ionic-photo-gallery-server v0.0.6
Ionic Photo Gallery
A hybrid app with authentication that allows registered users view a gallery of photos they have uploaded via the camera phone. The blog post I have written about this project can be found on my blog.
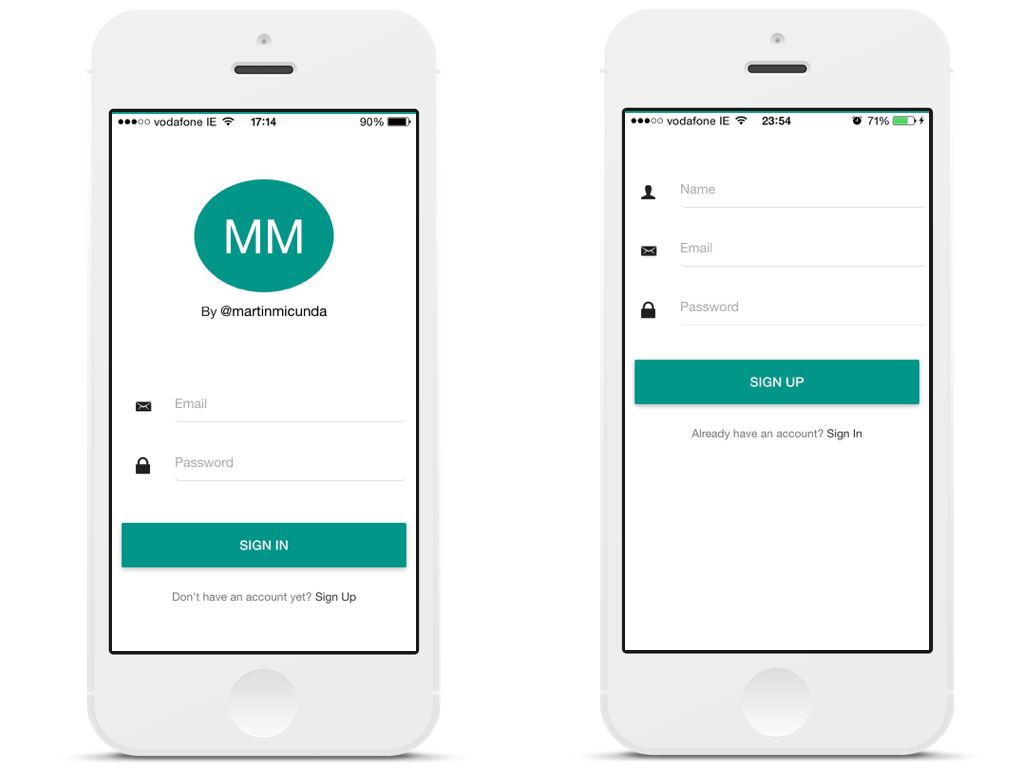
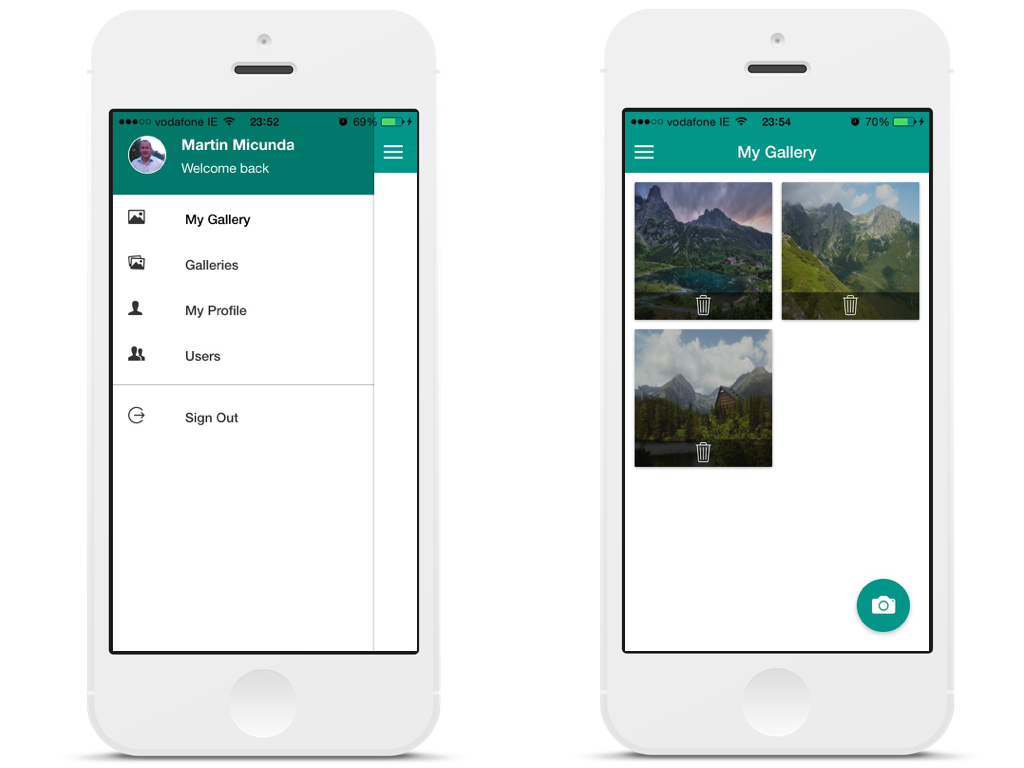
Table of Contents
- Technologies Used
- Architecture Diagram
- Installation & Configuration
- Running App
- Building for iOS
- Building for Android
- Vagrant
- Ansible
- FAQ
- License
Technologies Used
| Mobile Side | Server Side | DevOps |
|---|---|---|
| Angular.js | Node.js | Gulp |
| Ionic | MongoDB | NPM |
