sails-police v0.1.1
Simple and flexible authentication workflows for sails inspired by devise and passportjs.
Note: This requires Sails v0.11.0+. If v0.11.0+ isn't published to NPM yet, you'll need to install it via Github.
Guide
Install
$ npm install --save sails-policeQuick start
Quick Setup
Model Setup
Apply sails-police model mixins in your application User model.
//in your models/User.js
var police = require('sails-police');
var User = {};
//mixin police morphs into User model
police.model.mixin(User);
//implement sendEmail
//which will be called by
//sails police when
//whenever it want to send email
User.attributes.sendEmail = function(type, user, done) {
//your send email logic
done();
};
module.exports = UserController Setup
Apply sails-police controller mixins in your AuthController
//in controllers/AuthController.js
var police = require('sails-police');
module.exports = police.controller.mixin({
//your custom controller
//codes goes here
});Routes Setup
Apply sails-police routes mixins in your routes
//in your config/routes,js
var police = require('sails-police');
//then use routes.mixin to add
//sails-police routes
module.exports.routes = police.routes.mixin({
//then continue adding your routes
//as you normally do
//with sails routes
'/': 'HomeController.index'
});Policies Setup
Apply sails-police policies mixins into your policies
//in your config/policies.js
var police = require('sails-police');
//then use policies.mixin
//to add sails-police mixins
module.exports.policies = police.policies.mixin({
//continue define your policies
//as you do with sails police normally
});Middlewares Setup
Apply sails-police middlewares mixins into your http.js
//in your config/http.js
//uncomment the exports
//then
var police = require('sails-police');
//the use middlewares.mixin
//to add require sails-police middlewares
//which wrap the initial module.exports.http
module.exports.http = police.middlewares.mixin({
//initial content of sails http
//exports definition goes here
});Authentication Policy Setup
Export sails-police Auth policy in your policies folder
//in your api/policies/Auth.js
module.exports = require('sails-police').policies.isAuthenticated;Add Auth policy in your policies to restrict your routes
//in config/policies.js
//add to restrict all routes
'*': 'Auth'Thats all need to add sails-police in your application.
Detailed Setup
sails-police expose mixins that will extend different parts of sails application and easy your setup. It expose the following mixins:
Model Mixin
It extend valid sails model with sails-police morphs to make it a viable canditate to be used in sails-police.
By convection, you must have a User model in your models/User.js. After creating the User model then your will have to mix sails-police morphs into it.
To setup your model for sails-police do as bellow:
//in model/User.js
var police = require('sails-police');
//your User model definition
var User = {
//your user attributes
//please check which attributes you want to
//add before, cause sails-police add some for you
};
//then mixin sails-police morphs
police.model.mixin(User);
//done
//export your model
module.exports = User;The model mixed with sails-police morphs will have all required attributes and methods to make it work out of the box with sails-police. To know what attributes and methods added please consult Modules section.
Controller Mixin
contoller.mixin aim to be used with AuthController in your sails aplication. It will extend your AuthController with all authentication workflows handlers. You can setup your AuthController for sails-police as below
//in your controllers/AuthController.js
//require sails-police
var police = require('sails-police');
module.exports = police.controller.mixin({
//other Http handlers ...
});Thats all needed, sails-police will add its Http handlers in your AuthController.
Routes Mixin
Its extend sails routes to setup all required sails-police routes. To mix sails-police routes in your routes do as bellow:
//in your config/routes,js
var police = require('sails-police');
//then use routes.mixin to add
//sails-police routes
module.exports.routes = police.routes.mixin({
//then continue adding your routes
//as you normally do
//with sails routes
'/': 'HomeController.index'
});After mixin sails-police routes, the following routes will get added into sails router
'get /signin': 'AuthController.getSignin',
'post /signin': 'AuthController.postSignin',
'get /signout': 'AuthController.deleteSignout', //TODO make use of DELETE
'get /signup': 'AuthController.getSignup',
'post /signup': 'AuthController.postSignup',
'get /confirm/:token': 'AuthController.getConfirm', //TODO make use of PUT
'get /forgot': 'AuthController.getForgot',
'post /forgot': 'AuthController.postForgot',
'get /recover/:token': 'AuthController.getRecover',
'post /recover': 'AuthController.postRecover',
'get /unlock/:token': 'AuthController.getUnlock',
'get /change': 'AuthController.getChange',
'post /change': 'AuthController.postChange'Policies Mixin
It extend your policies with the requires sails-police polices to make it work out of box.
