trid v0.1.2
trid
Trivial request ID generator - crafts random id for a process and adds fast sequential ids on each call. Designed for request/response logging and error tracking.

It uses crypto for random string generation, has no external dependencies and
is thoroughly tested in production. The reason this package has been created is
that hyperid (the package I originally used) has too long random parts. Also
I felt like I don't need encoding/decoding. TRID ids are url-safe and
NATS-subject-safe.
Install
npm i tridHow to use
Initialize TRID with the rest of your service:
const TRID = require('trid');
const id = new TRID({prefix: 'srv1', length: 4});Get service instance id with trid.base():
console.log(`Starting server instance: ${id.base()}`);Starting server instance: srv1.4D2mUse trid.seq() to identify requests (as well as responses) or other activity:
...
console.log(`${timestamp} ${LEVEL} [${id.seq()}] performing request...`)...
2018-04-02T12:17:12.654Z DEBUG [srv1.4D2m.42] performing request...API
new TRID({...})- you can define the following parameters while constructing a trid instance:prefixis added to the beginning of an id (default - empty string),lengthof the random part (default -5)count- starting sequential counter value. An id basically is generated like this:{prefix}.{random}.{counter}
trid.base()- returns base part of the id ({prefix}.{random}). Good for server instance identification.trid.seq()- returns sequential id:{prefix}.{random}.{counter}. Note: when counter reaches Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER, the base value is regenerated and the counter is restarted
Examples
This is how trid ids look in tasu:
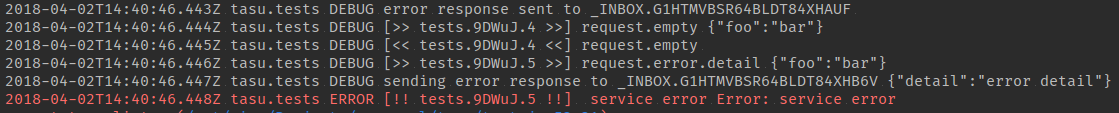
(code)