| Material Design | Express.js | Vagrant |
| Cordova | Redis |
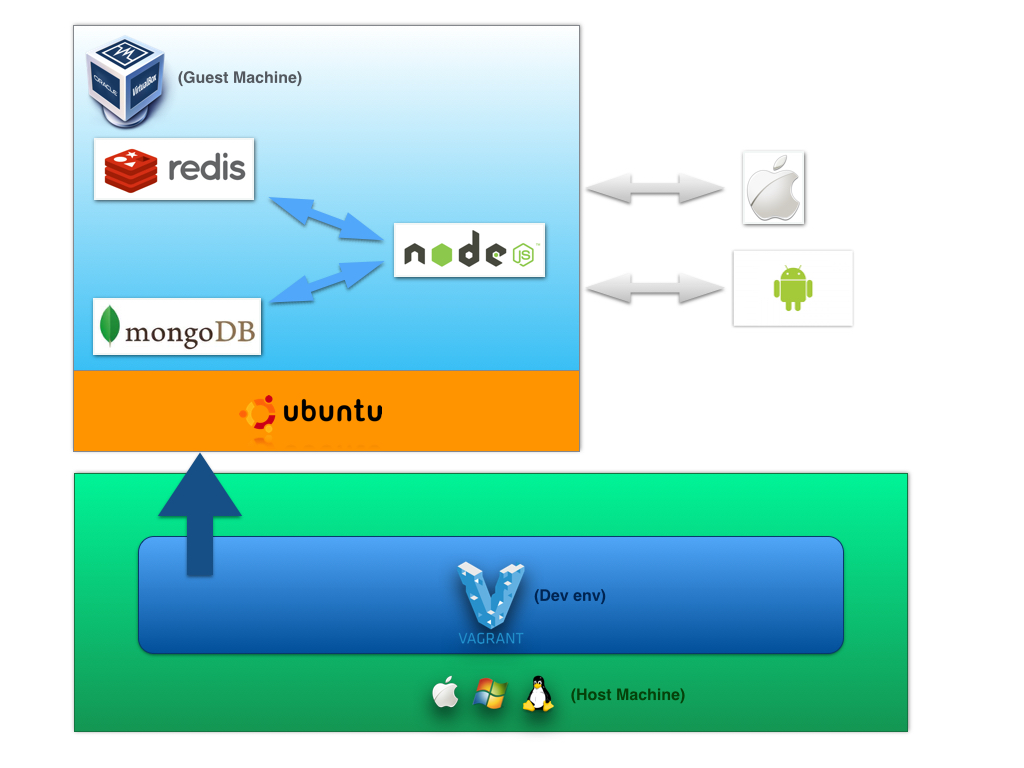
Architecture Diagram
Development
Installation & Configuration
Platform & Tools
You need to have installed follow tools on your machine:
- Virtualbox 4.3.16+
- Vagrant 1.6.2+
- Ansible 1.7.0+
Installation
1. Clone main repository:
$ git clone https://github.com/martinmicunda/ionic-photo-gallery.git
$ cd ionic-photo-gallery2. The following command would add a new ubuntu trusty64 box, and if an existing one is found, it will override it:
$ vagrant box add ubuntu/trusty64 --forceNOTE: This process may take a while, as most Vagrant boxes will be at least 200 MB big.