To mixin sails-police into your policies do as bellow:
//in your config/policies.js
var police = require('sails-police');
//then use policies.mixin
//to add sails-police mixins
module.exports.policies = police.policies.mixin({
//continue define your policies
//as you do with sails police normally
});After sails-police policies mixin the following policies will be added into your policies definition:
''AuthController': {
getSignin: true,
postSignin: true,
getSignup: true,
postSignup: true,
getConfirm: true,
getForgot: true,
postForgot: true,
getRecover: true,
postRecover: true,
getUnlock: true
}Middlewares Mixin
It extend sails http config with policies middlewares and patch the middleware order so that sails-police can achieve its intended purpose.
To mixin sails-police middlewares do as bellow:
//in your config/http.js
//uncomment the exports
//then
var police = require('sails-police');
//the use middlewares.mixin
//to add require sails-police middlewares
//which wrap the initial module.exports.http
module.exports.http = police.middlewares.mixin({
//initial sails http exports definition goes here
});sails-police middleware mixins are divided into:
policeLocals: Which extendsrequest.localswitherror,warningandsuccesskey so that at any time if you assign a value to them they will get displayed in the view.policeInit: Which is the wrapper around passportjs initialize but also provide a hook point wheresails-policesetup its passportjs. And what it does is to add passportjs initialize intosails middlewaresaspoliceInitandmiddlewares orderaspoliceInit.policeSession: Which is the wrapper around passportjs session. And what it does is to add passportjs session initialization intosails middlewaresaspoliceSessionandmiddlewares orderaspoliceSession.
All of the above middlewares are injected before sails router middleware, in case of any issue please lets discuss.
Modules
Authenticable
It lays down the infrastructure for authenticating a user in sails-police application. It extend model supplied to it with the following:
email: An attribute used to store user email address.sails-policeopt to use email address but in future we will add support to custom attribute.username: An attribute which used to store username.password: An attribute which is used to store user password hash.encryptPassword(callback(error,authenticable)): An instance method which encrypt the current model instance password using bcryptjs.
Example
var faker = require('faker');
var password = faker.internet.password();
//create new user instance
var user = User.new({
password: password
});
//encypt instance password
user
.encryptPassword(function(error, authenticable) {
if (error) {
console.log(error);
} else {
console.log(authenticable);
}
});comparePassword(password, callback(error,authenticable)): An instance method which takes in apasswordand compare with the instance password hash to see if they match.
Example
var faker = require('faker');
var password = faker.internet.password();
//after having model instance
user
.comparePassword(password,function(error, authenticable) {
if (error) {
console.log(error);
} else {
console.log(authenticable);
}
});authenticate(credentials, callback(error,authenticable)): A model static method which takes in credentials in the format of :
var faker = require('faker');
var credentials = {
email: faker.internet.email(),
password: faker.internet.password()
};where email is valid email and password is valid password of
already registered user. It will then authenticate the given credentials. If they are valid credential a user with the supplied credentials will be returned otherwise corresponding errors will be returned.
Example
var faker = require('faker');
//you may obtain this credentials from anywhere
//this is just a demostration for how credential must
var credentials = {
email: faker.internet.email(),
password: faker.internet.password()
};
User
.authenticate(function(error, authenticable) {
if (error) {
console.log(error);
} else {
console.log(authenticable);
}
});Confirmable
Provide a means to confirm user registration. It extend model with the following:
confirmationToken: An attribute which used to store current user confirmation token.confirmationTokenExpiryAt: An attribute that keep tracks of when the confirmation token will expiry. Beyond that, new confirmation token will be generated and notification will be send.confirmedAt: An attribute that keep tracks of when user account is confrimed.confirmationSentAt: An attribute that keep tracks of when confirmation request is sent.generateConfirmationToken(callback(error,confirmable)): This instance method will generateconfirmationTokenandconfirmationTokenExpiryAttime. It also update and persist an instance before return it.
