object.
inclusive
A boolean indicating whether to include the end element. Default is true.
Return value
A new BTreeMap iterator object.
Examples
// Returns an iterator for all keys
btm.keys();
// Returns an iterator for keys 1 through 10
btm.keys(1, 10);
// Returns an iterator for keys from the lowest key to 10
btm.keys(undefined, 10)
// Returns an iterator for keys 10 up through the highest key
btm.keys(10, undefined);
// Returns an iterator for keys 1 up to but not including 10
btm.keys(1, 10, false)BTreeMap.values()
Returns a new iterator object that contains the values in the BTreeMap object sorted by key order.
Syntax
values([start, end, inclusive])If start or end are provided, returns values for keys within the range from start to end. Note that if configured for non-unique keys, each value yielded will be one of an array of values.
Parameters
start
The lowest key that should be included in the iterator. Default is the lowest key in the BTreeMap object.
end
The highest key that should be included in the iterator. Default is the highest key in the BTreeMap object.
inclusive
A boolean indicating whether to include the end element. Default is true.
See keys for examples of how start, end, and inclusive can be used.
Return value
A new BTreeMap iterator object.
BTreeMap.entries()
Returns a new iterator object that contains the key, value pairs in the BTreeMap object sorted by key order. If configured for non-unique keys, a key, value pair will be yielded for each value in a key's array of associated values; that is, more than one key, value pair may be yielded for a given key.
Syntax
entries([start, end, inclusive])If start or end are provided, returns key, value pairs for keys within the range from start to end.
Parameters
start
The lowest key that should be included in the iterator. Default is the lowest key in the BTreeMap object.
end
The highest key that should be included in the iterator. Default is the highest key in the BTreeMap object.
inclusive
A boolean indicating whether to include the end element. Default is true.
See keys for examples of how start, end, and inclusive can be used.
Return value
A new BTreeMap iterator object.
Functional methods
BTreeMap.forEach()
Executes a provided function once per each key/value pair in the BTreeMap object in sorted order. If configured for non-unique keys, applies the supplied function to each individual element of a key's array of associated values.
Syntax
forEach(function, [start, end, inclusive])If start or end are provided, executes the function for keys within the range from start to end.
Parameters
function
The function to be executed, invoked with three arguments: the value, the key, and the BTreeMap object.
start
The lowest key for which the function should be executed. Default is the lowest key in the BTreeMap object.
end
The highest key for which the function should be executed. Default is the highest key in the BTreeMap object.
inclusive
A boolean indicating whether to execute the function for the end element. Default is true.
See keys for examples of how start, end, and inclusive can be used.
Return value
undefined
Input/Output methods
BTreeMap.load()
Creates a new BTreeMap object using data from a file.
Syntax
load(path)Parameters
path
The path to a file containing BTreeMap data.
Return value
undefined
BTreeMap.save()
Saves a BTreeMap map object's data to a file.
Syntax
save(path)Parameters
path
The path to a file where the BTreeMap object's data should be saved. The file is created if it doesn't exist, and overwritten if it does.
Return value
undefined
BTreeMap.toString()
Returns a string representing the BTreeMap object.
Syntax
toString()Return value
A string representing the BTreeMap object.
Benchmarks
Twenty rounds of benchmark tests were conducted to compare btreemap with sorted-btree and bplus-index. Each test involved the following for ascending and descending integer keys, and a randomly generated mix of integer and character keys:
- Inserting key/value pairs in batches of 1000, 10000, 100000, and 1000000
- Retrieving values for a random 20% of the keys
- Updating values for a random 10% of the keys
- Deleting a random 1% of the keys
Times were captured at nanosecond scale using process.hrtime.bigint() and the results were converted into measures of operations per millisecond. The benchmark script, raw data output, and an Excel spreadsheet with a pivot chart, are all available in the "benchmarks" folder.