Verify that box was installed by running the list subcommand that will list the boxes installed within Vagrant along with the provider that backs the box:
$ vagrant box list
ubuntu/trusty64 (virtualbox, 14.04)3. The following command would install an ansible roles for this project, and if an existing one is found, it will override it:
$ bash bin/ansible-install-roles.shVerify that ansible roles were installed by running the list subcommand that will list the installed roles:
$ ansible-galaxy list
- DavidWittman.redis, 1.0.3
- laggyluke.direnv, v2.6.0
- martinmicunda.common, v1.0.1
- martinmicunda.ionic, v1.0.0
- martinmicunda.nodejs, v1.0.1
- nickp666.android-sdk, v0.0.1
- Stouts.mongodb, 2.1.8
- williamyeh.oracle-java, master4. Now, run vagrant up that will create and provisioning default VM box.
$ vagrant upNOTE: Vagrant will provision the virtual machine only once on the first run, any subsequent provisioning must be executed with the
--provisionflag eithervagrant up --provisionorvagrant reload --provisionorvagrant provisionif vagrant box is already running. The provisioning will re-run also if you destroy the VM and rebuild it withvagrant destroyandvagrant up.
If there have been no errors when executing the above commands, the machines default should be created. The following command would outputs status of the vagrant machine:
$ vagrant status
Current machine states:
default running (virtualbox)Now you should be able to ssh into box:
$ vagrant ssh Running App
Server
1. To start the server you need to ssh into box:
$ vagrant ssh2. Install the server dependencies:
$ cd server
$ npm install3. Start the server:
$ npm startNOTE: The direnv is use as an environment variable manager so when you first time cd into server directory with a
.envrcfile in it, it will refuse to load the file. This is to protect you, since the contents of the .envrc will be executed by your shell, and they might come from untrusted sources. Simply rundirenv allow, and it will trust that file until the next time it changes.
Ionic
1. To start the server you need to ssh into box:
$ vagrant ssh2. Install the ionic dependencies:
$ cd ionic
$ npm install3. Start the ionic:
$ npm startOpen up your browser and navigate to http://127.0.0.1:8100 and you should see ionic app up and running.
Building for iOS
1. ssh into box:
$ vagrant ssh2. Add support for the iOS platform:
$ cd ionic
$ ionic platform add ios3. Build the project:
$ ionic build ios4. Open ionic-photo-gallery.xcodeproj in the ionic-photo-gallery/ionic/platforms/ios folder.
5. In Xcode, run the application on a device connected to your computer or in the iOS emulator.
Building for Android
1. ssh into box:
$ vagrant ssh2. Add support for the Android platform:
$ cd ionic
$ ionic platform add android3. Build the project:
$ ionic build androidNOTE: (martin) work in progress!!
- Start Genymotion
- Open Genymotion Shell
- Run follow command to get IP address
$ devices listyou should see something like this:
Genymotion virtual device 0 is off. Please select a new virtual device with command : devices select
Available devices:
Id | Select | Status | Type | IP Address | Name
----+--------+---------------+----------+-----------------+---------------
0 | | On | virtual | 192.168.58.101 | Samsung Galaxy S4 - 4.4.4 - API 19 - 1080x1920- Go to vagrant box using 'vagrant up' and 'vagrant ssh'.
- Type:
adb connect 192.168.56.101andadb devices. You should see something like this:
vagrant@vagrant-ubuntu-trusty-64:~$ adb connect 192.168.58.101
connected to 192.168.58.101:5555
vagrant@vagrant-ubuntu-trusty-64:~$ adb devices
List of devices attached
192.168.58.101:5555 device- Run
ionic run android
Vagrant
There’s a ton of commands you can use to talk to Vagrant. For a full list see the official docs, but here are the more common ones.
vagrant up- use this command tostartyour virtual environmentvagrant halt- use this command tostopyour virtual environmentvagrant suspend- use this command topauseyour virtual environment, make sure you do this before shutting down your computer to safely be able to restore the environment later.vagrant destroy- use this command toremovesyour virtual environment from your machinevagrant reload- use this command to your virtual environment, if you add the--provisionflag, it will reprovision the box as well; this is useful with removing or adding things to the server via Ansible.vagrant ssh- use this command toconnectto the virtual server
Ansible
To get better understanding how Ansible works check the official docs. Ansible installs the following software:
The mongodb and redis services are started after provisioning takes place.
FAQ
What if I want to uninstall application?
1. The following command would permanently removes the default virtual box from your machine:
$ vagrant destroy2. The following command would uninstall an ansible roles for this project:
$ bash bin/ansible-uninstall-roles.sh4. The following command would remove trusty64 box:
$ vagrant box remove trusty64What if I want a fresh install?
If you wish to destroy the default virtual boxe to make sure you have a fresh start, you can do these steps:
$ vagrant destroy
$ vagrant upLicense
The MIT License
Copyright (c) 2015 Martin Micunda
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in
all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN
THE SOFTWARE.