Example
var user = User.new();
user
.generateConfirmationToken(function(error, confirmable) {
if (error) {
console.log(error);
} else {
console.log(confirmable);
}
})sendConfirmation(callback(error,confirmable)): This instance method utilize the configured transport and send the confirmation notification. On successfully send it will updateconfirmationSentAtinstance attribute with the current time stamp and persist the instance before return it.
Note: send confirmation use the transport api provide on setTranport configuration.
Example
var user = User.new({
email: faker.internet.email(),
password: faker.internet.password()
});
user
.sendConfirmation(function(error, confirmable) {
if (error) {
consle.log(error);
} else {
consle.log(confirmable);
}
});confirm(confirmationToken, callback(error,confirmable)): This static/class method taken the givenconfirmationTokenand confirm any un confirmed registration found with that confirmation token. It will updateconfirmedAtinstance attribute and persist the instance before return it.
Example
User
.confirm('confirmationToken',function(error, confirmable) {
if (error) {
console.log(error);
} else {
console.log(confirmable);
}
});Lockable
Provide a means of locking an account after a specified number of failed sign-in attempts (defaults to 5 attempts). Can unlock account through unlock instructions sent. It extend the model with the following:
failedAttempt: An attribute which keeps track of failed login attempts.lockedAt: An attribute which keeps track of when account is locked.unlockedAt: An attribute which keeps track of when and account is unlocked.unlockToken: An attribute which store the current unlock token of the locked account.unlockTokenSentAt: An attribute which keeps track of when the unlock token notification sent.unlockTokenExpiryAt: An attribute which keep track ofunlockTokenexpiration. IfunlockTokenis expired new will get generated and set.generateUnlockToken(callback(error,lockable)): An instance method that generateunlockTokenandunlockTokenExpiryAt. Instance will get persisted before returned otherwise corresponding errors will get returned.
Example
var user = User.new();
user
.generateUnlockToken(function(error, lockable) {
if (error) {
console.log(error)
} else {
console.log(lockable)
}
});sendLock(callback(error,lockable)): An instance method which send account locked notification to the owner. It will setunlockTokenSentAtto track when the lock notification is sent. Instance will get update before returned otherwise corresponding errors will get returned.
Example
var faker = require('faker');
var user = User.new({
email: faker.internet.email(),
password: faker.internet.password()
});
user
.sendLock(function(error, lockable) {
if (error) {
console.log(error);
} else {
console.log(lockable);
}
});lock(callback(error,lockable)): An instance method that used to lock an account. when called it will check if the number offailedAttemptsis greater that the configured maximum login attempts, if so the account will get locked by settinglockedAtto the current timestamp oflockinvocation. Instance will get persisted before returned otherwise corresponding errors will get returned.
Example
var faker = require('faker');
var user = User.new({
email: faker.internet.email(),
password: faker.internet.password(),
failedAttempt: 5
});
user
.lock(function(error, lockable) {
if (error) {
console.log(error);
} else {
console.log(lockable);
}
});unlock(unlockToken, callback(error,lockable)): A model static method which unlock a locked account with the providedunlockToken. If the token expired the newunlockTokenwill get generated. If token is valid, locked account will get unlocked andunlockedAtattribute will be set to current timestamp andfailedAttemptswill get set to 0. Instance unlcoked will get persisted before returned otherwise corrensponding errors will get returned.
Example
User
.unlock(unlockToken,
function(error, lockable) {
if (error) {
console.log(error);
} else {
console.log(lockable);
}
});Recoverable
Lays out infrastructure of resets the user password and sends reset instructions. It extend model with the following:
recoveryToken: An attribute that store recovery tokenrecoveryTokenExpiryAt: An attribute that track when the recoverable token is expiring.recoverySentAt: An attribute that keep track as of when the recovery notification is sent.recoveredAt: An attribute which keeps track of when the password was recovered.generateRecoveryToken(callback(error,recoverable)): An instance method which used to generaterecoveryTokenand setrecoveryTokenExpiryAttimestamp. Instance will get persisted before returned othewise corresponding errors will get returned.
Example
var user = User.new();
user
.generateRecoveryToken(function(error, recoverable) {
if (error) {
console.log(error)
} else {
console.log(recoverable);
}
});sendRecovery(callback(error,recoverable)): An instance method which is used to send recovery notification to the user. It will setrecoveryTokenSentAttimestamp. Instance will get persisted before returned othewise corresponding errors will get returned.
Example
var faker = require('faker');
var user = User.new({
email: faker.internet.email(),
password: faker.internet.password()
});
user
.sendRecovery(function(error, recoverable) {
if (error) {
console.log(error);
} else {
console.log(recoverable);
}
});recover(recoveryToken, newPassword, callback(error,recoverable)): A model static method which is used to recover an account with the matchedrecoverToken. ThenewPasswordprovided will get encrypted before set as user password. It will setrecoveredAtbefore persist the model.
Example
var faker = require('faker');
User
.recover(
recoveryToken,
faker.internet.password(),
function(error, recoverable) {
if (error) {
console.log(error);
} else {
console.log(recoverable);
}
});Registerable
Handles signing up users through a registration process, also allowing them to edit and destroy their account. It extend model with the following:
registeredAt: An attribute which keeps track of whn an account is registered.unregisteredAt: An attribute which keep tracks of when an account is unregistered.register(credentials, callback(error,registerable)): A model static method which is used to register provided credentials. It takes care of checking if email is taken and validating credentials. It will return registered user otherwise corresponding registration errors.
Example
var faker = require('faker');
var credentials = {
email: faker.internet.email(),
password: faker.internet.password()
}
User
.register(credentials, function(error, registerable) {
if (error) {
console.log(error);
} else {
console.log(registerable);
}
});unregister(callback(error,registerable)): An instance method which allow to unregister(destroy a user). The currently implementation is to setunregiesteredAtto current timestamp of the invocation. Instance will get persisted before returned otherwise corresponding errors will be returned.
Example:
use
.unregister(function(error, registerable) {
if (error) {
console.log(error);
} else {
console.log(registerable);
}
});Trackable
Provide a means of tracking user signin activities. It extend provided model with the followings:
signInCount: Keeps track of number of count a user have been sign in into you APIcurrentSignInAt: Keeps track of the latest time when user signed in into you APIcurrentSignInIpAddress: Keeps track of the latest IP address a user used to log with into your APIlastSignInAt: Keeps track of the previous sign in time prior to the current sign in.lastSignInIpAddress: Keeps track of the previous IP address user used to log with into your APItrack(ipAddress,callback(error,trackable)): This is model instance method, which when called with the IP address, it will update current tracking details and set the provided IP address as thecurrentSignInIpAddress. On successfully tracking, a providedcallbackwill be get invoked and provided with error if occur and the current updated model instance.
Example
User
.findOneByEmail('validEmail')
.exec(function(error,user){
if(error){
console.log(error);
}
else{
user
.track('validIpAddress',function(error,trackable){
if(error){
console.log(error);
}
else{
console.log(trackable);
}
});
}
});Sending Email
The default implementation of sails-police to send email is noop. This is because there are different use case(s) when it come on sending email notification.
Due to that reason, sails-police requires your model to implement sendEmailmethod which accept type, authentication, done as it argurments.
type: Refer to the type of email notifcation to be sent. There are just three types which areEMAIL_REGISTRATION_CONFIRMATON,EMAIL_UNLOCKandEMAIL_PASSWORD_RECOVERYwhich are sent when new account is registered, an account is locked and need to be unlocked and when account is requesting to recover the password repsectively.authenticable: Refer to the model instance that you have mixinsails-police morphs.done: Is the callback that you must call after finish sending the notification. By default this callback will update notification send details based on the usage.
How to implement a sendEmail
Simple add sendEmail into your model instance attributes.
//in your models/User.js
var police = require('sails-police');
//define your model
var User = {};
//mixin police to it
User = police.model.mixin(User);
//the add sendEmail
User.attributes.sendEmail = function(type, authenticable, done) {
//your transport implementation
console
.log(
'Notification type: %s.\nAuthenticable: %s \n',
type,
JSON.stringify(authenticable)
);
done();
};Thats all needed and sails-police will be able to utilize your sendEmail implementation.
Sending Email Issues
It is recommended to use job queue like kue when implementing your sendEmail to reduce your API response time.
Screenshots
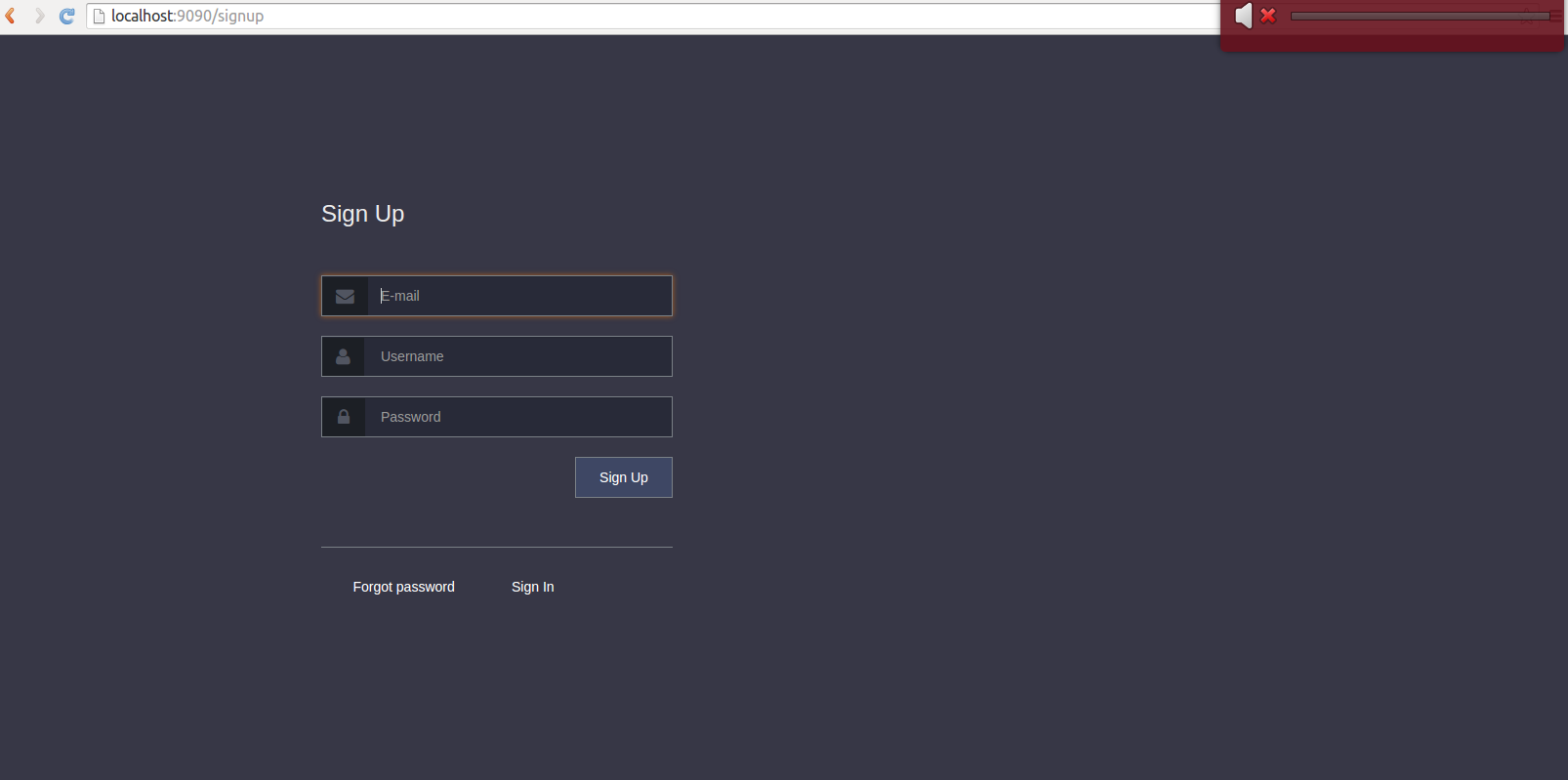
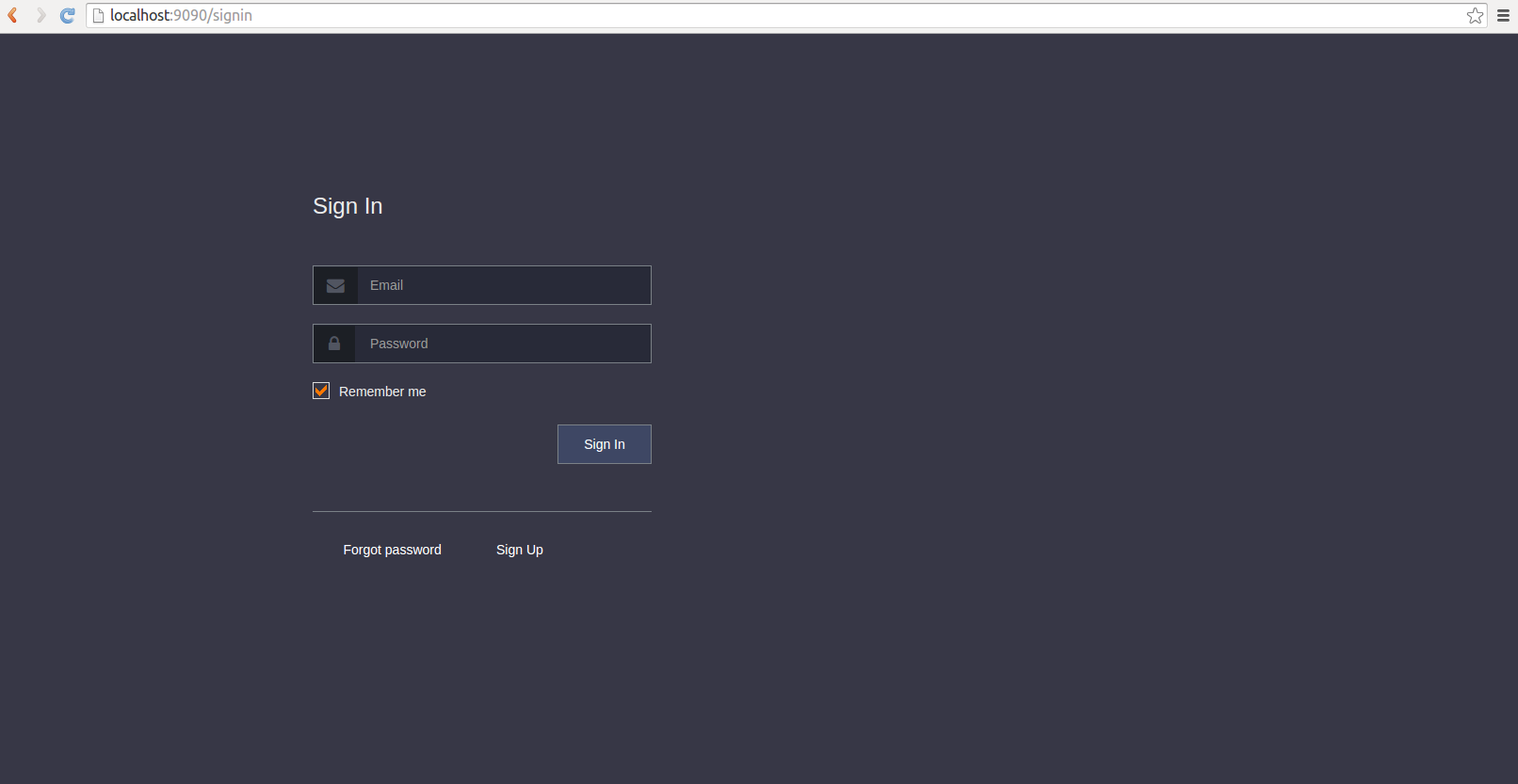
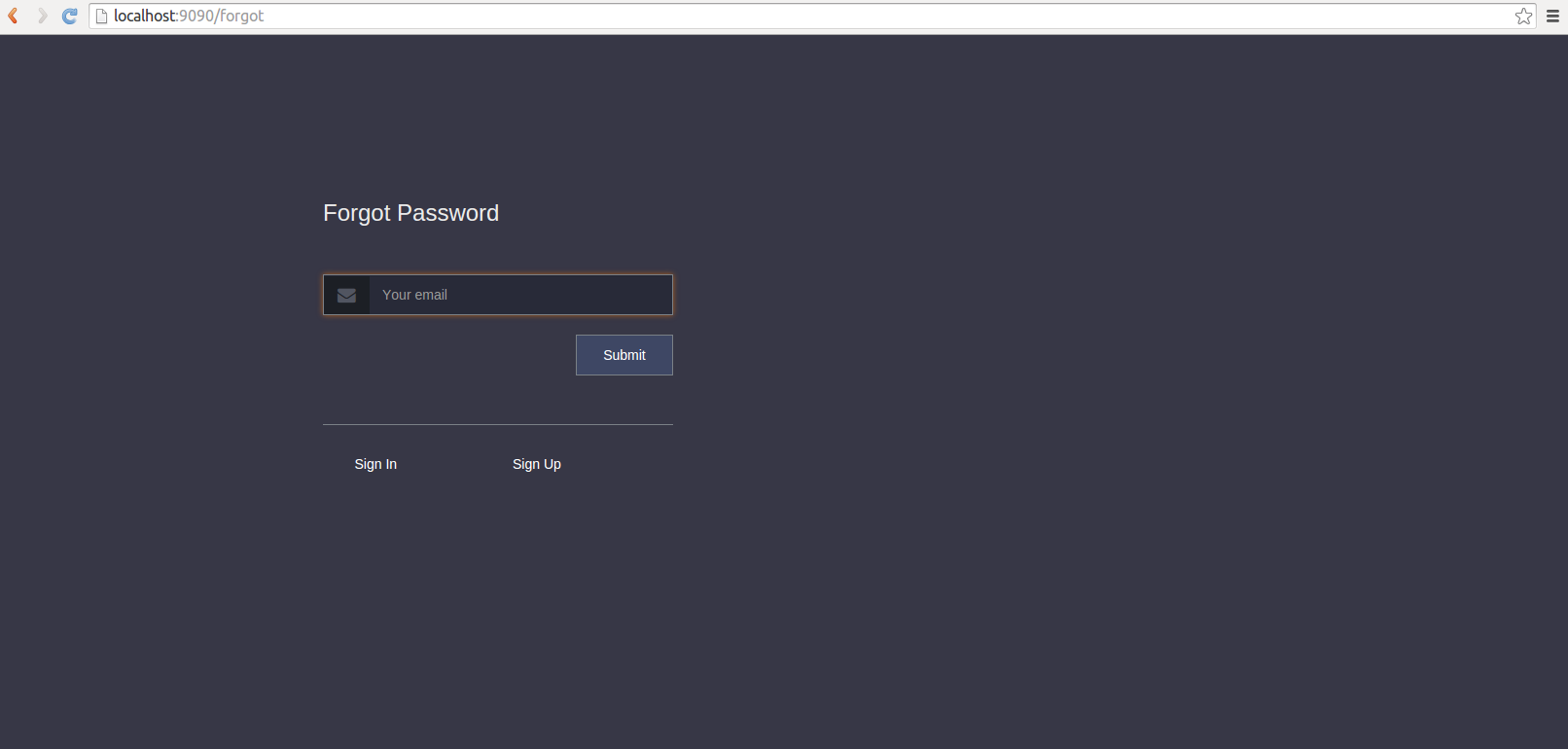
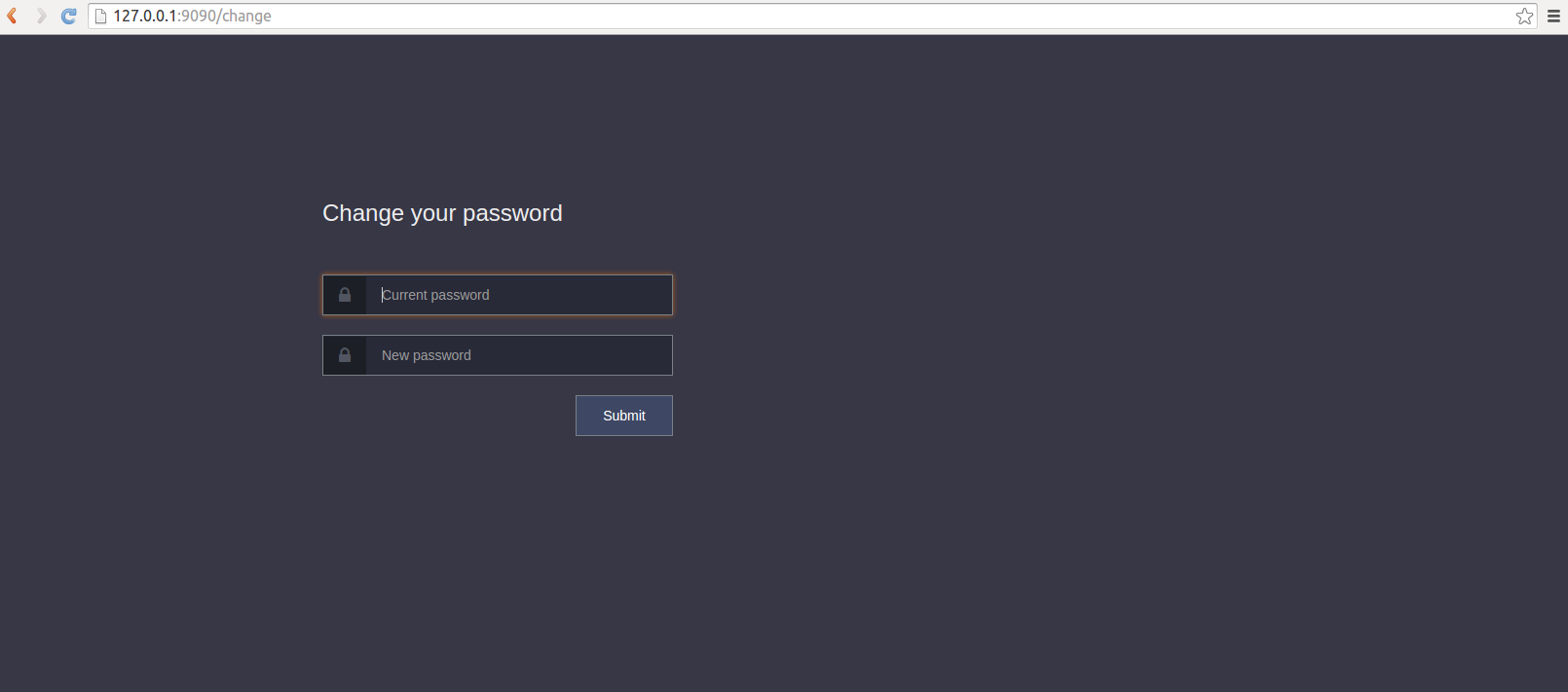
Demo
sails-police has a sample application inside its repo. It writes all sent emails into .tmp/email.txt. So you will have to copy sent links to simulate the workflow. To run the sample application, do the following:
Clone this repository
Install all dependencies
$ npm install- Then run development
$ npm run dev- Then access the dev application by navigating to http://localhost:9090 in your favourite browser
Testing
Clone this repository
Install all development dependencies
$ npm install- Then run test
$ npm testContribute
Fork this repo and push in your ideas. Do not forget to add a bit of test(s) of what value you adding.
It will be nice, if you add it as an issue so that we can know what is going on.Also I have some form of todo, check it before start working on your brilliant idea or feature.
Licence
The MIT License (MIT)
Copyright (c) 2014 sails-police
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the “Software”), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED “AS IS”, WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.


